Learning aim B: Understand the homeostasis mechanisms used by the human
body
Title: Homeostatic control of body systems
Homeostasis:
The maintenance of a constant environment is known as homeostasis.
Homeostasis is caused by a natural resistance to change when in optimal
conditions, and it is maintained by a variety of regulatory systems. For the
variable being regulated, all homeostatic control mechanisms contain at least
three interdependent components: a receptor, a control centre, and an
effector.
Setpoint:
The setpoint is the physiological value around which the normal range varies is
referred to as a set point. The normal range is a restricted set of values that is
optimally healthy and stable. Physiological factors such as body temperature
and blood pressure, for example, tend to fluctuate within a typical range a few
degrees above and below the set point for normal human body temperature,
which is roughly 37°C (98.6°F). The brain's control centres are involved in
controlling physiological parameters and keeping them within normal range.
Any considerable deviation from the normal range will be resisted and
equilibrium restored through a process known as a feedback loop as the body
strives to preserve homeostasis.
Feedback loop:
There are three essential components to a feedback loop. A sensor, often
called a receptor, is a part of a feedback system that measures a physiological
value. It is in charge of sensing changes in the environment. The control centre
receives this value. The control centre of a feedback system compares the
,value to the typical range. The control centre activates an effector if the value
deviates too much from the set point. In a feedback system, an effector is the
component that causes a change to reverse the situation and return the value
to its normal range. Muscles and glands are effectors.
Negative feedback loop:
Negative feedback is a mechanism in which a response to a stimulus has the
effect of turning off or weakening the initial stimulus. The body's most
common mechanisms for maintaining homeostasis are negative feedback
loops. Negative feedback is used to maintain homeostasis throughout the body
at all times, therefore understanding negative feedback is essential for
understanding human physiology.
Positive feedback amplifies rather than reverses a change in the body's
physiological condition. When the system deviates from the typical range, it
experiences greater change and goes further away from the normal range.
Only when there is a clear end point to positive feedback in the body is it
considered normal. The body's response to blood loss is an example of a
positive feedback loop that is not normal but is activated when needed.
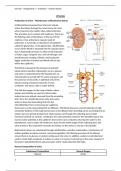
, Gland Location Secretion Main function
Exocrine Sweat gland Dermis layer Sweat Lower body
of the skin temperature
Brunner's Duodenum Alkaline mucus Neutralises acid
glands from the stomach
Endocrine Thyroid Below the Thyroxine Regulation of
larynx in the metabolic rate
neck
Parathyroid Behind the Parathyroid Regulation of
thyroid hormone calcium levels
gland in the
neck
Pituitary Base of Thyroid Controls several
brain stimulating other glands-
hormone adrenals, thyroid
Growth
hormone
Prolactin
Adrenocorticotr