French Revolution 1789-1799
Most significant political and social transformations
Birth of European modernity
Impact on similar political and social transformations in other parts of the
world eg: Haiti
European Enlightenment:
Intellectual movement that elevated human reason, scientific rationalism,
undermined power of the Church, questioned the notion of a divinely ordained
ruler and social inequality
American Revolution (1775-1783):
Successful revolution by American colonists to overthrow British rule, led to
the establishment of the United States of America
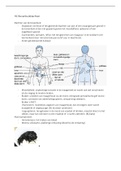
First Estate (clergy) owned 10% of the land. Exempt from tax and hierarchically divided
Second Estate (nobility) who owned 25-30% of land. Dominated leadership in government, the military and law
courts. Extremely privileged and paid no taxes
Third Estate (commoners) were hierarchicalluy divided based on education, occupation and wealth. Rural
peasants (70-80% of total population) owned 35-40% of land. They paid tithes and fees to the landowners for use
of village facilities. Bourgeoisie/middle classes (8% of population) were shop owners, bankers, lawyers... and they
were excluded from privileges of the nobility. Politically and socially rigid society with a wealthy privileged minority
and underprivileged majority
, Immediate causes were largely economic:
o General economic crisis fueled by manufacturing depression, rising
inflation and food prices made worse by bad harvests in 1787/89
o Food shortages and unemployment reached crisis point in 1788/89
o Collapse of state finances caused by extravagant lifestyle of the king
and queen
o Wars with European neighbours
Bastille Day 14 July 1789
Revokes broke out throughout France and peasant
rebellions in the countryside were focussed on attackin Estates General met 5 May 1789: Third Estate
landowners, their major grievance was the landholding demanded every representative be given a vote
system
King could no longer rely on troops - collapse of royal First and Second Estates resisited: locked the Third
authority Estate out
A mob of Parisians stromed the Bastille, royal armoury
and symbol of power, 14 July and freed seven prisoners 500 members signed Tennis Court Oath and
and killed seven gaurds established National Assembly on 17 June 1789
King sided with the First and Second Estate as this act
was illegal and threatened to dissolve the Estates-
General
Most significant political and social transformations
Birth of European modernity
Impact on similar political and social transformations in other parts of the
world eg: Haiti
European Enlightenment:
Intellectual movement that elevated human reason, scientific rationalism,
undermined power of the Church, questioned the notion of a divinely ordained
ruler and social inequality
American Revolution (1775-1783):
Successful revolution by American colonists to overthrow British rule, led to
the establishment of the United States of America
First Estate (clergy) owned 10% of the land. Exempt from tax and hierarchically divided
Second Estate (nobility) who owned 25-30% of land. Dominated leadership in government, the military and law
courts. Extremely privileged and paid no taxes
Third Estate (commoners) were hierarchicalluy divided based on education, occupation and wealth. Rural
peasants (70-80% of total population) owned 35-40% of land. They paid tithes and fees to the landowners for use
of village facilities. Bourgeoisie/middle classes (8% of population) were shop owners, bankers, lawyers... and they
were excluded from privileges of the nobility. Politically and socially rigid society with a wealthy privileged minority
and underprivileged majority
, Immediate causes were largely economic:
o General economic crisis fueled by manufacturing depression, rising
inflation and food prices made worse by bad harvests in 1787/89
o Food shortages and unemployment reached crisis point in 1788/89
o Collapse of state finances caused by extravagant lifestyle of the king
and queen
o Wars with European neighbours
Bastille Day 14 July 1789
Revokes broke out throughout France and peasant
rebellions in the countryside were focussed on attackin Estates General met 5 May 1789: Third Estate
landowners, their major grievance was the landholding demanded every representative be given a vote
system
King could no longer rely on troops - collapse of royal First and Second Estates resisited: locked the Third
authority Estate out
A mob of Parisians stromed the Bastille, royal armoury
and symbol of power, 14 July and freed seven prisoners 500 members signed Tennis Court Oath and
and killed seven gaurds established National Assembly on 17 June 1789
King sided with the First and Second Estate as this act
was illegal and threatened to dissolve the Estates-
General