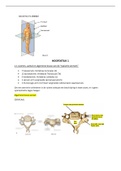
Memory:
Short and long term memory:
Coding - The format that information is stored
Capacity - The amount of information that can be stored
Duration - How long the information can be stored for
Sensory Register Short Term Memory Long Term Memory
Coding Any of the senses (Sight,Sound) Acoustically Semantically
Capacity Very High 7 +/- 2 Potentially Unlimited
Duration Less than 0.5 seconds 15-30 Seconds Potentially Unlimited
depending on
material
Baddeley Jacobs Miller Peterson & Peterson Bahrick
Aim Understand coding in long Capacity of short term Capacity of Duration of short term Duration of long term
and short term memory memory short term memory memory
memory in
chunks
Method Different list of words with Participant to recall Chunking Memorise a letter 400 people of various
some acoustically similar set of digits in order triad while counting ages (17-74) tested on
the other semantically they presented back in 3’s from a photo recognition of
similar. number classmates and free call
Recall immediately, recall recognition
after 20 mins
Results Recalling immediately Mean digit span = 9.3 If you chunk 3 seconds = 75% participants within 15 yr
found acoustically similar Mean letter span = 7.3 your things 18 seconds = 12.5% of graduation were 90%
words harder together you increased intervals = accurate
After 20 mins found can remember less % correct After 45 yrs it was 70%
semantically similar words more for photo recognition.
harder 60% accurate at 15 yr
for free recall and 30%
after 48yrs
Conclusion Information is coded Capacity of STM is 7 7 +/- 2 duration is around Duration might not be
acoustically in STM and +/- 2 which he called it 15-30 seconds but if unlimited but declines
semantically in LTM the magic number we rehearsed it isn't after 15ys
very long
Evaluation - lacks ecological - Old - ecological - confounding
validity Research validity variables
- Artificial task + Reliable - Artificial task + realistic
+ actually tests
LTM
, Types of Long Term Memory:
Episodic Memory:
● Personal Memories of events
● Contains contextual details plus emotional tone
● Specific details of event, context and emotion
Semantic Memory:
● Shared memories for facts and knowledge
● Can be concrete or abstract
● Begins as an episodic memory due to personal experience
● gradually turns into semantic as information is generalised
● can still be linked to when are where it was learn
Procedural Memory:
● Memory of how to do things
● Automatic as result of repeated practice
● Remembering how to do something rather than the rules of what to do
● Less aware of these memories as they are automatic
● Thinking too much about these memories can prevent acting on them
● important they are automatic so we can focus on other tasks
Evaluation:
+ Brain Scan Evidence - Indicates that three types of memory are found in different parts
of brain and are therefore separate
+ Supporting evidence from case studies - supports distinction between procedural and
declarative memories therefore supports existence of multiple LTM types
Short and long term memory:
Coding - The format that information is stored
Capacity - The amount of information that can be stored
Duration - How long the information can be stored for
Sensory Register Short Term Memory Long Term Memory
Coding Any of the senses (Sight,Sound) Acoustically Semantically
Capacity Very High 7 +/- 2 Potentially Unlimited
Duration Less than 0.5 seconds 15-30 Seconds Potentially Unlimited
depending on
material
Baddeley Jacobs Miller Peterson & Peterson Bahrick
Aim Understand coding in long Capacity of short term Capacity of Duration of short term Duration of long term
and short term memory memory short term memory memory
memory in
chunks
Method Different list of words with Participant to recall Chunking Memorise a letter 400 people of various
some acoustically similar set of digits in order triad while counting ages (17-74) tested on
the other semantically they presented back in 3’s from a photo recognition of
similar. number classmates and free call
Recall immediately, recall recognition
after 20 mins
Results Recalling immediately Mean digit span = 9.3 If you chunk 3 seconds = 75% participants within 15 yr
found acoustically similar Mean letter span = 7.3 your things 18 seconds = 12.5% of graduation were 90%
words harder together you increased intervals = accurate
After 20 mins found can remember less % correct After 45 yrs it was 70%
semantically similar words more for photo recognition.
harder 60% accurate at 15 yr
for free recall and 30%
after 48yrs
Conclusion Information is coded Capacity of STM is 7 7 +/- 2 duration is around Duration might not be
acoustically in STM and +/- 2 which he called it 15-30 seconds but if unlimited but declines
semantically in LTM the magic number we rehearsed it isn't after 15ys
very long
Evaluation - lacks ecological - Old - ecological - confounding
validity Research validity variables
- Artificial task + Reliable - Artificial task + realistic
+ actually tests
LTM
, Types of Long Term Memory:
Episodic Memory:
● Personal Memories of events
● Contains contextual details plus emotional tone
● Specific details of event, context and emotion
Semantic Memory:
● Shared memories for facts and knowledge
● Can be concrete or abstract
● Begins as an episodic memory due to personal experience
● gradually turns into semantic as information is generalised
● can still be linked to when are where it was learn
Procedural Memory:
● Memory of how to do things
● Automatic as result of repeated practice
● Remembering how to do something rather than the rules of what to do
● Less aware of these memories as they are automatic
● Thinking too much about these memories can prevent acting on them
● important they are automatic so we can focus on other tasks
Evaluation:
+ Brain Scan Evidence - Indicates that three types of memory are found in different parts
of brain and are therefore separate
+ Supporting evidence from case studies - supports distinction between procedural and
declarative memories therefore supports existence of multiple LTM types