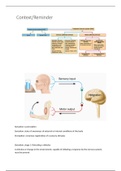
The Synapse and Neurotransmitters
Communication in the central nervous system
- Each neuron has 1000’s of synaptic inputs
- Simpls output: AP
- Neural Computation
Neurotransmitters
Many different neurotransmitters
- Acetylcholine
- Noradrenalin
- Dopamine
- Serotonin
- GABA
Each NT may have more than one type of receptor but each receptor will only
bind with one NT (Lock and Key)
May have excitatory or inhibatroy effect
Acetylcholine
- First known NT
- At nerve-muscle connections of all voluntary and many involuntary
muscles
- Generally excibatory
- Particularly prevalent in hippocampus
Noradrenalin/Norapinephrine
- A monamine
- Involved in mediation of emergency responses
- Involved in arousal, sleep, mood
- Drugs that effect NA will effect mood
- Drugs affecting NA = cocaine, amphetamines, lithium
Dopamine (DA)
- Implicated in movement, attention, learning and reward, attachment
- Low levels of DA in parkinsons disease
- Different levels and pathwasy
Seotonin (5HT)
- Very versatile; many functions throughout the whole body
, - Involved in: temperature regulation, onset of sleep, feeding, senosry
perception
- Changes in 5HT neurons are related to action of psychedelic drugs
- Disturbances in function implicated in, depression, anxiety, migrane,
eating disorders
- Derived from tryptophan
GABA (Gamma aminobutyric acid)
- Amino acid NT
- Occurs almost exclusively in brain
- Inhibatory effects
- Thought to be involved in epilepsy
- Affects accentuated by bensoiazepines, barbituates and alcohol
Agnoists and Antagonsists
Inhibitors- drugs that inhibit normal functioning of proteins involved in synaptic
transmission
Inhibitors of receptors = Receptors antagonists
Receptor agonists- drugs that bind to reeptors and mimic normal
neurotransmissions
Inverse agonists- opposite effect of agonists
Communication in the central nervous system
- Each neuron has 1000’s of synaptic inputs
- Simpls output: AP
- Neural Computation
Neurotransmitters
Many different neurotransmitters
- Acetylcholine
- Noradrenalin
- Dopamine
- Serotonin
- GABA
Each NT may have more than one type of receptor but each receptor will only
bind with one NT (Lock and Key)
May have excitatory or inhibatroy effect
Acetylcholine
- First known NT
- At nerve-muscle connections of all voluntary and many involuntary
muscles
- Generally excibatory
- Particularly prevalent in hippocampus
Noradrenalin/Norapinephrine
- A monamine
- Involved in mediation of emergency responses
- Involved in arousal, sleep, mood
- Drugs that effect NA will effect mood
- Drugs affecting NA = cocaine, amphetamines, lithium
Dopamine (DA)
- Implicated in movement, attention, learning and reward, attachment
- Low levels of DA in parkinsons disease
- Different levels and pathwasy
Seotonin (5HT)
- Very versatile; many functions throughout the whole body
, - Involved in: temperature regulation, onset of sleep, feeding, senosry
perception
- Changes in 5HT neurons are related to action of psychedelic drugs
- Disturbances in function implicated in, depression, anxiety, migrane,
eating disorders
- Derived from tryptophan
GABA (Gamma aminobutyric acid)
- Amino acid NT
- Occurs almost exclusively in brain
- Inhibatory effects
- Thought to be involved in epilepsy
- Affects accentuated by bensoiazepines, barbituates and alcohol
Agnoists and Antagonsists
Inhibitors- drugs that inhibit normal functioning of proteins involved in synaptic
transmission
Inhibitors of receptors = Receptors antagonists
Receptor agonists- drugs that bind to reeptors and mimic normal
neurotransmissions
Inverse agonists- opposite effect of agonists