Biod 331 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Mod 1- Questions and Answers
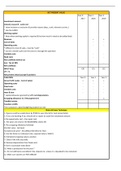
1. Define pathophysiology Change to body (total function, organ and cellular level) caused by
disease
2. Define pathology Studying structural and functional changes that occur in cells, tissues
and organs b/c of disease
3. Define physiology Study of the function of the body
4. Define disease Illness leading to abnormal physiological function of an organ, body
structure, or entire system
- can be born w/ disease, or can acquire
5. 6 disease process steps Etiology, pathogenesis
Morphologic changes
Clinical manifestations
Diagnoses
Clinical courses
6. What are etiologic fac- Causes of disease
tors?
7. What do etiologic factors -Can attect several organs, or an entire system, or multiple systems
affect? (examples include sickle cell anemia, CF)
-Some may only attect single organ/structure ( broken bone, isolated
burn)
- most disease processes start d/t multiple etologic factors (cancers
heart disease, diabetes)
8. What are the 6 etiologic Physical forces
factors? Chemical agents
Biologic agents
Genetic predisposition
, Biod 331 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Mod 1- Questions and Answers
Nutritional excess/deficiencies
Idiopathic
9. Etiologic factors: exam- Trauma, burns, radiation
ples of physical forces
10. Etiologic factors: exam- Poisons, alcohol
ples of chemical agents
11. Etiologic factors: exam- Bacteria, viruses
ples of biologic agents
12. Etiologic factors: define Most etiologies have unknown cause
idiopathic
13. What are risk factors? What predisposes someone to disease
14. What are the 2 risk fac- -Congenital: born with it (hereditary, environmental factors, or both)
tors? - Aquired: after birth (injury, exposure dietary deficiency/excess)
Its believed most diseases are a result of hereditary and environment
15. What is pathogenesis? Development of disease- multiple events occurring at cellular and tissue
level from initial contact w/ etiological agent manifests disease
16. What is morphology? Structure of cells or tissues- morphologic changes can be microscopic
17. What is histology? Study of cells at tissue level
18. 7 stages of disease devel-
opment
19. Define clinical manifesta- Signs + symptoms (the way disease presents itself)
tions
1. Define pathophysiology Change to body (total function, organ and cellular level) caused by
disease
2. Define pathology Studying structural and functional changes that occur in cells, tissues
and organs b/c of disease
3. Define physiology Study of the function of the body
4. Define disease Illness leading to abnormal physiological function of an organ, body
structure, or entire system
- can be born w/ disease, or can acquire
5. 6 disease process steps Etiology, pathogenesis
Morphologic changes
Clinical manifestations
Diagnoses
Clinical courses
6. What are etiologic fac- Causes of disease
tors?
7. What do etiologic factors -Can attect several organs, or an entire system, or multiple systems
affect? (examples include sickle cell anemia, CF)
-Some may only attect single organ/structure ( broken bone, isolated
burn)
- most disease processes start d/t multiple etologic factors (cancers
heart disease, diabetes)
8. What are the 6 etiologic Physical forces
factors? Chemical agents
Biologic agents
Genetic predisposition
, Biod 331 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Mod 1- Questions and Answers
Nutritional excess/deficiencies
Idiopathic
9. Etiologic factors: exam- Trauma, burns, radiation
ples of physical forces
10. Etiologic factors: exam- Poisons, alcohol
ples of chemical agents
11. Etiologic factors: exam- Bacteria, viruses
ples of biologic agents
12. Etiologic factors: define Most etiologies have unknown cause
idiopathic
13. What are risk factors? What predisposes someone to disease
14. What are the 2 risk fac- -Congenital: born with it (hereditary, environmental factors, or both)
tors? - Aquired: after birth (injury, exposure dietary deficiency/excess)
Its believed most diseases are a result of hereditary and environment
15. What is pathogenesis? Development of disease- multiple events occurring at cellular and tissue
level from initial contact w/ etiological agent manifests disease
16. What is morphology? Structure of cells or tissues- morphologic changes can be microscopic
17. What is histology? Study of cells at tissue level
18. 7 stages of disease devel-
opment
19. Define clinical manifesta- Signs + symptoms (the way disease presents itself)
tions