Aliya Hussain
The lymphatic system
Context
diagram of the anatomy of the Page 2
lymphatic system – P3
Main Lymphatic organs-functions, Page 3-9
structure and location – P3
How lymph is formed and its role in the Page 10
health of the body – P3
Formation and transport of lymphocytes Page 10
and lymph – P3
Removal of interstitial fluid from Page 10-11
tissues – P3
Maintenance of hydrostatic pressure Page 11
– P3
Absorption of fats from the digestive Page 11
system – P3
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma – P4 Page 12-13
The effect of Hodgkin’s lymphoma is Page 13
on the normal function of the
lymphatic system – M2
corrective treatments used to Page 13-14
overcome your chosen disorder – M2
Evaluate the effects of treatments – Page 14-20
D2
1
,Aliya Hussain
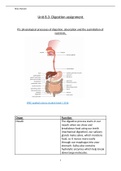
Diagram of the lymphatic system
BTEC National
Applied Science
Student Book 1 2016
BTEC National Applied Science Student
Book 1 2016
2
, Aliya Hussain
The lymphatic system consists of all lymphatic vessels, lymph and lymphatic
organs. For example, the lymph nodes, spleen, thymus as well as the lymphatic
tissue found in the small intestine and throat.
Main Lymphatic organs-functions, structure and location
Tonsils: The tonsils are a pair of soft tissue masses located at the rear of the
throat. Each tonsil is composed of tissue similar to lymph nodes. The main
function of tonsils is to trap germs (bacteria and viruses) which you may
breathe in. Proteins called antibodies produced by the immune cells in the
tonsils help to kill germs and help to prevent throat and lung infections.
https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/picture-of-the-tonsils
Thymus gland: Located in the upper chest, this gland's primary function is to
promote the development of cells of the immune system called T lymphocytes.
T lymphocytes, or T-cells, are white blood cells that protect against foreign
organisms (bacteria and viruses) that manage to infect body cells. They also
protect the body from itself by controlling cancerous cells.
3
The lymphatic system
Context
diagram of the anatomy of the Page 2
lymphatic system – P3
Main Lymphatic organs-functions, Page 3-9
structure and location – P3
How lymph is formed and its role in the Page 10
health of the body – P3
Formation and transport of lymphocytes Page 10
and lymph – P3
Removal of interstitial fluid from Page 10-11
tissues – P3
Maintenance of hydrostatic pressure Page 11
– P3
Absorption of fats from the digestive Page 11
system – P3
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma – P4 Page 12-13
The effect of Hodgkin’s lymphoma is Page 13
on the normal function of the
lymphatic system – M2
corrective treatments used to Page 13-14
overcome your chosen disorder – M2
Evaluate the effects of treatments – Page 14-20
D2
1
,Aliya Hussain
Diagram of the lymphatic system
BTEC National
Applied Science
Student Book 1 2016
BTEC National Applied Science Student
Book 1 2016
2
, Aliya Hussain
The lymphatic system consists of all lymphatic vessels, lymph and lymphatic
organs. For example, the lymph nodes, spleen, thymus as well as the lymphatic
tissue found in the small intestine and throat.
Main Lymphatic organs-functions, structure and location
Tonsils: The tonsils are a pair of soft tissue masses located at the rear of the
throat. Each tonsil is composed of tissue similar to lymph nodes. The main
function of tonsils is to trap germs (bacteria and viruses) which you may
breathe in. Proteins called antibodies produced by the immune cells in the
tonsils help to kill germs and help to prevent throat and lung infections.
https://www.webmd.com/oral-health/picture-of-the-tonsils
Thymus gland: Located in the upper chest, this gland's primary function is to
promote the development of cells of the immune system called T lymphocytes.
T lymphocytes, or T-cells, are white blood cells that protect against foreign
organisms (bacteria and viruses) that manage to infect body cells. They also
protect the body from itself by controlling cancerous cells.
3