Chapter 17
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A)
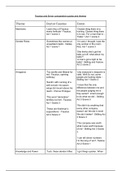
Introduction
2 ways a firm can expand its operations:
o Acquisition of LT operation assets OR
o Via a takeover
Types of mergers (often divided into 3 broad groups)
Horizontal mergers
o When 2 firms in the same industry merge
Example: Shoprite and Checkers
Vertical mergers
o Occur where firms either expands forward to the customer OR
o Expands backwards to the raw material supplier stage
Example: merger between a shoe manufacturer and a shoe
retailer
Conglomerate mergers
o Occur were firms in unrelated lines of business decide to merge
Reasons for mergers:
A merger should result in synergy benefits
A merger should take place ONLY if the value of the combined entity is
GREATER THAN the value of the separate entities added together:
V xy >V x +V y
Operating economies:
o A merger may result in economies in production or distribution such as:
Lower unit costs through
Higher production runs
o Operating economies can be effected by the following means: (REC3S)
Reduction in the number of retail outlets (reduce distribution costs)
Economies in purchasing
Combination of production facilities in the number of products
Combination of IT and administrative functions
Consolidation of research and development (R&D)programmes
AND
Standardisation and reduction in number of products
o A merger may result in a reduction in competitive pressures
Allowing the combined company to raise prices WITHOUT losing
market share
, o Mergers may also be driven by strategic reasons such as:
Ensuring the supply of key materials AND
Obtaining sales outlets for the company’s products
Managerial skills
o A firm with strong management resources
o may decide to take-over a firm currently earning low returns
o to introduce improved management and
o Reap the benefits of expected increased returns
Use for excess liquidity (H20):
o A company with surplus cash resources may decide to utilise H 2O to
acquire other companies
o Also, a take-over may take place for the acquirer to obtain the benefits
of the strong liquidity position
Diversification
o A company in a certain business field my decide to enter into an
unrelated business area and
o THEREFORE would obtain the benefits of diversification
Lower financing costs (LFC):
o Where merged company (P+S) makes better use of it debt capacity
o This (LFC) may also be due to the fact that (P+S) effectively guarantee
each other’s debt
Thereby reducing the risk to the lender and
Increasing the risk to the firms
Replacement costs:
o Where the firms wants to INCREASE production capacity… it may be
cheaper to do so via the acquisition route
If the value of the target company→ substantially BELOW the→
replacement cost of the target company’s assets
Products, product pipeline and reserves:
o A merger may be undertaken to obtain access to the target company’s
product range (particularly branded products)
Tax considerations- tax shields and assessed losses:
o If a takeover is structured as a sale of the business
Then a company will be able to deduct the interest payments
Made on the debt used to finance the acquisitions
o If the company is highly leveraged and then starts to incur losses
These tax shields will be deferred (at best) in the company
reverts back to profitability in future
Otherwise the tax shields will be LOST as the company will be
accumulating losses
o One reason for undertaking a merger:
To obtain the benefit of the tax assessed loss of the target
company BUT
, The acquirer should take note that just because there is an
assessed loss
DOES NOT automatically mean that the subsidiary will
be able to utilise this assessed loss to protect its future
income from tax
S103(2) of Income Tax Act:
Where a change in shareholding has been effected mainly
for utilising assessed loss to avoid taxes
SARS will disallow the set-off of such income against the
assessed loss
Technology:
o The acquirer may use the technological expertise of the target
company to improve its own products
o THUS providing a strong incentive to merge
The structuring of takeover offers and taxation
A may wish to acquire B, so that B → subsidiary of A OR
A new company C could be formed to hold shares of A and B
Note: if A acquires >50% of the shares of B it maintains majority control
Financing costs
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A)
Introduction
2 ways a firm can expand its operations:
o Acquisition of LT operation assets OR
o Via a takeover
Types of mergers (often divided into 3 broad groups)
Horizontal mergers
o When 2 firms in the same industry merge
Example: Shoprite and Checkers
Vertical mergers
o Occur where firms either expands forward to the customer OR
o Expands backwards to the raw material supplier stage
Example: merger between a shoe manufacturer and a shoe
retailer
Conglomerate mergers
o Occur were firms in unrelated lines of business decide to merge
Reasons for mergers:
A merger should result in synergy benefits
A merger should take place ONLY if the value of the combined entity is
GREATER THAN the value of the separate entities added together:
V xy >V x +V y
Operating economies:
o A merger may result in economies in production or distribution such as:
Lower unit costs through
Higher production runs
o Operating economies can be effected by the following means: (REC3S)
Reduction in the number of retail outlets (reduce distribution costs)
Economies in purchasing
Combination of production facilities in the number of products
Combination of IT and administrative functions
Consolidation of research and development (R&D)programmes
AND
Standardisation and reduction in number of products
o A merger may result in a reduction in competitive pressures
Allowing the combined company to raise prices WITHOUT losing
market share
, o Mergers may also be driven by strategic reasons such as:
Ensuring the supply of key materials AND
Obtaining sales outlets for the company’s products
Managerial skills
o A firm with strong management resources
o may decide to take-over a firm currently earning low returns
o to introduce improved management and
o Reap the benefits of expected increased returns
Use for excess liquidity (H20):
o A company with surplus cash resources may decide to utilise H 2O to
acquire other companies
o Also, a take-over may take place for the acquirer to obtain the benefits
of the strong liquidity position
Diversification
o A company in a certain business field my decide to enter into an
unrelated business area and
o THEREFORE would obtain the benefits of diversification
Lower financing costs (LFC):
o Where merged company (P+S) makes better use of it debt capacity
o This (LFC) may also be due to the fact that (P+S) effectively guarantee
each other’s debt
Thereby reducing the risk to the lender and
Increasing the risk to the firms
Replacement costs:
o Where the firms wants to INCREASE production capacity… it may be
cheaper to do so via the acquisition route
If the value of the target company→ substantially BELOW the→
replacement cost of the target company’s assets
Products, product pipeline and reserves:
o A merger may be undertaken to obtain access to the target company’s
product range (particularly branded products)
Tax considerations- tax shields and assessed losses:
o If a takeover is structured as a sale of the business
Then a company will be able to deduct the interest payments
Made on the debt used to finance the acquisitions
o If the company is highly leveraged and then starts to incur losses
These tax shields will be deferred (at best) in the company
reverts back to profitability in future
Otherwise the tax shields will be LOST as the company will be
accumulating losses
o One reason for undertaking a merger:
To obtain the benefit of the tax assessed loss of the target
company BUT
, The acquirer should take note that just because there is an
assessed loss
DOES NOT automatically mean that the subsidiary will
be able to utilise this assessed loss to protect its future
income from tax
S103(2) of Income Tax Act:
Where a change in shareholding has been effected mainly
for utilising assessed loss to avoid taxes
SARS will disallow the set-off of such income against the
assessed loss
Technology:
o The acquirer may use the technological expertise of the target
company to improve its own products
o THUS providing a strong incentive to merge
The structuring of takeover offers and taxation
A may wish to acquire B, so that B → subsidiary of A OR
A new company C could be formed to hold shares of A and B
Note: if A acquires >50% of the shares of B it maintains majority control
Financing costs