animals
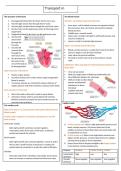
The structure of the heart The blood vessels
1. Deoxygenated blood into the heart via the vena cava. Arteries= carry blood away from the heart
2. Into the right atrium then through the AV valve.
Inner layer- wall is folded so lumen can expand as blood
3. Into the right ventricle then through the semi lunar valve.
flow increases, they can stretch and recoil to maintain
4. Out the heart via the pulmonary artery to the lungs to be
blood pressure.
oxygenated.
Middle layer- smooth muscle.
5. Oxygenated blood in the heart via the pulmonary vein.
Outer layer- provides strength to withstand pressure and
6. Into the left
recoil to maintain it.
atrium then
Lumen is small to maintain high pressure.
through the
AV valve. Veins= carry blood back to the heart
7. Into the left
ventricle then Blood is at low pressure, so walls don’t need to be thick.
through the Lumen is large to ease the flow of blood.
semi lunar valve. Have valves to prevent backflow.
8. Out the heart via No need to stretch and recoil so have thinner muscle
the aorta to the walls.
rest of the body to
Capillaries= allow exchange of material between blood and
be deoxygenated.
tissue fluid
Outer structure of the heart:
Very narrow lumen
Mainly cardiac muscle Walls are single layers of flattened endothelial cells.
Coronary arteries over surface which supply oxygenated Short diffusion distance for exchange.
blood to muscle. Walls are leaky to allow blood
If coronary arteries are restricted it reduces delivery of plasma and dissolved
oxygen, glucose and other nutrients causing a heart attack. substances to leave
the blood.
Inner structure of the heart: Capillary beds link
arteries and veins.
Atria- thin walls as they don’t need to pump blood.
Ventricles- thicker walls to pump blood, left ventricle
thickest as blood is pumped out aorta needs pressure to
overcome the resistance. Capillary beds
The cardiac cycle
Role of the heart= to create pressure that pushes blood around
blood vessels
Cardiac cycle= sequence of muscular contractions in one full
beat of heart.
Ventricular systole: 1) At the arteriole end- there is high hydrostatic pressure and
- Both right and left ventricles contract together, lower oncotic pressure. This forces blood out of the
contraction starts at the base of the heart, so blood is capillary to become tissue fluid which surrounds body cells
pushed up towards the arteries. so respiration can occur.
2) At the venule end- there is low hydrostatic pressure and
Atrial systole: higher oncotic pressure, so tissue fluid returns to capillary
carrying waste products from respiration.
- Both right and left atria contract together, muscle in wall is
3) Excess tissue fluid is directed straight to the lymph system
thin so only a small increase in pressure is created, this
to be drained, contains lymphocytes.
pushes blood to ventricles to stretch the walls to fill them.
Feature PLASMA TISSUE FLUID LYMPH
Diastole:
Hydrostatic High Low low
- Muscular walls of all 4 chambers relax elastic recoil causes pressure
them to increase in volume so blood can flow from veins. Oncotic More negative Less negative Less negative
pressure