Problem 1: A keen eye
Learning goals case 1:
1. What is the anatomical structure of the eye?
Keywords: blind/yellow spot and retina
Learning goals case 2:
1. What is the function of the retina and how does it react to light?
2. How does the retina reflect the image?
3. What are the different problems with eyes?
4. How does wearing glasses affect how we see? How do glasses work in comparison to
our actual lenses?
Keywords: lens, pupil, cornea → which part of the eye are responsible for curving the
eye?
Learning goals case 3:
1. How do contrast and illusion affect our perception?
2. How does filling in incomplete images work?
3. How does the optical illusion occur in each of the three cases?
Keywords: Lateral inhibition
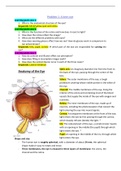
Optic axis: An imaginary diameter line from the front to
Anatomy of the Eye the back of the eye, passing through the centre of the
lens.
Sclera: The outer membrane of the eye; a tough
protective covering whose visible portion is the white of
the eye.
Choroid: The middle membrane of the eye, lining the
interior of the sclera and containing most of the blood
vessels that supply the inside of the eye with oxygen and
nutrients.
Retina: The inner membrane of the eye, made up of
neurons, including the photoreceptors that convert the
light entering the eye into neural signals.
Cornea: A transparent membrane at the front of the eye;
light enters the eye by first passing through the cornea,
which sharply refracts (bends) the light. *
Iris: The coloured part of the eye—a small circular muscle
with an opening in the middle (the pupil) through which
light enters the eye. *
Pupil: An opening in the middle of the iris, through which
Shape and size: light enters the eye.
- The human eye is roughly spherical, with a diameter of about 24 mm. the spherical
shape makes it easy to rotate and move.
- Three membranes, the eye is encased in three layers of membrane: the sclera, the
choroid and the retina.
, - *more on cornea: the refraction of light by the cornea is part of the process of
focusing light on the retina—in fact, the cornea performs most of this focusing
process. However, the cornea is rigid and cannot adjust how much the light passing
through it is refracted. This is left to the flexible lens, which performs the fine
adjustments necessary to bring light into sharp focus.
- *more on the iris: the iris controls the size of the pupil by contracting and relaxing,
mainly in response to the intensity of light entering the eye. Intense light makes the
iris contract, which makes the pupil smaller and thus reduces the amount of light
that can enter the eye. In dim light the iris relaxes which makes the pupil larger and
thus increases the amount of light that can enter the eye. This completely automatic
process is known as the pupillary reflex. → the pupil can range from about 2mm to
8mm. constricts (small), dilates (big) → both pupils simultaneously at the same
degree.
Three chambers:
Anterior chamber: the space between the cornea and the iris, filled with aqueous humor.
Posterior chamber: the space between the iris and the lens, filled with aqueous humor.
Aqueous humor: a clear, thin fluid filling the anterior and posterior chambers of the eye.
More than 99% water.
Vitreous chamber: the main interior portion of the eye, filled with vitreous humor.
Vitreous humor: a clear, somewhat gel-like fluid filling the vitreous chamber of the eye. More
than 99% water.
→ both aqueous and vitreous humors also slightly refract light, but like the cornea, the
amount of refraction they perform can’t be adjusted.
Intraocular pressure: the pressure of the fluids in the three chambers of the eye—must be
greater than air pressure to prevent the eyes from collapsing like deflated basketballs.
(However, the intraocular pressure must not be too great; if it is, it can cause a condition
known as glaucoma.)
Lens: a transparent structure near the front of the eye that refracts the light passing through
the pupil so that the light focuses properly on the retina. The power of any lens to refract light
determines its focal length.
→ weak lens: doesn’t refract light much; it is relatively thin and flat and has a long focal
length.
→ strong lens: refracts light sharply; it is relatively thick and rounded and has a short focal
length.
Focal length: the distance from a lens at which the image of an object is in focus when the
object is far away from the lens (at “optical infinity”, where the light rays from the object are
effectively parallel to one another).
Diopters: units used to express the power of a lens; diopters = 1/(focal length) in meters. The
greatest the power of a lens, the shorter the focal length.
