Significant ideas
● The atmosphere is a dynamic system which is essential to life on Earth.
● The behaviour, structure and composition of the atmosphere influence variations in all ecosystems.
Applications and skills
● Discuss the role of the albedo effect from clouds in regulating global average temperature.
● Outline the role of the greenhouse effect in regulating temperature on Earth.
Understandings
1. The atmosphere is a dynamic system (with inputs, outputs, flows and storages) that has undergone
changes throughout geological time.
2. The atmosphere is predominantly a mixture of nitrogen and oxygen, with smaller amounts of carbon
dioxide, argon, water vapour and other trace gases.
3. Human activities impact atmospheric composition through altering inputs and outputs of the system.
Changes in the concentrations of atmospheric gases—such as ozone, carbon dioxide, and water
vapour—have significant effects on ecosystems.
4. Most reactions connected to living systems occur in the inner layers of the atmosphere, which are the
troposphere (0–10 km above sea level) and the stratosphere (10–50 km above sea level).
5. Most clouds form in the troposphere and play an important role in the albedo effect of the planet.
6. The greenhouse effect of the atmosphere is a natural and necessary phenomenon maintaining
suitable temperatures for living systems.
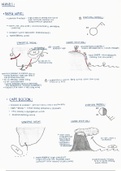
Atmospheric system
The atmosphere is a dynamic system with
inputs, outputs, storages and flows.
Heat and pollutants are carried
across the Earth by air currents
in the atmosphere.
, ● the atmosphere is approximately 1,100 km in depth.
● the stratosphere (10–50 km) and the troposphere (<10 km) are where most reactions affecting life
occur, e.g. ozone and cloud formation.
● human activities and activities by other organisms impact the atmospheric composition through altering
inputs and outputs of the system.
Past atmospheric changes
Climate is unstable and has fluctuated greatly in the past due to:
● Abiotic factors – mainly temperature and precipitation.
● Biotic factors – plants and animals.
, Greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect is a natural and necessary phenomenon maintaining suitable temperatures for living
systems.
● a natural process that warms the Earth’s surface.
● allows life on Earth to exist.
● Earth’s average surface temperature is 15°C, 33°C warmer than it would be without the greenhouse
effect.
Steps:
1. Solar radiation reaches the Earth's atmosphere - some of this is reflected back into space.
2. The rest of the sun's energy is absorbed by the land and the oceans, heating the Earth.
3. Heat radiates from Earth towards space.
4. Some of this heat is trapped by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Greenhouse gases
The gases that are responsible for global warming.
● absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range.
● the primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane,
nitrous oxide and ozone.
● human activities increase emissions of greenhouse gases, contributing to global warming.
Ozone layer
The ozone layer is a layer of gas in the atmosphere that protects the Earth from harmful radiation from the Sun.
● 15-35 kilometres above Earth’s surface.
● lies within the stratosphere of the Earth’s atmosphere.
● contains relatively high concentrations of ozone (O3).
● absorbs 97-99% of the sun's high-frequency ultraviolet light, which can be damaging to life on Earth.
Climate change vs Global warming
Climate change
The long-term alterations of weather patterns.
● change in the properties of the climate system that persists for decades.
● may be due to natural processes (e.g. volcanoes) or human activities (land use).
Global warming
The rise in the average temperature of the Earth’s surface.
● caused by the increase in carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases (human-caused).