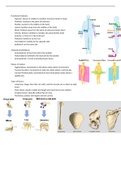
Functional Anatomy
- Superior: above on relation to another structure/closer to head
- Proximal: nearest to the point of reference
- Medial: nearest to the midline of the body
- Lateral: furthest away from the midline of the body
- Distal: furthest away from the point of reference/lower down
- Inferior: below in relation to another structure/further head
- Anterior: in front or in the front part
- Posterior: behind or to the rear
- Contralateral: relating to the opposite side
- Ipsilateral: on the same side
Anatomical definitions:
- Anterolateral: to the front and to the outside
- Posterolateral: behind/to the back and to the outside
- Anteroinferior: in front and below/lower down
Planes of motion:
- Sagittal plane: movements in this plane rotate about a frontal axis
- Transverse plane: movements in axial axis rotate about a vertical axis
- Coronal/Frontal plane: movements in the frontal plane rotate about a
sagittal axis
Types of bones:
- Long bone: longer than they are wide, and the muscles act on them as rigid
levers
- Short bones: equal in width and length and clued across one another
- Irregular bones: typically neither flat nor long
- Flat bones: protect soft organs and are curved.
, Joints of the lower body: pelvis and hip joint
Knee joint: Ankle joint and bones of the feet:
Muscles of the lower body: Naming conventions: size, shape, action, location, number of origins
Size: Shape: Action: Number of origins:
- Maximus: largest - Deltoid: triangular - Flexor: decreases a joint angle - Biceps: 2 origins
- Longus: long - Trapezius: trapezoid - Extensor: increases a joint angle - Triceps: 3 origins
- Longissimus: - Serratus: - Abductor: moves away from the midline of
- Quadriceps: 4 origins
body
longest sawtoothed
- Adductor: towards midline of the body
- Vastus: huge - Rhomboid: diamond - Levator: raises or elevates
- Magnus: large - Orbicularis: circular - Depressor: lowers
- Minimus: - Pectinate: combilike - Supinator: supinates foot/hand to face
smallest - Piriformis: pear outwards
- Brevis: short shaped - Pronator: pronates foot/hand to face inwards
- Latissimus: - Tensor: makes a body part rigid, provides
- Platys: flat
widest stability
- Quadratus: square
- Major: larger - Rotator: rotates around a longitudinal axis
- Minor: smaller - Gracilis: slender - Sphincter: decreases size of opening
- Superior: above on relation to another structure/closer to head
- Proximal: nearest to the point of reference
- Medial: nearest to the midline of the body
- Lateral: furthest away from the midline of the body
- Distal: furthest away from the point of reference/lower down
- Inferior: below in relation to another structure/further head
- Anterior: in front or in the front part
- Posterior: behind or to the rear
- Contralateral: relating to the opposite side
- Ipsilateral: on the same side
Anatomical definitions:
- Anterolateral: to the front and to the outside
- Posterolateral: behind/to the back and to the outside
- Anteroinferior: in front and below/lower down
Planes of motion:
- Sagittal plane: movements in this plane rotate about a frontal axis
- Transverse plane: movements in axial axis rotate about a vertical axis
- Coronal/Frontal plane: movements in the frontal plane rotate about a
sagittal axis
Types of bones:
- Long bone: longer than they are wide, and the muscles act on them as rigid
levers
- Short bones: equal in width and length and clued across one another
- Irregular bones: typically neither flat nor long
- Flat bones: protect soft organs and are curved.
, Joints of the lower body: pelvis and hip joint
Knee joint: Ankle joint and bones of the feet:
Muscles of the lower body: Naming conventions: size, shape, action, location, number of origins
Size: Shape: Action: Number of origins:
- Maximus: largest - Deltoid: triangular - Flexor: decreases a joint angle - Biceps: 2 origins
- Longus: long - Trapezius: trapezoid - Extensor: increases a joint angle - Triceps: 3 origins
- Longissimus: - Serratus: - Abductor: moves away from the midline of
- Quadriceps: 4 origins
body
longest sawtoothed
- Adductor: towards midline of the body
- Vastus: huge - Rhomboid: diamond - Levator: raises or elevates
- Magnus: large - Orbicularis: circular - Depressor: lowers
- Minimus: - Pectinate: combilike - Supinator: supinates foot/hand to face
smallest - Piriformis: pear outwards
- Brevis: short shaped - Pronator: pronates foot/hand to face inwards
- Latissimus: - Tensor: makes a body part rigid, provides
- Platys: flat
widest stability
- Quadratus: square
- Major: larger - Rotator: rotates around a longitudinal axis
- Minor: smaller - Gracilis: slender - Sphincter: decreases size of opening