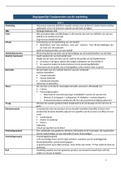
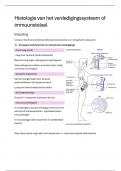
Psychology
Approaches
Behavioural: born with tabula rosa (blank slate). All behaviour is learned via classical and operant
conditioning. Lab experiments- objective way of measuring behaviour.
Classical Conditioning (Pavlov’s Dogs): UCS – food. UCR – saliva.
UCS – food + NS – bell UCR – saliva
CS – bell CR – saliva
Generalisation: CR occurs in presence of similar stimuli.
Discrimination: response to only one stimulus.
Extinction: If the CS is not paired with UCS, the response fades.
Spontaneous Recovery: After extinction, the CR occurs again.
Operant Conditioning: consequences of behaviour – Thorndyke 1911 (puzzle box)
Thorndyke – Trial and Error kept trying anything. Cat escaped quicker than last time.
Skinner: Positive Reinforcement = a reward that increases likelihood that a behaviour or action will
be repeated.
Negative Reinforcement = unpleasant experience is removed after behaviour, increases likelihood of
behaviour repeated.
Punishment = weakens behaviour because its t and we avoid it.
Skinner’s Box: the rat activates a lever and its rewarded (positive reinforcement), conditioned to
avoid unpleasant stimuli (electric shock)
Reinforcement Schedule- vary response rate.
Variable Ratio Reinforcement Schedule/ partial reinforcement produces a fast response rate and is
resistant to extinction.
Evaluation
Scientific Credibility: controlled lab settings.
Real Life Applications: helped to develop therapies, explains development of addictions.
Mechanistic: machine-like, no insight into behaviour
Too Deterministic: culmination of reinforcement history, ignores free will – behaviour is
predetermined by conditioning.
Ethical issues: Little Albert (shocks), use of animals, inhumane therapies.
Social Learning Theory: Bandura, mental processes mediate.
Imitation – copying behaviour of others.
Identification – when a person associates themselves with a role model and wants to be like them.
Modelling – imitating the behaviour of a particular role model.
Vicarious Reinforcement – learning from seeing model being either reinforced or punished. Not
directly experienced.
Bandura (1961): recorded the behaviour of young children who watched an adult behave in an
aggressive way towards a bobo doll. Children behaved more aggressively towards the doll.
(imitation).
Bandura and Walters (1963): Grp 1 – saw adult praised for aggressively. Grp 2 – saw adult punished.
Grp 3 – control group, no consequences. (vicarious reinforcement)
Meditational Processes:
Attention- notice certain behaviours
,Retention- how well the behaviour is remembered
Motor Production- ability to perform the behaviour
Motivation- desire to perform, depends on whether its rewarded or punished.
Evaluation
Practical Application: SLT applied to primary schools, Star of the Week.
Experimental support: Fagot, observed 2yr olds playing at home – boys and girls reinforced for
different behaviours ‘gender appropriate play’
Cognitive Factors: Attention, Retention, Motor Production and Motivation.
Ignores Biological Factors: boys more aggressive due to testosterone.
Reductionist and Deterministic: Reductionist = too simplified. Deterministic = soft determinism, we
have some free will.
Lacks External Validity: demand characteristics.
Cognitive Approach: inference, computer analogy.
Schema- mental set of beliefs and expectations developed from experience.
Inference – draw conclusions based on observable behaviour
Internal Mental Processes- private operations of the mind
Cognitive Neuroscience- scientific study of biological structures.
Computer Models: processing, encoding and storage.
Theoretical Models- information processing approach e.g. multi store model of memory.
Schema – sets of ideas. Born with simple motor schema for sucking and grasping. Process lots of info
very quickly, inaccurate schema can distort interpretation of a situation and lead to errors.
Cognitive Neuroscience: brain fingerprinting – brainwave pattern that happens when people are
lying, can analyse patterns of eyewitnesses.
FMRI and PET scans
Evaluation
Scientific Methods: lab experiments
Soft Determinism: internal and external factors, exert some free will.
Real Life Applications: CBT
Machine Reductionist: brain is like a computer but ignores emotional responses.
Lack External Validity: artificial lab settings, cannot generalise.
Biological Approach: brain structures, the mind IS the brain.
Genes – code psychological and physical features.
Genotype – set of genes that a person possesses
Phenotype- characteristics of an individual
Genotype + Environment = Phenotype
Phenylketonuria (PKU) – inherited condition controlled by diet, no meat, dairy products.
Genetics: MZ twins- monozygotic share 100% of genes.
