PROBLEM 2. MEMORY AND LEARNING
Chapter 15: Temporal Lobes
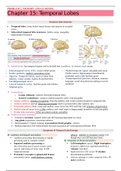
Temporal Lobe Anatomy
Temporal lobes: tissue below lateral fissure and anterior to occipital
cortex
Subcortical temporal lobe structures: limbic cortex, amygdala,
hippocampal formation
Subdivisions: the temporal regions can be divided into i) auditory, ii) ventral visual stream
o Inferotemporal cortex (TE): visual ventral stream o Medial temporal region: amygdala and uncus
o Insula: gustatory, auditory association cortex (limbic cortex), hippocampus (entorhinal &
o Superior Temporal Sulcus: receives input from perirhinal cortex) and fusiform gyrus
auditory, visual, somatic regions & parietal lobes o Temporoparietal junction: attention, memory,
o Parahippocampal cortex language, social tests-decision making in social
o Lateral temporal cortex: fusiform gyrus and inferior situations
temporal gyrus
Connections:
o Corpus callosum: connects left-right temporal lobes
o Anterior commissure: connects medial temporal cortex with amygdala
1. Sensory pathway: stimulus recognition, from the auditory and visual (ventral streams) to temporal lobe
2. Auditory pathway (dorsal) directing movements (ends in parietal lobe) after auditory info
3. Polymodal pathway from visual and auditory assoc.areas into STS and help with stimulus categorization
4. Medial temporal projections: LTM; auditory and visual input to hippocampal formation or/and amygdala.
5. Frontal-lobe projection: STM, movement control, and affect
Ventral Stream Anatomy:
1. Extends to striatum: supports habit and skill learning dependent on vision
2. Amygdala projections: emotional salience
3. Inferotemporal -Ventral striatum (n.accumbens-basal ganglia): valence
4. Medial temporal-LTM: Orbitofrontal: Reward association & Ventrolateral prefrontal: WM
Symptoms of Temporal Lobe Damage
Auditory and Speech perception aphasia , inability to recognize words even
Auditory processing discriminates i) rapidly though they can still hear pure tones
presenting and ii) complex stimuli Disorders of Music perception
Impaired auditory processing in Left hemisphere: speed , Right hemisphere:
discriminating speech quick sounds, quick frequency differences (spectral sensitivity),
speech, and temporal order (esp. in left- Amusia: tone deaf
temporal lesions) Right posterior STG lesion rhythm
Wernicke’s (receptive) aphasia-left lesions: discrimination problems
association cortex, word deafness: extreme Anterior damage to either temporal lobes
meter problems
, PROBLEM 2. MEMORY AND LEARNING
Primary auditory cortex pitch
discrimination problems
Disorders of Visual perception tasks & sematic categories (recognize broad but
Right-temporal lesions or lobectomy: poor visual not specific categories)
perception (e.g. Rey-Complex-Figure Test, Inability to use contextual information
Mooney test) Right temporal lobectomies
General impairment in facial recognition + they Memory impairment
are not able to perceive social signals & their Media temporal lobe (hippocampus and
significance amygdala) anterograde amnesia: forgetting all
Disturbance of visual and auditory input events after surgery
selection Inferotemporal cortex: problems w/ conscious
Auditory: maintain right-ear advantage but left- information recollection
temporal lobe lesion the performance drops Left-temporal lobe: impaired recall of verbal
significantly information
Difficulty of focus on only one ear or in Right temporal lobe: impaired recall of non-
processing input simultaneously verbal input e.g. faces, tunes, geometric drawings
Visual: right lesions: bilateral deficits, left Altered affect, personality and sexual behavior
lesions: unilateral right t.lobe in selective Temporal cortex stimulation feelings of fear
attention of vs Temporal-lobe personality (right): pedantic
Impaired organization and categorization speech, egocentricity, perseveration in discussions
Left-temporal lobe lesions: impaired of personal problems, paranoia, preoccupation
categorization of single words or pictures of with religion, and proneness to aggressive
familiar objects, difficulty in simple categorization outbursts (personality)
Bilateral temporal damage release of sexual
behavior (not observe in unilateral damage)
Assessment of temporal lobe damage
Wechsler Memory Scale-IV: subtests used separately
because memory is maybe affected by attentional deficits
Rey Complex-Figure Test : nonverbal memory function of
the right temporal lobe (“copy figure” after 45 minutes ask
them to recall and draw as much as possible)
o Limitation: depressed ppl refuse to remember
Token test: language comprehension
o Limitation: difficulty localizing the damage
Chapter 19:
Language
Language structure
Acoustic language, visual nature of reading
(touch language), movement language (sign)
Language is recognized by presence of words
and word components, use of syllables made up of consonants and vowels
Producing sound
Air from lungs drives oscillations of the vocal cords of the larynx energy filtered in vocal tract (sound
waves = formants) produce final product
Core language skills
1. Categorization: categories of sensory info perceive and later retrieve info (ventral visual stream through
temporal lobes and dorsal stream by making automatic distinctions)
Chapter 15: Temporal Lobes
Temporal Lobe Anatomy
Temporal lobes: tissue below lateral fissure and anterior to occipital
cortex
Subcortical temporal lobe structures: limbic cortex, amygdala,
hippocampal formation
Subdivisions: the temporal regions can be divided into i) auditory, ii) ventral visual stream
o Inferotemporal cortex (TE): visual ventral stream o Medial temporal region: amygdala and uncus
o Insula: gustatory, auditory association cortex (limbic cortex), hippocampus (entorhinal &
o Superior Temporal Sulcus: receives input from perirhinal cortex) and fusiform gyrus
auditory, visual, somatic regions & parietal lobes o Temporoparietal junction: attention, memory,
o Parahippocampal cortex language, social tests-decision making in social
o Lateral temporal cortex: fusiform gyrus and inferior situations
temporal gyrus
Connections:
