Replication and division of nuclei and cells
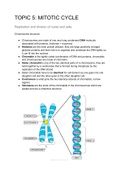
Chromosome structure:
● Chromosomes are made of one very long condensed DNA molecule
associated with proteins. (histones + enzymes)
● Histones are the main protein present, they are large positively charged
globular proteins and their role is to organise and condense the DNA tightly so
it can fit into the nucleus.
● Chromatin is the tightly coiled combination of DNA and proteins, chromatids
and chromosomes are made of chromatin.
● Sister chromatid is one of the two identical parts of a chromosome, they are
held together by a centromere that is formed during interphase by the
replication of the DNA strand.
● Sister chromatids have to be identical for cell division as one goes into one
daughter cell and the other goes to the other daughter cell.
● Centromere is what joins the two identical strands of chromatids, narrow
regions.
● Telomeres are the ends of the chromatids in the chromosomes which are
sealed and are a protective structure.
, The importance of Mitosis
- Mitosis is the division of a nucleus into two so that the two daughter cells have
exactly the same number and type of chromosomes as the parent cell.
● Growth of multicellular organisms:
- Two daughter cells produced are identical (clones) and have the same
number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
- Enables unicellular zygotes to grow into multicellular organisms.
- Growth may occur across the whole body of the organism or be
confined to certain regions such as growing points of plants.
● Replacement of cells & repair of tissues:
- Damaged tissues can be repaired by mitosis and cell division.
- As cells are constantly dying they have to be continually replaced by
genetically identical cells.
- In humans, cell replacement occurs rapidly in the skin and lining of the
gut.
- Some animals can regenerate body parts.
● Asexual reproduction:
- Is the production of new individuals by a single parent organism, the
offspring are genetically identical to the parent.
- For unicellular organisms, cell division results in genetically identical
offspring.
- For multicellular organisms new individuals grow from the parent
organism by cell division and detach from the parent in different ways.
Cell Cycle:
- The sequence of events that takes place from one cell division until the next; it
is made up of interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis.
- Length of cycle varies depending on environmental conditions, cell type and
organism.