Ch .
2 Bouic
correjh
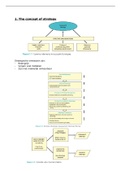
IT is
increasely presentin modern
our
society inputs computers output, . e .
..
keyboard screen
Horrdware : -
injus .
keyboard, mouse,,...
+ external storage spaces
-
autjut : screen, sound ,,...
external storage spaces
+
computer CPU Central unit !
·
processing
-
-
:
internal RAM/ ROM
memory
-
:
-external hard disk USB stick CD external harddrives
...
memory
:
, , ,
RAM く> External
memory
internal external
cleared when there is
memory no
electricity memory preserved after turning
the PC
off
much
Capacity rather small
capacity longer
Softiars Programs : :
-requence of order formulated by programs
Conversion into machine
language thesetofthittemully binary form thatne a
-
in
-
module . · reuse ,
complex i plitting into sub- problems
len , ,
·
error module easier to
find, collaboration with several people
Data besides also be Data
programs software
:
,
com !
Databas data stored in
organized collection of computer
e -
a
-
rational database
Network multiple computers to
: communicas and
exchange data
within the broader
organization or
-
S e r v e:
rs computer only for calculation andstorage no screen
,
no
keyboard ,
s .
g
.. mail server web serves , ...
Internet the :
biggest internetwork
, Computer architecture Fundamental
:
organization ofthe computer system
Phasex :
moinframe
Phase 2 : PC& client server
Phase 3: browebsX cloud
Processes A busine process in a
ofstepactione with the am of generating product service
sequence
: a or
Information System : the combination
of IT hardwars ,
software , processes and people
who use it
, .
Ch 3
Algorithm
methods to solvs
↳ = a a problem
- a
sequence ofactions /commands rule ,
starting from given initialsituation
-
as
,
-leading to a certain
goal
within time
a
finite .
-
the Commands be understood in
> must an
unambiguous
↳
ondubbetsinnig way
Steps programming in :
1) Problem
definition :
define the problem fully and accurately from which initio situation
: in started
,
which resulti must be obtained and what is the link between both
.
Solution
2)
strategy : the choice
of a solution method and
ofthe data representation :
to divide the problem into smaller
-tryingwath sub problems I modules
-
happen will
problem
agreeing :
each sub in
3)
Representation of algorithm p flow chart, nowsi schneidermann diagram piendo
the e . .
.
,
cools ....
4
Programming:
when encoding the elaborated
,
bromilated into the
algorithm programming language
translation into machine
5)
Compiling
to detect eventual
syntax errors ,
languagebinaryco
compiler ve
interpreter
-
6)
Testing : result mint also be
logically correct , Compos with results obtained in a
different way ,
-
test all
different cases
7)
Documenting information that willhelp third parties to understand modify, improve complete the program ,
as
8) Maintenames.
after a while the
program eventually hou to be updated
-report changes in the documentation !
2 Bouic
correjh
IT is
increasely presentin modern
our
society inputs computers output, . e .
..
keyboard screen
Horrdware : -
injus .
keyboard, mouse,,...
+ external storage spaces
-
autjut : screen, sound ,,...
external storage spaces
+
computer CPU Central unit !
·
processing
-
-
:
internal RAM/ ROM
memory
-
:
-external hard disk USB stick CD external harddrives
...
memory
:
, , ,
RAM く> External
memory
internal external
cleared when there is
memory no
electricity memory preserved after turning
the PC
off
much
Capacity rather small
capacity longer
Softiars Programs : :
-requence of order formulated by programs
Conversion into machine
language thesetofthittemully binary form thatne a
-
in
-
module . · reuse ,
complex i plitting into sub- problems
len , ,
·
error module easier to
find, collaboration with several people
Data besides also be Data
programs software
:
,
com !
Databas data stored in
organized collection of computer
e -
a
-
rational database
Network multiple computers to
: communicas and
exchange data
within the broader
organization or
-
S e r v e:
rs computer only for calculation andstorage no screen
,
no
keyboard ,
s .
g
.. mail server web serves , ...
Internet the :
biggest internetwork
, Computer architecture Fundamental
:
organization ofthe computer system
Phasex :
moinframe
Phase 2 : PC& client server
Phase 3: browebsX cloud
Processes A busine process in a
ofstepactione with the am of generating product service
sequence
: a or
Information System : the combination
of IT hardwars ,
software , processes and people
who use it
, .
Ch 3
Algorithm
methods to solvs
↳ = a a problem
- a
sequence ofactions /commands rule ,
starting from given initialsituation
-
as
,
-leading to a certain
goal
within time
a
finite .
-
the Commands be understood in
> must an
unambiguous
↳
ondubbetsinnig way
Steps programming in :
1) Problem
definition :
define the problem fully and accurately from which initio situation
: in started
,
which resulti must be obtained and what is the link between both
.
Solution
2)
strategy : the choice
of a solution method and
ofthe data representation :
to divide the problem into smaller
-tryingwath sub problems I modules
-
happen will
problem
agreeing :
each sub in
3)
Representation of algorithm p flow chart, nowsi schneidermann diagram piendo
the e . .
.
,
cools ....
4
Programming:
when encoding the elaborated
,
bromilated into the
algorithm programming language
translation into machine
5)
Compiling
to detect eventual
syntax errors ,
languagebinaryco
compiler ve
interpreter
-
6)
Testing : result mint also be
logically correct , Compos with results obtained in a
different way ,
-
test all
different cases
7)
Documenting information that willhelp third parties to understand modify, improve complete the program ,
as
8) Maintenames.
after a while the
program eventually hou to be updated
-report changes in the documentation !