DZ twins – dizygotic twins, share 50% of genes
Concordance (correlations) – environment plays a role in intelligence as cannot be fully controlled by
genes. Genes 70% Environment 30%
Genotype- genetic makeup. Phenotype- genes are expresses.
Phenotype affected by environmental factors.
Evolution: Charles Darwin, theory of natural selection.
, Adaptive advantages:
Good memory – remembering what food is poisoned
Secure Attachment – more likely to survive
Mental Disorder – OCD – repeated washing so no disease etc.
Evaluation
Scientific Methods: FMRI’s, EEG, drug trials.
Real Life Applications: psychoactive drugs have developed for depression and schizophrenia.
Assumes Causation: lack of drug is a cause of the disorder.
Deterministic: no free will.
Problems separating Nature from Nurture: genes or environment?
Humanistic Approach: subjective for self determination, believes we have free will, active agents.
3rd force of psychology.
Free will: self determining, we are active agents determine own development, person- centred
approach.
Self Actualisation: achieve their full potential. Growth need.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: What motivates people.
Self Actualisation = morality, lack of prejudice.
Esteem = self esteem
Love/belonging = friendships, family
Safety = security of body, employment
Physiological = breathing, food, water.
Can only self actualise if basic needs are met first.
Self, Congruence and Conditions of Worth:
Rogers- concept of self have congruence with ideal self. If the gap is too large, experience
incongruence as negative feelings become a barrier for self actualisation.
Low self esteem and worthlessness have roots in childhood. Lack of unconditional positive regard.
Conditions of worth creates low self esteem.
Rogerian Therapy: person- centred therapy.
Non-directive. Helped to find their own solutions to their problems.
Atmosphere = warm, supportive, and non- judgmental.
Therapists provide- Genuineness, Empathy and Unconditional Positive Regard.
Increases persons self worth, reduce incongruence.
Evaluation
Not Reductionist: advocate holism – looking at the whole person not just biology or reinforcement
history.
Positive Approach: positive image of human condition. Contrasts Freuds ‘common unhappiness and
absolute despair’
Limited Application: little impact, anti-science, loose set of abstract ideas.
Untestable Concepts: vague and difficult to test. Rogers attempted to introduce Q-Sort measure.
Lacks empirical evidence.
Cultural Biases: Western appeal to individual freedom and personal growth, Collectivist focuses on
group needs.
Rogerian Therapy: only effective for ‘mild’ psychological problems.
Psychodynamic Approach
Approaches
Behavioural: born with tabula rosa (blank slate). All behaviour is learned via classical and operant
conditioning. Lab experiments- objective way of measuring behaviour.
Classical Conditioning (Pavlov’s Dogs): UCS – food. UCR – saliva.
UCS – food + NS – bell UCR – saliva
CS – bell CR – saliva
Generalisation: CR occurs in presence of similar stimuli.
Discrimination: response to only one stimulus.
Extinction: If the CS is not paired with UCS, the response fades.
Spontaneous Recovery: After extinction, the CR occurs again.
Operant Conditioning: consequences of behaviour – Thorndyke 1911 (puzzle box)
Thorndyke – Trial and Error kept trying anything. Cat escaped quicker than last time.
Skinner: Positive Reinforcement = a reward that increases likelihood that a behaviour or action will
be repeated.
Negative Reinforcement = unpleasant experience is removed after behaviour, increases likelihood of
behaviour repeated.
Punishment = weakens behaviour because its t and we avoid it.
Skinner’s Box: the rat activates a lever and its rewarded (positive reinforcement), conditioned to
avoid unpleasant stimuli (electric shock)
Reinforcement Schedule- vary response rate.
Variable Ratio Reinforcement Schedule/ partial reinforcement produces a fast response rate and is
resistant to extinction.
Evaluation
Scientific Credibility: controlled lab settings.
Real Life Applications: helped to develop therapies, explains development of addictions.
Mechanistic: machine-like, no insight into behaviour
Too Deterministic: culmination of reinforcement history, ignores free will – behaviour is
predetermined by conditioning.
Ethical issues: Little Albert (shocks), use of animals, inhumane therapies.
Social Learning Theory: Bandura, mental processes mediate.
Imitation – copying behaviour of others.
Identification – when a person associates themselves with a role model and wants to be like them.
Modelling – imitating the behaviour of a particular role model.
Vicarious Reinforcement – learning from seeing model being either reinforced or punished. Not
directly experienced.
Bandura (1961): recorded the behaviour of young children who watched an adult behave in an
aggressive way towards a bobo doll. Children behaved more aggressively towards the doll.
(imitation).
