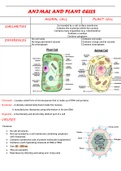
ANIMAL AND PLANT CELLS
ANIMAL CELL PLANT CELL
Surrounded by a cell surface membrane
SIMILARITIES Contains the nucleolus within the nucleus
Contains many organelles (e.g.: mitochondria)
Contains a nucleus
Contains cytoplasm
No cell walls Contains cell walls
DIFFERENCES No large permanent vacuole Contains a large central vacuole
No chloroplasts Contains chloroplasts
Chromatin – Loosely coiled form of chromosomes that is made up of DNA and proteins
Nucleolus – A densely stained body found inside the nucleus
It manufactures ribosomes using information in its own DNA
Organelle – A functionally and structurally distinct part of a cell
VIRUSES
Features:
• No cell structures
• Not surrounded by a cell membrane containing cytoplasm
with ribosomes
• Contains a protective coat of protein molecules (capsomere)
• Contains a self-replicating molecule of DNA or RNA
• Size: 20 – 300 nm
• They are parasitic
• Reproduce by infecting and taking over living cells
, PROKAROTIC AND EUKARYOTIC CELLS
PROKARYOTES EUKARYOTES
Diameter: 0.5 – 5 micro meters Diameter: 40 micro meters
Circular DNA No circular DNA
DNA lies freely in the cytoplasm DNA contained in nucleus
Naked DNA DNA is associated with proteins to make chromosomes
Small 70s ribosomes Larger 80s ribosomes
No Endoplasmic Reticulum Contains Endoplasmic Reticulum (sometimes with
ribosomes)
Cell wall present Cell wall sometimes present (plants and fungi)
(made up of murein, a peptidoglycan)
Very few organelles Many organelles
• No membrane: ribosomes, centrioles, microtubule
• Single membrane: lysosomes, Golgi body, vacuole
• Double membrane: nucleus, mitochondrion,
chloroplast
Bacteria Animals, plants, fungi, protoctists
COMMON STRUCTURES IN PROKARYOTES AND BACTERIA
• Cell wall
• Cell surface membrane
• Cytoplasm
• Circular DNA
• Ribosomes
ADDITIONAL STRUCTURES IN BACTERIA AND THEIR FUNCTONS
• Flagellum - Locomotion
• Capsule - Protection
• Plasmid – Small circle of DNA
• Pili – For attachment to other cells/ surfaces, for sexual reproduction
• Cell membrane infoldings – For nitrogen fixation
, ORGANELLES
organelle structure function
Nucleus • Surrounded by 2 membranes called the • Nuclear pores control the
nuclear envelope exchange between the
nucleus and the cytoplasm
• Nuclear envelope has small nuclear • Substances leaving the
pores nucleus:
• mRNA, ribosomes
• It contains chromosomes in the form of • Substances entering the
chromatin nucleus:
• Chromosomes contain DNA • Proteins
• DNA is organized into genes • Genes control cell activities
and inheritance
• Nucleolus makes ribosome
Ribosomes • Has 2 subunits: large and small • Protein synthesis
• Made up of RNA and protein
Endoplasmic Reticulum • Membranes form an extended system
of flattened compartments called sacs • Smooth ER makes lipids an
• Its continuous with the outer steroids (cholesterol,
membrane of the nuclear envelope oestrogen, testosterone)
• Rough ER: covered with ribosomes • Rough ER synthesizes
• Smooth ER: not covered with proteins
ribosomes
Golgi body • A stack of flattened sacks • Collects, processes and
• Made when vesicles break off from the sorts molecules for
ER transport in Golgi vesicles
either to other parts of the
cell or out of the cell.
