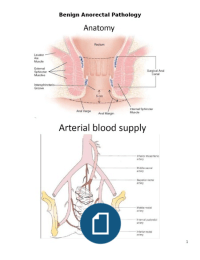
Coding, capacity and duration
Coding – the format in which information is stored in the The multi-store of memory
various memory stores. Atkinson and Shiffrin. Describes how information flows through the memory system. Memory is made up of 3 stores linked by proces
Baddeley gave different lists of words to 4 groups. Participants sensory register, comprised of registers for each of the senses. Coding in each store is modality specific. Duration of material in senso
asked to recall in correct order. from STM they tended to do second. The SRS has very high capacity. Information passes further if you pay attention to it. Information in STM is coded acoustically
worse with acoustically similar words. When recalled after seconds unless rehearsed – STM is a temporary store. STM is a limited capacity store – can only store a certain number of things befo
20min they did worse with semantically similar words. Suggest maintenance rehearsal occurs when we repeat material to ourselves. We can keep this information in our STMs if we rehearse it. If re
information is coded acoustically in STM and semantically in passes to LTM. LTM is permanent memory store for information that has been rehearsed. Coded semantically. Duration may be a lifeti
LTM . When we recall information from LTM it must be transferred back into STM by retrieval.
Clear difference between two memories. STM – acoustic and - Studies show STM and LTM are different. Baddeley found that we tend to mix up words that sound similar when using STMs, but w
LTM – semantic still applies. Led to multi-story model. meanings when using our LTMs. This shows that STM and LTM are separate and independent memory stores. However, many of s
Used artificial stimuli rather than meaningful material. May not MSM use no useful material. Consonant syllables, digits and letters have no meaning, lacks external validity.
tell us much about coding in real-life. More meaningful - Evidence of more than one STM store. Shallice and Warrington studied client with amnesia. STM for digits was poor when read to
information people use semantic coding even for STM.
could be another STM store for non-verbal sounds. MSM is wrong in claiming one STM store processing all types of info.
- Prolonged rehearsal is not needed for transfer to LTM. Craik and Watkins found type of rehearsal is more important than amount.
Capacity – the amount of information that can be held in a
memory store.
needed for LTM. Link information to existing knowledge or consider meaning. MSM cannot explain LTM storage.
- Recent research suggested LTM is also not a single memory store. Combined with research showing there is more than one type S
Jacobs found capacity by measuring digit span. Researcher reads
out 4 digits and participant recalls these out loud in order. type of rehearsal. MSM is over simplified.
researcher reads out 5 digits and so on until participant cannot
correctly recall. Indicates individual’s digit span. Mean span was
9.4 items and 7.3 letters.
Replicated. Early studies can lack adequate control, despite this
findings confirmed by more controlled studies.
Miller noted that things in everyday come in 7. Miller thought Types of long-term memory
that the span of STM is 7+/- 2 . He also noted we recall 5 words
Tulving realised that MSM was too simplistic. He proposed that there were in fact 3 LTM stores, containing different info types. He cal
as easily as 5 letters. We do this by chunking.
Overestimated STM capacity. Cowan reviewed other research
semantic and procedural memory.
and concluded capacity is only about 4 chunks. This suggests Episodic – ability to recall events from our lives. Complex memories. Time-stamped. Singular episode can include several intertwined
that Miller’s estimate was too high. conscious effort to recall episodic memories.
Semantic – store of shared knowledge of the world. Combination of an encyclopedia and dictionary. Include impressive number of co
Duration - the length of time information can be held in stamped. Less personal, constantly added to and less vulnerable to distortion.
memory. Procedural – memory of actions and skills. Can recall without conscious awareness. Might find hard to explain to others. If you try to
Peterson and Peterson – 24 students in 8 trials. Each given more difficult.
consonant syllable and 3-digit number to remember. Student - Study of HM and Clive Wearing. Episodic memory impaired due to brain damage. Semantic memory unaffected. Still understood m
counted back from this number until told to stop and recall Procedural memory was also intact. Supports Tulving’s view that different memory store of LTM exist. However, lack control of var
consonant syllable. 3 second – 80% recall. 18 second - 3%. STM unexpected. Researcher has no way of controlling participant before or during injury. No knowledge of individuals memory before
duration is about 18 seconds if info not repeated. - Conflicting research linking types of LTM to areas of brain. Buckner and Petersen reviewed evidence regarding location of semanti
Artificial stimulus. Lacks external validity. is located in left prefrontal cortex and episodic on the right. However, other research links left and right prefrontal cortex to encod
Bahrick – 392 Americans 17-74. Photo recognition recall – 15 episodic memory. Poor agreement on where each type of memory is located, challenging neuropsychological evidence to support
years 90%. 48 years 70% recognition. Free recall – 15 years -60% - Understanding LTM allows treatment of memory problems. Research shows memory loss in old age is episodic. Belleville devised
but 30% after 48. LTM may last a lifetime. episodic memory. Trained participants performed better than control group.