Bandura and Walters (1963): Grp 1 – saw adult praised for aggressively. Grp 2 – saw adult punished.
Grp 3 – control group, no consequences. (vicarious reinforcement)
Meditational Processes:
Attention- notice certain behaviours
,Retention- how well the behaviour is remembered
Motor Production- ability to perform the behaviour
Motivation- desire to perform, depends on whether its rewarded or punished.
Evaluation
Practical Application: SLT applied to primary schools, Star of the Week.
Experimental support: Fagot, observed 2yr olds playing at home – boys and girls reinforced for
different behaviours ‘gender appropriate play’
Cognitive Factors: Attention, Retention, Motor Production and Motivation.
Ignores Biological Factors: boys more aggressive due to testosterone.
Reductionist and Deterministic: Reductionist = too simplified. Deterministic = soft determinism, we
have some free will.
Lacks External Validity: demand characteristics.
Cognitive Approach: inference, computer analogy.
Schema- mental set of beliefs and expectations developed from experience.
Inference – draw conclusions based on observable behaviour
Internal Mental Processes- private operations of the mind
Cognitive Neuroscience- scientific study of biological structures.
Computer Models: processing, encoding and storage.
Theoretical Models- information processing approach e.g. multi store model of memory.
Schema – sets of ideas. Born with simple motor schema for sucking and grasping. Process lots of info
very quickly, inaccurate schema can distort interpretation of a situation and lead to errors.
Cognitive Neuroscience: brain fingerprinting – brainwave pattern that happens when people are
lying, can analyse patterns of eyewitnesses.
FMRI and PET scans
Evaluation
Scientific Methods: lab experiments
Soft Determinism: internal and external factors, exert some free will.
Real Life Applications: CBT
Machine Reductionist: brain is like a computer but ignores emotional responses.
Lack External Validity: artificial lab settings, cannot generalise.
Biological Approach: brain structures, the mind IS the brain.
Genes – code psychological and physical features.
Genotype – set of genes that a person possesses
Phenotype- characteristics of an individual
Genotype + Environment = Phenotype
Phenylketonuria (PKU) – inherited condition controlled by diet, no meat, dairy products.
Genetics: MZ twins- monozygotic share 100% of genes.
DZ twins – dizygotic twins, share 50% of genes
Concordance (correlations) – environment plays a role in intelligence as cannot be fully controlled by
genes. Genes 70% Environment 30%
Genotype- genetic makeup. Phenotype- genes are expresses.
Phenotype affected by environmental factors.
Evolution: Charles Darwin, theory of natural selection.
, Adaptive advantages:
Good memory – remembering what food is poisoned
Secure Attachment – more likely to survive
Mental Disorder – OCD – repeated washing so no disease etc.
Evaluation
Scientific Methods: FMRI’s, EEG, drug trials.
Real Life Applications: psychoactive drugs have developed for depression and schizophrenia.
Assumes Causation: lack of drug is a cause of the disorder.
Deterministic: no free will.
Problems separating Nature from Nurture: genes or environment?
Humanistic Approach: subjective for self determination, believes we have free will, active agents.
3rd force of psychology.
Free will: self determining, we are active agents determine own development, person- centred
approach.
Self Actualisation: achieve their full potential. Growth need.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: What motivates people.
Self Actualisation = morality, lack of prejudice.
Esteem = self esteem
Love/belonging = friendships, family
Safety = security of body, employment
Physiological = breathing, food, water.
Can only self actualise if basic needs are met first.
Self, Congruence and Conditions of Worth:
Rogers- concept of self have congruence with ideal self. If the gap is too large, experience
incongruence as negative feelings become a barrier for self actualisation.
Low self esteem and worthlessness have roots in childhood. Lack of unconditional positive regard.
Conditions of worth creates low self esteem.
Rogerian Therapy: person- centred therapy.
Non-directive. Helped to find their own solutions to their problems.
Atmosphere = warm, supportive, and non- judgmental.
Therapists provide- Genuineness, Empathy and Unconditional Positive Regard.
Increases persons self worth, reduce incongruence.
Evaluation
Not Reductionist: advocate holism – looking at the whole person not just biology or reinforcement
history.
Positive Approach: positive image of human condition. Contrasts Freuds ‘common unhappiness and
absolute despair’
Limited Application: little impact, anti-science, loose set of abstract ideas.
Untestable Concepts: vague and difficult to test. Rogers attempted to introduce Q-Sort measure.
Lacks empirical evidence.
Cultural Biases: Western appeal to individual freedom and personal growth, Collectivist focuses on
group needs.
Rogerian Therapy: only effective for ‘mild’ psychological problems.
Psychodynamic Approach