Monomers and Polymers
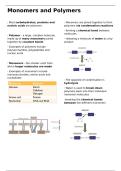
: Most carbohydrates, proteins and : Monomers are joined together to form
nucleic acids are polymers polymers via condensation reactions
- forming a chemical bond between
molecules
: Polymer - a large, complex molecule
made up of many monomers joined - releasing a molecule of water as a by-
together by covalent bonds product
- Examples of polymers include
polysaccharides, polypeptides and
nucleic acids
: Monomers - the smaller units from
which larger molecules are made
- Examples of monomers include
monosaccharides, amino acids and
nucleotides
: The opposite of condensation is
hydrolysis
: Water is used to break down
polymers back into their individual
monomer molecules
-breaking the chemical bonds
between the different monomers
: Most carbohydrates, proteins and : Monomers are joined together to form
nucleic acids are polymers polymers via condensation reactions
- forming a chemical bond between
molecules
: Polymer - a large, complex molecule
made up of many monomers joined - releasing a molecule of water as a by-
together by covalent bonds product
- Examples of polymers include
polysaccharides, polypeptides and
nucleic acids
: Monomers - the smaller units from
which larger molecules are made
- Examples of monomers include
monosaccharides, amino acids and
nucleotides
: The opposite of condensation is
hydrolysis
: Water is used to break down
polymers back into their individual
monomer molecules
-breaking the chemical bonds
between the different monomers