Genomes and gene expression in prokaryotes
E-Book - Chapters 1, 2, 3
Life = genetic program + metabolism + growth = replication
This generalisation came out from long history of genetics, in particular its 3
landmarks:
1. Discovery existence of genes
2. Discovery the substance of genes
3. Explaining how genes work
From observations to the main principle of genetics:
1. All progenies (hybrids) after the first cross between parents with
alternation forms of a trait (ex. colour of a flower) inherit the trait from
only one parents (the dominant trait) = the low of dominance
2. In the second cross between individuals of the first generation, the trait
segregates into two initial forms with the ratio 3:1 = the segregation
low
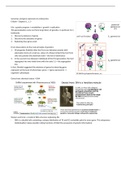
In fact, Mendel suggested the existence of genes by observing gene
expression at the level of phenotype: genes → (gene expression) →
organism's phenotype
Genes have chemical nature = DNA
Watson and Crick: a model of DNA structure explaining life
- DNA is a double helix containing a unique distribution of TA and GC nucleotide pairs for every gene. This uniqueness
(individuality) makes possible coding functions of DNA (the possession of genetic information).
, Relocation of DNA - is a core process that makes possible the existence of heredity
(based on the transmission of properties from a mother cell to daughter cells during
cell divisions). The mechanism of DNA replication is semi-conservative:
- Every DNA strand serves as a template for the synthesis of the complementary
strand. NB: complementarity is a basic DNA property with various implications in
molecular processes and research methodologies
Prokaryotic cell
- DNA - nucleoid (no nucleus) and it’s circular
A genome is a complete set of DNA of an organism, including all of its genes and non-coding regions
- Circular DNA is easier to replicate, prokaryotes have telemeric cups on each end of the DNA to protect it
- 1kb = 10^3 = 1000kb
- Animals mostly have introns, mitochondrial DNA, and it originates from prokaryotic DNA
- DS - double stranded; SS - single stranded
E-Book - Chapters 1, 2, 3
Life = genetic program + metabolism + growth = replication
This generalisation came out from long history of genetics, in particular its 3
landmarks:
1. Discovery existence of genes
2. Discovery the substance of genes
3. Explaining how genes work
From observations to the main principle of genetics:
1. All progenies (hybrids) after the first cross between parents with
alternation forms of a trait (ex. colour of a flower) inherit the trait from
only one parents (the dominant trait) = the low of dominance
2. In the second cross between individuals of the first generation, the trait
segregates into two initial forms with the ratio 3:1 = the segregation
low
In fact, Mendel suggested the existence of genes by observing gene
expression at the level of phenotype: genes → (gene expression) →
organism's phenotype
Genes have chemical nature = DNA
Watson and Crick: a model of DNA structure explaining life
- DNA is a double helix containing a unique distribution of TA and GC nucleotide pairs for every gene. This uniqueness
(individuality) makes possible coding functions of DNA (the possession of genetic information).
, Relocation of DNA - is a core process that makes possible the existence of heredity
(based on the transmission of properties from a mother cell to daughter cells during
cell divisions). The mechanism of DNA replication is semi-conservative:
- Every DNA strand serves as a template for the synthesis of the complementary
strand. NB: complementarity is a basic DNA property with various implications in
molecular processes and research methodologies
Prokaryotic cell
- DNA - nucleoid (no nucleus) and it’s circular
A genome is a complete set of DNA of an organism, including all of its genes and non-coding regions
- Circular DNA is easier to replicate, prokaryotes have telemeric cups on each end of the DNA to protect it
- 1kb = 10^3 = 1000kb
- Animals mostly have introns, mitochondrial DNA, and it originates from prokaryotic DNA
- DS - double stranded; SS - single stranded