o Corpus callosum: connects left-right temporal lobes
o Anterior commissure: connects medial temporal cortex with amygdala
1. Sensory pathway: stimulus recognition, from the auditory and visual (ventral streams) to temporal lobe
2. Auditory pathway (dorsal) directing movements (ends in parietal lobe) after auditory info
3. Polymodal pathway from visual and auditory assoc.areas into STS and help with stimulus categorization
4. Medial temporal projections: LTM; auditory and visual input to hippocampal formation or/and amygdala.
5. Frontal-lobe projection: STM, movement control, and affect
Ventral Stream Anatomy:
1. Extends to striatum: supports habit and skill learning dependent on vision
2. Amygdala projections: emotional salience
3. Inferotemporal -Ventral striatum (n.accumbens-basal ganglia): valence
4. Medial temporal-LTM: Orbitofrontal: Reward association & Ventrolateral prefrontal: WM
Symptoms of Temporal Lobe Damage
Auditory and Speech perception aphasia , inability to recognize words even
Auditory processing discriminates i) rapidly though they can still hear pure tones
presenting and ii) complex stimuli Disorders of Music perception
Impaired auditory processing in Left hemisphere: speed , Right hemisphere:
discriminating speech quick sounds, quick frequency differences (spectral sensitivity),
speech, and temporal order (esp. in left- Amusia: tone deaf
temporal lesions) Right posterior STG lesion rhythm
Wernicke’s (receptive) aphasia-left lesions: discrimination problems
association cortex, word deafness: extreme Anterior damage to either temporal lobes
meter problems
, PROBLEM 2. MEMORY AND LEARNING
Primary auditory cortex pitch
discrimination problems
Disorders of Visual perception tasks & sematic categories (recognize broad but
Right-temporal lesions or lobectomy: poor visual not specific categories)
perception (e.g. Rey-Complex-Figure Test, Inability to use contextual information
Mooney test) Right temporal lobectomies
General impairment in facial recognition + they Memory impairment
are not able to perceive social signals & their Media temporal lobe (hippocampus and
significance amygdala) anterograde amnesia: forgetting all
Disturbance of visual and auditory input events after surgery
selection Inferotemporal cortex: problems w/ conscious
Auditory: maintain right-ear advantage but left- information recollection
temporal lobe lesion the performance drops Left-temporal lobe: impaired recall of verbal
significantly information
Difficulty of focus on only one ear or in Right temporal lobe: impaired recall of non-
processing input simultaneously verbal input e.g. faces, tunes, geometric drawings
Visual: right lesions: bilateral deficits, left Altered affect, personality and sexual behavior
lesions: unilateral right t.lobe in selective Temporal cortex stimulation feelings of fear
attention of vs Temporal-lobe personality (right): pedantic
Impaired organization and categorization speech, egocentricity, perseveration in discussions
Left-temporal lobe lesions: impaired of personal problems, paranoia, preoccupation
categorization of single words or pictures of with religion, and proneness to aggressive
familiar objects, difficulty in simple categorization outbursts (personality)
Bilateral temporal damage release of sexual
behavior (not observe in unilateral damage)
Assessment of temporal lobe damage
Wechsler Memory Scale-IV: subtests used separately
because memory is maybe affected by attentional deficits
Rey Complex-Figure Test : nonverbal memory function of
the right temporal lobe (“copy figure” after 45 minutes ask
them to recall and draw as much as possible)
o Limitation: depressed ppl refuse to remember
Token test: language comprehension
o Limitation: difficulty localizing the damage
Chapter 19:
Language
Language structure
Acoustic language, visual nature of reading
(touch language), movement language (sign)
Language is recognized by presence of words
and word components, use of syllables made up of consonants and vowels
Producing sound
Air from lungs drives oscillations of the vocal cords of the larynx energy filtered in vocal tract (sound
waves = formants) produce final product
Core language skills
1. Categorization: categories of sensory info perceive and later retrieve info (ventral visual stream through
temporal lobes and dorsal stream by making automatic distinctions)