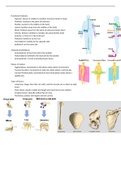
The cardiovascular (CV) system:
- 75 trillion cells in the body
- Needs to have: nutrients, oxygen and appropriate environment
- CV supplies the needs above, and the system consists of a pump, a system of
vessels and blood
The conduction system:
- Sinoatrial node: causes atria to contract (P wave) - pacemaker potentials
- Atrioventricular node: links between atria and ventricles, the delay allows the
atria and ventricles to contract at different times
- Signal spreads through the Bundle of His also called Purkinje
fibers
CNS input:
- Heart rate is controlled by the CNS
- Cardiac muscle shows autorhythmicity: no CNS input = about
100bpm
- Normal bpm is 60bpm
- Vagal restraint
- Increased HR = removal of parasympathetic (acetylcholine)
and addition of sympathetic (catecholamines - epinephrine
and norepinephrine) - acts on SA node
The vascular system:
1. Arteries
a. Arterioles (capillaries)
b. Venules
2. Veins
Arterioles and blood pressure:
1. Blood pressure reduces throughout vascular system
a. Flow is proportional to pressure gradient divided by resistance
b. Resistance is altered by changing diameter of vessel
c. Vasodilation and vasoconstriction - controlling blood flow to organs
2. Arterioles effectively control blood flow to organs
a. Constriction or dilation
b. Major effect on blood pressure
c. Changes in diameter due to contraction or relaxation of smooth muscle
d. Smooth muscle responds to local factors and CNS
Local control of blood flow:
1. Active hyperemia (increase in local blood flow). Increase in metabolism leads to metabolite accumulation locally
a. Metabolites act on smooth muscle causing dilation
b. No CNS input needed
2. Autoregulation: similar idea but regulating pressure ex. Cerebral vasculature very sensitive to pressure
, Extrinsic control of blood flow:
1. Nerves and hormones:
a. Arterioles have little parasympathetic innervation
b. Sympathetic innervation utilises norepinephrine
c. Stimulate alpha-adrenergic receptors
d. Sympathetic innervation causes constriction
e. Dilation due to reduced sympathetic tone
2. Epinephrine (sympathetic): contraction of blood vessels, relation of other smooth muscle ex. In airways
3. Angiotensin 2: causes contraction
4. Vasopressin: causes contraction
5. Atrial Natriuretic factor: causes relaxation
Recap of CV functions:
- Mean of arterial pressure (MAP) = cardiac output (CO) x total peripheral resistance (TPR)
- CO = heart rate (HR) x stroke volume (SV)
a. HR increase with sympathetic tone
b. SV determined by end-diastolic volume and venous return
- TPR: constriction of arterioles
Acute cardiovascular response to exercise
Resistance exercise:
- Systolic pressures can increase to 240 mmHg
- Increase in diastolic pressure
- Physical compression of vessels by muscle forces
- Increased sympathetic tone
- More muscle activated = greater effect on MAP
- Caution - prescription of exercise in hypertensive individuals
Steady state aerobic exercise
- Steady state results in acute increase in systolic blood
- 140-160mmHg
- Increased HR and SV leads to increased CO
- Sympathetic tone and muscle pumps (compression of veins to increases blood flow back to heart)
- Reduces as exercise continues - reduced TPR due to dilation of arterioles
Graded aerobic exercise:
- Graded increase in intensity leads to acute increase in systolic blood
pressure
- Linear increase with exercise intensity
- Increased HR and SV = increased CO
- Systolic pressures can reach 200mmHg
Upper vs lower body exercise:
- Upper body exercise results in greater increase than lower body exercise
- Smaller vessels and muscle mass
- 75 trillion cells in the body
- Needs to have: nutrients, oxygen and appropriate environment
- CV supplies the needs above, and the system consists of a pump, a system of
vessels and blood
The conduction system:
- Sinoatrial node: causes atria to contract (P wave) - pacemaker potentials
- Atrioventricular node: links between atria and ventricles, the delay allows the
atria and ventricles to contract at different times
- Signal spreads through the Bundle of His also called Purkinje
fibers
CNS input:
- Heart rate is controlled by the CNS
- Cardiac muscle shows autorhythmicity: no CNS input = about
100bpm
- Normal bpm is 60bpm
- Vagal restraint
- Increased HR = removal of parasympathetic (acetylcholine)
and addition of sympathetic (catecholamines - epinephrine
and norepinephrine) - acts on SA node
The vascular system:
1. Arteries
a. Arterioles (capillaries)
b. Venules
2. Veins
Arterioles and blood pressure:
1. Blood pressure reduces throughout vascular system
a. Flow is proportional to pressure gradient divided by resistance
b. Resistance is altered by changing diameter of vessel
c. Vasodilation and vasoconstriction - controlling blood flow to organs
2. Arterioles effectively control blood flow to organs
a. Constriction or dilation
b. Major effect on blood pressure
c. Changes in diameter due to contraction or relaxation of smooth muscle
d. Smooth muscle responds to local factors and CNS
Local control of blood flow:
1. Active hyperemia (increase in local blood flow). Increase in metabolism leads to metabolite accumulation locally
a. Metabolites act on smooth muscle causing dilation
b. No CNS input needed
2. Autoregulation: similar idea but regulating pressure ex. Cerebral vasculature very sensitive to pressure
, Extrinsic control of blood flow:
1. Nerves and hormones:
a. Arterioles have little parasympathetic innervation
b. Sympathetic innervation utilises norepinephrine
c. Stimulate alpha-adrenergic receptors
d. Sympathetic innervation causes constriction
e. Dilation due to reduced sympathetic tone
2. Epinephrine (sympathetic): contraction of blood vessels, relation of other smooth muscle ex. In airways
3. Angiotensin 2: causes contraction
4. Vasopressin: causes contraction
5. Atrial Natriuretic factor: causes relaxation
Recap of CV functions:
- Mean of arterial pressure (MAP) = cardiac output (CO) x total peripheral resistance (TPR)
- CO = heart rate (HR) x stroke volume (SV)
a. HR increase with sympathetic tone
b. SV determined by end-diastolic volume and venous return
- TPR: constriction of arterioles
Acute cardiovascular response to exercise
Resistance exercise:
- Systolic pressures can increase to 240 mmHg
- Increase in diastolic pressure
- Physical compression of vessels by muscle forces
- Increased sympathetic tone
- More muscle activated = greater effect on MAP
- Caution - prescription of exercise in hypertensive individuals
Steady state aerobic exercise
- Steady state results in acute increase in systolic blood
- 140-160mmHg
- Increased HR and SV leads to increased CO
- Sympathetic tone and muscle pumps (compression of veins to increases blood flow back to heart)
- Reduces as exercise continues - reduced TPR due to dilation of arterioles
Graded aerobic exercise:
- Graded increase in intensity leads to acute increase in systolic blood
pressure
- Linear increase with exercise intensity
- Increased HR and SV = increased CO
- Systolic pressures can reach 200mmHg
Upper vs lower body exercise:
- Upper body exercise results in greater increase than lower body exercise
- Smaller vessels and muscle mass