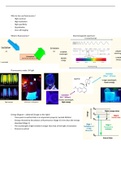
Why do we use fluorescence?
- High contrast
- High resolution
- High specificity
- Quantitative
- Live cell imaging
What is fluorescence? Electromagnetic spectrum:
Fluorescence under UV light
Energy Diagram - Jablonski (image on the right)
- Time spent in excited state is an important property ‘excited lifetime’
- Energy released by the photon as fluorescence (Stage 3) is less than the energy
absorbed (Stage 1)
- The wavelength of light emitted is longer than that of the light of excitation
- Process is cyclical
, Photobleaching:
- Irreversible destruction of the fluorophore
- Cannot be promoted to the excited state
- Ability to fluoresce is lost
Excitation and Emission spectra
Fluorophores
Fluorescence Detection:
- An excitation source
- A fluorophore (in sample)
- wavelength filters (to isolate emission photons from excitation photons)
- A detection instrument to record emission photons
Fluorescent Microscope:
- An excitation source - Illumination via Xenon or Mercury lamp, LED or laser
- A fluorophore - Ab or flu protein in the sample
- wavelength filters (to select appropriate excitation wavelength and detect only
excitation photons)
- A detection instrument to record emission photons - eye or camera
- Magnifying lens (objective)
- High contrast
- High resolution
- High specificity
- Quantitative
- Live cell imaging
What is fluorescence? Electromagnetic spectrum:
Fluorescence under UV light
Energy Diagram - Jablonski (image on the right)
- Time spent in excited state is an important property ‘excited lifetime’
- Energy released by the photon as fluorescence (Stage 3) is less than the energy
absorbed (Stage 1)
- The wavelength of light emitted is longer than that of the light of excitation
- Process is cyclical
, Photobleaching:
- Irreversible destruction of the fluorophore
- Cannot be promoted to the excited state
- Ability to fluoresce is lost
Excitation and Emission spectra
Fluorophores
Fluorescence Detection:
- An excitation source
- A fluorophore (in sample)
- wavelength filters (to isolate emission photons from excitation photons)
- A detection instrument to record emission photons
Fluorescent Microscope:
- An excitation source - Illumination via Xenon or Mercury lamp, LED or laser
- A fluorophore - Ab or flu protein in the sample
- wavelength filters (to select appropriate excitation wavelength and detect only
excitation photons)
- A detection instrument to record emission photons - eye or camera
- Magnifying lens (objective)