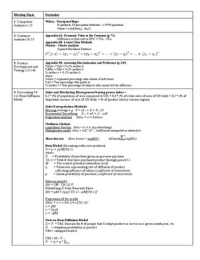
Physics
Electricity
Friction, when two insulators move relative to each other result in both objects becoming
electrically charged. One of the objects becomes positively charged, and the other negatively
charged ex hair being combed
Conductors, become charged but only retain that charge when insulated from their
surroundings otherwise, any charge that builds up will leak away.
Induction, process of objects becoming charged
Magnetic induction, piece of iron becomes magnetised when placed near a magnet
Electrostatic induction, neutral object near a charged object can become charged
If one end of an object charged by induction is momentarily earthed, allowing the charge
that has accumulated at that end to leak away, then the object becomes permanently
charged.
Electrostatically charged, friction can result in electrons being transferred causing the
objects to become charged. Electrons move away from the atoms that attract them less
strongly, and towards the atoms that attract them more strongly.
Like charges repel each other ex + and +
Unlike charges attract each other ex + and -
Sparking, air between two objects becomes ionised by a large voltage and starts conducting
therefore two charged objects can discharge by a spark between them causing risk of fire.
Earthing, eliminates risk of sparking by connecting the objects together by a wire or if one of
them is connected to Earth by a wire) then electrostatic charging.
Direct current (dc), current always in the same direction ex cells or batteries
Alternating current (ac), current repeatedly changes direction, usually very rapidly with a
frequency therefore forming a wave pattern (sinusoidal but can be any shape) ex generator
in power stations
Symbol for an ac supply:
The output from a power supply from mains electricity can be converted from ac to dc using
diodes as a ‘rectifier’
Examples of good conductors:
Metals, particularly copper, gold and silver
Carbon in the form of graphite
Ionic solutions
Examples of good insulators:
Most non-metals, particularly plastics, rubber, dry wood, air, vacuum.
Water, unless extremely pure, so wet or damp materials are not good insulators.
I, current, rate of flow of electric charge (A or C/s)
Q, charge (C)
t, time (s)
V, voltage (V or J/C)
E, energy (J)
, Q, charge (C)
Voltmeter, measures voltage, connected in parallel with a component and very high
resistance
Ammeter, measures current, connected in series with a component and very low resistance
R, resistance for an ohmic conductor (ohm)
V, voltage (V)
I, current (A)
Thermistor, resistance that depends on its temperature ex NTC, negative
temperature coefficient type, as its temperature increases, its resistance
decreases.
Light dependent resistor (LDR), resistance that depends on the intensity of
light that falls on it. As the light intensity increases, the resistance of the LDR
decreases.
Ideal diode, component that only allows a current in one direction shown by
the arrowhead
P, power (W)
I, current (A)
V, voltage (V)
E, energy (J)
V x I = P, power (W)
t, time (s)
Electric circuit, consists of a supply and a load (resistor) connected together in a complete
loop in which charged particles travel around, picking up energy at the supply, carrying out
around one side of the loop to the load and then returning to the supply around the other
side of the loop.
Series circuits: Parallel circuits:
Itot = I1 = I2 etc. Itot = I1 + I2 etc.
Vtot = V1 + V2 etc. Vtot = V1 = V2 etc.
Rtot = R1 + R2 etc. Rtot = 1/R1 + 1/R2 etc.
Magnetism
Magnets forces, force magnets exerted on one another when
they are placed close together.
Like poles repel ex N and N or S and S
Unlike poles attract ex N and S or S and N
North-seeking, north pole on a bar magnet is attracted to the north geographic pole of Earth.
(Earth’s north geographic pole is therefore a south-seeking pole) ex compass
Magnetic field, region in which magnetic forces act on magnets or magnetic materials
represented by drawing magnetic field lines that go from N to S
Soft magnetic materials, easy to magnetise, also easily lose their magnetization ex iron,
electromagnets and a coil
Electricity
Friction, when two insulators move relative to each other result in both objects becoming
electrically charged. One of the objects becomes positively charged, and the other negatively
charged ex hair being combed
Conductors, become charged but only retain that charge when insulated from their
surroundings otherwise, any charge that builds up will leak away.
Induction, process of objects becoming charged
Magnetic induction, piece of iron becomes magnetised when placed near a magnet
Electrostatic induction, neutral object near a charged object can become charged
If one end of an object charged by induction is momentarily earthed, allowing the charge
that has accumulated at that end to leak away, then the object becomes permanently
charged.
Electrostatically charged, friction can result in electrons being transferred causing the
objects to become charged. Electrons move away from the atoms that attract them less
strongly, and towards the atoms that attract them more strongly.
Like charges repel each other ex + and +
Unlike charges attract each other ex + and -
Sparking, air between two objects becomes ionised by a large voltage and starts conducting
therefore two charged objects can discharge by a spark between them causing risk of fire.
Earthing, eliminates risk of sparking by connecting the objects together by a wire or if one of
them is connected to Earth by a wire) then electrostatic charging.
Direct current (dc), current always in the same direction ex cells or batteries
Alternating current (ac), current repeatedly changes direction, usually very rapidly with a
frequency therefore forming a wave pattern (sinusoidal but can be any shape) ex generator
in power stations
Symbol for an ac supply:
The output from a power supply from mains electricity can be converted from ac to dc using
diodes as a ‘rectifier’
Examples of good conductors:
Metals, particularly copper, gold and silver
Carbon in the form of graphite
Ionic solutions
Examples of good insulators:
Most non-metals, particularly plastics, rubber, dry wood, air, vacuum.
Water, unless extremely pure, so wet or damp materials are not good insulators.
I, current, rate of flow of electric charge (A or C/s)
Q, charge (C)
t, time (s)
V, voltage (V or J/C)
E, energy (J)
, Q, charge (C)
Voltmeter, measures voltage, connected in parallel with a component and very high
resistance
Ammeter, measures current, connected in series with a component and very low resistance
R, resistance for an ohmic conductor (ohm)
V, voltage (V)
I, current (A)
Thermistor, resistance that depends on its temperature ex NTC, negative
temperature coefficient type, as its temperature increases, its resistance
decreases.
Light dependent resistor (LDR), resistance that depends on the intensity of
light that falls on it. As the light intensity increases, the resistance of the LDR
decreases.
Ideal diode, component that only allows a current in one direction shown by
the arrowhead
P, power (W)
I, current (A)
V, voltage (V)
E, energy (J)
V x I = P, power (W)
t, time (s)
Electric circuit, consists of a supply and a load (resistor) connected together in a complete
loop in which charged particles travel around, picking up energy at the supply, carrying out
around one side of the loop to the load and then returning to the supply around the other
side of the loop.
Series circuits: Parallel circuits:
Itot = I1 = I2 etc. Itot = I1 + I2 etc.
Vtot = V1 + V2 etc. Vtot = V1 = V2 etc.
Rtot = R1 + R2 etc. Rtot = 1/R1 + 1/R2 etc.
Magnetism
Magnets forces, force magnets exerted on one another when
they are placed close together.
Like poles repel ex N and N or S and S
Unlike poles attract ex N and S or S and N
North-seeking, north pole on a bar magnet is attracted to the north geographic pole of Earth.
(Earth’s north geographic pole is therefore a south-seeking pole) ex compass
Magnetic field, region in which magnetic forces act on magnets or magnetic materials
represented by drawing magnetic field lines that go from N to S
Soft magnetic materials, easy to magnetise, also easily lose their magnetization ex iron,
electromagnets and a coil