High external validity. Meaningful memory tested. More real
estimate of LTM.
Coding – the format in which information is stored in the The multi-store of memory
various memory stores. Atkinson and Shiffrin. Describes how information flows through the memory system. Memory is made up of 3 stores linked by proces
Baddeley gave different lists of words to 4 groups. Participants sensory register, comprised of registers for each of the senses. Coding in each store is modality specific. Duration of material in senso
asked to recall in correct order. from STM they tended to do second. The SRS has very high capacity. Information passes further if you pay attention to it. Information in STM is coded acoustically
worse with acoustically similar words. When recalled after seconds unless rehearsed – STM is a temporary store. STM is a limited capacity store – can only store a certain number of things befo
20min they did worse with semantically similar words. Suggest maintenance rehearsal occurs when we repeat material to ourselves. We can keep this information in our STMs if we rehearse it. If re
information is coded acoustically in STM and semantically in passes to LTM. LTM is permanent memory store for information that has been rehearsed. Coded semantically. Duration may be a lifeti
LTM . When we recall information from LTM it must be transferred back into STM by retrieval.
Clear difference between two memories. STM – acoustic and - Studies show STM and LTM are different. Baddeley found that we tend to mix up words that sound similar when using STMs, but w
LTM – semantic still applies. Led to multi-story model. meanings when using our LTMs. This shows that STM and LTM are separate and independent memory stores. However, many of s
Used artificial stimuli rather than meaningful material. May not MSM use no useful material. Consonant syllables, digits and letters have no meaning, lacks external validity.
tell us much about coding in real-life. More meaningful - Evidence of more than one STM store. Shallice and Warrington studied client with amnesia. STM for digits was poor when read to
information people use semantic coding even for STM.
could be another STM store for non-verbal sounds. MSM is wrong in claiming one STM store processing all types of info.
- Prolonged rehearsal is not needed for transfer to LTM. Craik and Watkins found type of rehearsal is more important than amount.
Capacity – the amount of information that can be held in a
memory store.
needed for LTM. Link information to existing knowledge or consider meaning. MSM cannot explain LTM storage.
- Recent research suggested LTM is also not a single memory store. Combined with research showing there is more than one type S
Jacobs found capacity by measuring digit span. Researcher reads
out 4 digits and participant recalls these out loud in order. type of rehearsal. MSM is over simplified.
researcher reads out 5 digits and so on until participant cannot
correctly recall. Indicates individual’s digit span. Mean span was
9.4 items and 7.3 letters.
Replicated. Early studies can lack adequate control, despite this
findings confirmed by more controlled studies.
Miller noted that things in everyday come in 7. Miller thought Types of long-term memory
that the span of STM is 7+/- 2 . He also noted we recall 5 words
Tulving realised that MSM was too simplistic. He proposed that there were in fact 3 LTM stores, containing different info types. He cal
as easily as 5 letters. We do this by chunking.
Overestimated STM capacity. Cowan reviewed other research
semantic and procedural memory.
and concluded capacity is only about 4 chunks. This suggests Episodic – ability to recall events from our lives. Complex memories. Time-stamped. Singular episode can include several intertwined
that Miller’s estimate was too high. conscious effort to recall episodic memories.
Semantic – store of shared knowledge of the world. Combination of an encyclopedia and dictionary. Include impressive number of co
Duration - the length of time information can be held in stamped. Less personal, constantly added to and less vulnerable to distortion.
memory. Procedural – memory of actions and skills. Can recall without conscious awareness. Might find hard to explain to others. If you try to
Peterson and Peterson – 24 students in 8 trials. Each given more difficult.
consonant syllable and 3-digit number to remember. Student - Study of HM and Clive Wearing. Episodic memory impaired due to brain damage. Semantic memory unaffected. Still understood m
counted back from this number until told to stop and recall Procedural memory was also intact. Supports Tulving’s view that different memory store of LTM exist. However, lack control of var
consonant syllable. 3 second – 80% recall. 18 second - 3%. STM unexpected. Researcher has no way of controlling participant before or during injury. No knowledge of individuals memory before
duration is about 18 seconds if info not repeated. - Conflicting research linking types of LTM to areas of brain. Buckner and Petersen reviewed evidence regarding location of semanti
Artificial stimulus. Lacks external validity. is located in left prefrontal cortex and episodic on the right. However, other research links left and right prefrontal cortex to encod
Bahrick – 392 Americans 17-74. Photo recognition recall – 15 episodic memory. Poor agreement on where each type of memory is located, challenging neuropsychological evidence to support
years 90%. 48 years 70% recognition. Free recall – 15 years -60% - Understanding LTM allows treatment of memory problems. Research shows memory loss in old age is episodic. Belleville devised
but 30% after 48. LTM may last a lifetime. episodic memory. Trained participants performed better than control group.
High external validity. Meaningful memory tested. More real
estimate of LTM.