RNA Silencing, mechanism and applications
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7GhfS7VMSd0 and https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5YsTW5i0Xro
Control of protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells
RNA interference (RNAi): an evolutionary conserved eukaryotic pathway which
1. Prevents (silences) the translation of native genes
2. Acts as a cellular defence mechanisms against viral infections
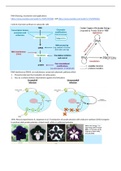
1990: Petunia experiments: R. Jorgensen et al: Transduction of purple petunias with chalcone synthase (CHS) transgene
to produce dark purple petunias. Actual result: white or patterned petunias
, - Results: Contrary to what was expected, the levels of endogenous and transgene CHS were 50-fold lower than in
wild-type petunias
- Hypothesis: The introduced transgene is “co-suppressing” the endogenous CHS gene.
- Mechanism: UNKNOWN
Anti-sense RNA
- 15-20 bases long oligonucleotides complementary to the
“sense” mRNA
- Inhibit protein translation by inducing the destruction of mRNA
Anti-sense RNA II
- 1963: synthetic anti-sense RNA blocks protein translation in cell-
free extracts
- 1981: natural anti-sense (NAT) RNA discovered in bacteria
80’s and 90’s: NAT RNA discovered in eukaryotes
- cis-NAT: ~15% of the human encoding genes produce also
antisense transcripts
- trans-NAT: transcribed from separate loci
Synthetic anti-sense RNA: Applications
- Research: to inhibit in vitro and in vivo the expression of genes of interest to study a loss-of-function phenotype
- Therapy: to treat diseases that are caused by the expression of deleterious genes, for example, viral infections,
cancer or inflammatory diseases
- 1995: Guo and Kemphues – 1 st silencing of a gene in animals using antisense RNA
The experiment of Guo and Kemphues
- PAR-1: required for early embryonic polarity in C. elegans
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7GhfS7VMSd0 and https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5YsTW5i0Xro
Control of protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells
RNA interference (RNAi): an evolutionary conserved eukaryotic pathway which
1. Prevents (silences) the translation of native genes
2. Acts as a cellular defence mechanisms against viral infections
1990: Petunia experiments: R. Jorgensen et al: Transduction of purple petunias with chalcone synthase (CHS) transgene
to produce dark purple petunias. Actual result: white or patterned petunias
, - Results: Contrary to what was expected, the levels of endogenous and transgene CHS were 50-fold lower than in
wild-type petunias
- Hypothesis: The introduced transgene is “co-suppressing” the endogenous CHS gene.
- Mechanism: UNKNOWN
Anti-sense RNA
- 15-20 bases long oligonucleotides complementary to the
“sense” mRNA
- Inhibit protein translation by inducing the destruction of mRNA
Anti-sense RNA II
- 1963: synthetic anti-sense RNA blocks protein translation in cell-
free extracts
- 1981: natural anti-sense (NAT) RNA discovered in bacteria
80’s and 90’s: NAT RNA discovered in eukaryotes
- cis-NAT: ~15% of the human encoding genes produce also
antisense transcripts
- trans-NAT: transcribed from separate loci
Synthetic anti-sense RNA: Applications
- Research: to inhibit in vitro and in vivo the expression of genes of interest to study a loss-of-function phenotype
- Therapy: to treat diseases that are caused by the expression of deleterious genes, for example, viral infections,
cancer or inflammatory diseases
- 1995: Guo and Kemphues – 1 st silencing of a gene in animals using antisense RNA
The experiment of Guo and Kemphues
- PAR-1: required for early embryonic polarity in C. elegans