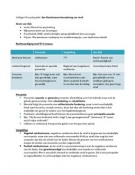
Hearsay
What does hearsay mean?
The law on hearsay is set out in the Criminal Justice Act 2003 (CJA) sections 114 -
136.
"Hearsay" means a "statement not made in oral evidence that is evidence of any
matter stated." (Section 114(1) CJA 2003).
Hearsay evidence is prohibited in criminal proceedings excluding anywhere there is
some statutory provision which decides it’s admissible or where a common law rule
making it admissible is preserved by section 118 CJA, or by agreement of all parties
to the proceedings, or where the court is satisfied that it is in the interests of justice
for it to be admissible (section 114(1) CJA 2003).
Section 115(2) defines a 'statement' as "any representation of fact or opinion made
by a person by whatever means"; and it includes a representation made in a sketch,
photo fit or other pictorial form.
Teper v R [1952] AC 480, 486 per Lord Normand:
‘[Hearsay evidence] is not the best evidence and it is not delivered on oath. The truthfulness
and accuracy of the person whose words are spoken to by another witness cannot be tested
by cross-examination, and the light which his demeanour would throw on his testimony is
lost.’
There are 4 hearsay dangers. This includes faulty perception, erroneous memory,
insincerity, lack of clarity in narration
Civil Proceedings: Civil Evidence Act 1995
• Section 1:
(1) In civil proceedings evidence shall not be excluded on the ground that it is hearsay.
...
• Section 2:
(1) A party proposing to adduce hearsay evidence in civil proceedings shall, subject to
the following provisions of this section, give to the other party or parties to the proceedings
–
(a) such notice (if any) of that fact, and
(b) on request, such particulars of or relating to the evidence, as is reasonable
and practicable in the circumstances for the purpose of enabling him or them to deal with
any matters arising from its being hearsay.
...
(4) A failure to comply with subsection (1) ... does not affect the admissibility of the
evidence but may be taken into account by the court –
(a) in considering the exercise of its powers with respect to the course of
proceedings and costs, and
What does hearsay mean?
The law on hearsay is set out in the Criminal Justice Act 2003 (CJA) sections 114 -
136.
"Hearsay" means a "statement not made in oral evidence that is evidence of any
matter stated." (Section 114(1) CJA 2003).
Hearsay evidence is prohibited in criminal proceedings excluding anywhere there is
some statutory provision which decides it’s admissible or where a common law rule
making it admissible is preserved by section 118 CJA, or by agreement of all parties
to the proceedings, or where the court is satisfied that it is in the interests of justice
for it to be admissible (section 114(1) CJA 2003).
Section 115(2) defines a 'statement' as "any representation of fact or opinion made
by a person by whatever means"; and it includes a representation made in a sketch,
photo fit or other pictorial form.
Teper v R [1952] AC 480, 486 per Lord Normand:
‘[Hearsay evidence] is not the best evidence and it is not delivered on oath. The truthfulness
and accuracy of the person whose words are spoken to by another witness cannot be tested
by cross-examination, and the light which his demeanour would throw on his testimony is
lost.’
There are 4 hearsay dangers. This includes faulty perception, erroneous memory,
insincerity, lack of clarity in narration
Civil Proceedings: Civil Evidence Act 1995
• Section 1:
(1) In civil proceedings evidence shall not be excluded on the ground that it is hearsay.
...
• Section 2:
(1) A party proposing to adduce hearsay evidence in civil proceedings shall, subject to
the following provisions of this section, give to the other party or parties to the proceedings
–
(a) such notice (if any) of that fact, and
(b) on request, such particulars of or relating to the evidence, as is reasonable
and practicable in the circumstances for the purpose of enabling him or them to deal with
any matters arising from its being hearsay.
...
(4) A failure to comply with subsection (1) ... does not affect the admissibility of the
evidence but may be taken into account by the court –
(a) in considering the exercise of its powers with respect to the course of
proceedings and costs, and