ANIMAL HUSBANDRY
• 70% world’s livestock population = INDIA AND CHINA , but
contribution = 25% i.e. productivity per unit is very low.
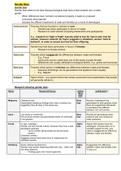
MANAGEMENT OF FARM AND FARM ANIMALS :
DAIRY FARM MANAGEMENT
(Quality of breeds)
1. Resistance to disease
2. Housed well
3. Adequate water
4. Quality & quantity fodders
5. Cleanliness and hygiene
6. Veterinary visits
7. Disease free
POULTRY FARM MANAGEMENT
• Typically include chicken - duck - turkey - geese meat (“poultry”).
• 14-16 hours of light including daylight required for egg production.
• Bird flu virus [influenza virus H5N1 and H7N9 ] - affected egg and
chicken consumption.
ANIMAL BREEDING :
Breed = Group of animals related by descent & similar in most characters
(appearance – feature – size – configuration etc. )
, Inbreeding = More closely related individuals within the same breed for 4-6
generations.
o Superior ♂️ bull that give rise to superior progeny
o Superior ♀️ for more milk per lactation
Inbreeding-
a. Increases homozygosity (thus important for pure line).
b. Expose harmful recessive gene that are eliminated by selection
c. Decreases fertility & productivity k/a Inbreeding depression.
Outbreeding
Breeding between-
▪ same breed but no common ancestors for 4-6 generation = Out Cross.
▪ different breeds k/a Cross Breeding.
▪ diff species k/a Inter – specific hybridization.
a. OUT CROSS
Best breeding method for below average features.
Single out cross can overcome Inbreeding depression.
b. CROSS BREEDING
For commercial production.
Subjected to some form of Inbreeding & selection to develop new stable
breeds
Bikaneri ewes X Merino rams
= Hisardale [ Punjab breed , sheep’s new breed ]
2