Learning goals case 1:
1. What is the anatomical structure of the eye?
Keywords: blind/yellow spot and retina
Learning goals case 2:
1. What is the function of the retina and how does it react to light?
2. How does the retina reflect the image?
3. What are the different problems with eyes?
4. How does wearing glasses affect how we see? How do glasses work in comparison to
our actual lenses?
Keywords: lens, pupil, cornea → which part of the eye are responsible for curving the
eye?
Learning goals case 3:
1. How do contrast and illusion affect our perception?
2. How does filling in incomplete images work?
3. How does the optical illusion occur in each of the three cases?
Keywords: Lateral inhibition
Optic axis: An imaginary diameter line from the front to
Anatomy of the Eye the back of the eye, passing through the centre of the
lens.
Sclera: The outer membrane of the eye; a tough
protective covering whose visible portion is the white of
the eye.
Choroid: The middle membrane of the eye, lining the
interior of the sclera and containing most of the blood
vessels that supply the inside of the eye with oxygen and
nutrients.
Retina: The inner membrane of the eye, made up of
neurons, including the photoreceptors that convert the
light entering the eye into neural signals.
Cornea: A transparent membrane at the front of the eye;
light enters the eye by first passing through the cornea,
which sharply refracts (bends) the light. *
Iris: The coloured part of the eye—a small circular muscle
with an opening in the middle (the pupil) through which
light enters the eye. *
Pupil: An opening in the middle of the iris, through which
Shape and size: light enters the eye.
- The human eye is roughly spherical, with a diameter of about 24 mm. the spherical
shape makes it easy to rotate and move.
- Three membranes, the eye is encased in three layers of membrane: the sclera, the
choroid and the retina.
, - *more on cornea: the refraction of light by the cornea is part of the process of
focusing light on the retina—in fact, the cornea performs most of this focusing
process. However, the cornea is rigid and cannot adjust how much the light passing
through it is refracted. This is left to the flexible lens, which performs the fine
adjustments necessary to bring light into sharp focus.
- *more on the iris: the iris controls the size of the pupil by contracting and relaxing,
mainly in response to the intensity of light entering the eye. Intense light makes the
iris contract, which makes the pupil smaller and thus reduces the amount of light
that can enter the eye. In dim light the iris relaxes which makes the pupil larger and
thus increases the amount of light that can enter the eye. This completely automatic
process is known as the pupillary reflex. → the pupil can range from about 2mm to
8mm. constricts (small), dilates (big) → both pupils simultaneously at the same
degree.
Three chambers:
Anterior chamber: the space between the cornea and the iris, filled with aqueous humor.
Posterior chamber: the space between the iris and the lens, filled with aqueous humor.
Aqueous humor: a clear, thin fluid filling the anterior and posterior chambers of the eye.
More than 99% water.
Vitreous chamber: the main interior portion of the eye, filled with vitreous humor.
Vitreous humor: a clear, somewhat gel-like fluid filling the vitreous chamber of the eye. More
than 99% water.
→ both aqueous and vitreous humors also slightly refract light, but like the cornea, the
amount of refraction they perform can’t be adjusted.
Intraocular pressure: the pressure of the fluids in the three chambers of the eye—must be
greater than air pressure to prevent the eyes from collapsing like deflated basketballs.
(However, the intraocular pressure must not be too great; if it is, it can cause a condition
known as glaucoma.)
Lens: a transparent structure near the front of the eye that refracts the light passing through
the pupil so that the light focuses properly on the retina. The power of any lens to refract light
determines its focal length.
→ weak lens: doesn’t refract light much; it is relatively thin and flat and has a long focal
length.
→ strong lens: refracts light sharply; it is relatively thick and rounded and has a short focal
length.
Focal length: the distance from a lens at which the image of an object is in focus when the
object is far away from the lens (at “optical infinity”, where the light rays from the object are
effectively parallel to one another).
Diopters: units used to express the power of a lens; diopters = 1/(focal length) in meters. The
greatest the power of a lens, the shorter the focal length.