• Makes glycoproteins
• Removes the 1st amino acid
methionine
• Makes lysosomes
Lysosomes • Spherical sacs • Digests old organelles or
• Surrounded by a single membrane whole cells
• No internal structure • In WBC, lysosomes are use
• Diameter: 0.1 – 0.5 micrometers to digest bacteria
• Contain digestive enzymes
Mitochondria • Diameter: 1 micrometer • Aerobic respiration (produc
ATP)
• Sausage shaped
• Lipid synthesis
• Double membrane bound
• Inner membrane is highly
• Inner membrane is folded to form
selective and controls what
cristae
ions and molecules can
• Matrix: interior solution
enter the membrane
• Intermembrane space is the space
between the 2 membranes
• Outer membrane has a transport
protein called porin
• Replicate independently of cell division
by dividing into 2
ANIMAL CELL PLANT CELL
Surrounded by a cell surface membrane
SIMILARITIES Contains the nucleolus within the nucleus
Contains many organelles (e.g.: mitochondria)
Contains a nucleus
Contains cytoplasm
No cell walls Contains cell walls
DIFFERENCES No large permanent vacuole Contains a large central vacuole
No chloroplasts Contains chloroplasts
Chromatin – Loosely coiled form of chromosomes that is made up of DNA and proteins
Nucleolus – A densely stained body found inside the nucleus
It manufactures ribosomes using information in its own DNA
Organelle – A functionally and structurally distinct part of a cell
VIRUSES
Features:
• No cell structures
• Not surrounded by a cell membrane containing cytoplasm
with ribosomes
• Contains a protective coat of protein molecules (capsomere)
• Contains a self-replicating molecule of DNA or RNA
• Size: 20 – 300 nm
• They are parasitic
• Reproduce by infecting and taking over living cells
, PROKAROTIC AND EUKARYOTIC CELLS
PROKARYOTES EUKARYOTES
Diameter: 0.5 – 5 micro meters Diameter: 40 micro meters
Circular DNA No circular DNA
DNA lies freely in the cytoplasm DNA contained in nucleus
Naked DNA DNA is associated with proteins to make chromosomes
Small 70s ribosomes Larger 80s ribosomes
No Endoplasmic Reticulum Contains Endoplasmic Reticulum (sometimes with
ribosomes)
Cell wall present Cell wall sometimes present (plants and fungi)
(made up of murein, a peptidoglycan)
Very few organelles Many organelles
• No membrane: ribosomes, centrioles, microtubule
• Single membrane: lysosomes, Golgi body, vacuole
• Double membrane: nucleus, mitochondrion,
chloroplast
Bacteria Animals, plants, fungi, protoctists
COMMON STRUCTURES IN PROKARYOTES AND BACTERIA
• Cell wall
• Cell surface membrane
• Cytoplasm
• Circular DNA
• Ribosomes
ADDITIONAL STRUCTURES IN BACTERIA AND THEIR FUNCTONS
• Flagellum - Locomotion
• Capsule - Protection
• Plasmid – Small circle of DNA
• Pili – For attachment to other cells/ surfaces, for sexual reproduction
• Cell membrane infoldings – For nitrogen fixation
, ORGANELLES
organelle structure function
Nucleus • Surrounded by 2 membranes called the • Nuclear pores control the
nuclear envelope exchange between the
nucleus and the cytoplasm
• Nuclear envelope has small nuclear • Substances leaving the
pores nucleus:
• mRNA, ribosomes
• It contains chromosomes in the form of • Substances entering the
chromatin nucleus:
• Chromosomes contain DNA • Proteins
• DNA is organized into genes • Genes control cell activities
and inheritance
• Nucleolus makes ribosome
Ribosomes • Has 2 subunits: large and small • Protein synthesis
• Made up of RNA and protein
Endoplasmic Reticulum • Membranes form an extended system
of flattened compartments called sacs • Smooth ER makes lipids an
• Its continuous with the outer steroids (cholesterol,
membrane of the nuclear envelope oestrogen, testosterone)
• Rough ER: covered with ribosomes • Rough ER synthesizes
• Smooth ER: not covered with proteins
ribosomes
Golgi body • A stack of flattened sacks • Collects, processes and
• Made when vesicles break off from the sorts molecules for
ER transport in Golgi vesicles
either to other parts of the
cell or out of the cell.
• Makes glycoproteins
• Removes the 1st amino acid
methionine
• Makes lysosomes
Lysosomes • Spherical sacs • Digests old organelles or
• Surrounded by a single membrane whole cells
• No internal structure • In WBC, lysosomes are use
• Diameter: 0.1 – 0.5 micrometers to digest bacteria
• Contain digestive enzymes
Mitochondria • Diameter: 1 micrometer • Aerobic respiration (produc
ATP)
• Sausage shaped
• Lipid synthesis
• Double membrane bound
• Inner membrane is highly
• Inner membrane is folded to form
selective and controls what
cristae
ions and molecules can
• Matrix: interior solution
enter the membrane
• Intermembrane space is the space
between the 2 membranes
• Outer membrane has a transport
protein called porin
• Replicate independently of cell division
by dividing into 2