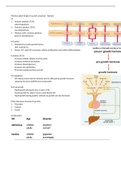
Pituitary gland weighs 0.5g and composed
of:
1. Anterior pituitary (75%):
adenohypophysis
2. Posterior pituitary (25%):
neurohypophysis
3. Pituitary stalk: connects pituitary
gland to hypothalamus
GH action:
1. Mediated by insulin growth factors
(IGF-I and IGF-II)
2. Action: IGF-I and IGF-II promote cellular proliferation and cellular differentiation
Functions of GH:
- Increases cellular uptake of amino acids
- Increases synthesis of proteins
- Increases blood (glucose)
- Increases fat metabolism
- Promotes epiphyseal bone growth
GH regulation:
- GH release shows diurnal variation and it’s affected by growth hormone
releasing hormone (GHRH) and somatostatin
Normal growth:
- Rapid growth during the first 2 years of life
- Steady growth for about 9 years controlled by GH
- Rapid growth during puberty controls by growth and sex hormones
Other hormones involved in growth:
1. Thyroxine
2. Cortisol
3. Insulin
GH disorders:
of:
1. Anterior pituitary (75%):
adenohypophysis
2. Posterior pituitary (25%):
neurohypophysis
3. Pituitary stalk: connects pituitary
gland to hypothalamus
GH action:
1. Mediated by insulin growth factors
(IGF-I and IGF-II)
2. Action: IGF-I and IGF-II promote cellular proliferation and cellular differentiation
Functions of GH:
- Increases cellular uptake of amino acids
- Increases synthesis of proteins
- Increases blood (glucose)
- Increases fat metabolism
- Promotes epiphyseal bone growth
GH regulation:
- GH release shows diurnal variation and it’s affected by growth hormone
releasing hormone (GHRH) and somatostatin
Normal growth:
- Rapid growth during the first 2 years of life
- Steady growth for about 9 years controlled by GH
- Rapid growth during puberty controls by growth and sex hormones
Other hormones involved in growth:
1. Thyroxine
2. Cortisol
3. Insulin
GH disorders: