Digestive System
Chapter 10
Digestive System Function
= Ingestion
= Digestion
- Mechanically + chemically breakdown food into smaller molecules to be
absorbed and used
= Absorption
- Nutrients go into circulatory
system
= Egestion/Elimination (excrete solid
waste) feces
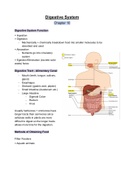
Digestive Tract - Alimentary Canal
- Mouth (teeth, tongue, salivary
gland)
- Esophagus
- Stomach (gastric acid, pepsin)
- Small Intestine (duodenum etc.)
- Large Intestine
- Sigmoid Colon
- Rectum
- Anus
Usually herbivores + omnivores have
longer tracts than carnivores since
cellulose walls in plants are more
difficult to digest so the longer tracts
allows more time for the digestion.
Methods of Obtaining Food
Filter Feeders
= Aquatic animals
, = Slurps water which gathers the organisms and then filters the organisms from the
water
Ex: Flamingoes
Substrate Feeders
= Live in/on their food source
= Eat their way through it
Ex: Caterpillars
Fluid Feeders
= Sucks/licks the nutrient-rich fluids from live plants/animals
= Mouthparts adapted to pierce skin/leaf tissue
Ex: Mosquitoes
Bulk Feeders
= Many animals + most vertebrates
= Eat large pieces of food
Ex: Humans
Parts of Digestive System
Mouth
= Ingestion (intake of food)
Chemical Digestion
- Salivary glands release saliva
- 3 pairs of SG in the mouth
- Saliva = Water + Enzyme (amylase)
- Breaks down the starches → simple
sugars
- Dissolves water-soluble food particles
- Stimulates taste buds
- Lubricates the food to swallow easier
Mechanical Digestion
- Teeth helps cut and grind food
Chapter 10
Digestive System Function
= Ingestion
= Digestion
- Mechanically + chemically breakdown food into smaller molecules to be
absorbed and used
= Absorption
- Nutrients go into circulatory
system
= Egestion/Elimination (excrete solid
waste) feces
Digestive Tract - Alimentary Canal
- Mouth (teeth, tongue, salivary
gland)
- Esophagus
- Stomach (gastric acid, pepsin)
- Small Intestine (duodenum etc.)
- Large Intestine
- Sigmoid Colon
- Rectum
- Anus
Usually herbivores + omnivores have
longer tracts than carnivores since
cellulose walls in plants are more
difficult to digest so the longer tracts
allows more time for the digestion.
Methods of Obtaining Food
Filter Feeders
= Aquatic animals
, = Slurps water which gathers the organisms and then filters the organisms from the
water
Ex: Flamingoes
Substrate Feeders
= Live in/on their food source
= Eat their way through it
Ex: Caterpillars
Fluid Feeders
= Sucks/licks the nutrient-rich fluids from live plants/animals
= Mouthparts adapted to pierce skin/leaf tissue
Ex: Mosquitoes
Bulk Feeders
= Many animals + most vertebrates
= Eat large pieces of food
Ex: Humans
Parts of Digestive System
Mouth
= Ingestion (intake of food)
Chemical Digestion
- Salivary glands release saliva
- 3 pairs of SG in the mouth
- Saliva = Water + Enzyme (amylase)
- Breaks down the starches → simple
sugars
- Dissolves water-soluble food particles
- Stimulates taste buds
- Lubricates the food to swallow easier
Mechanical Digestion
- Teeth helps cut and grind food