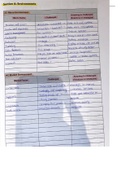
List - List a number of features or points without
Command words further elaboration
Name - Identify using a recognised technical term
Command words are the words and phrases used Outline - Set out main characteristics
in exams and other assessment tasks that tell Predict - Give a plausible outcome
students how they should answer the question. Relate - Give a technical term or its equivalent
The following command words are taken from Show - Provide structured evidence to reach a
Ofqual's official list of command words and their conclusion
meanings that are relevant to this subject. In
Sketch - Draw approximately
addition, where necessary, some of AQA’s own
State - Express in clear terms
command words and their meanings have also
been added to complement Ofqual's list. Suggest - Present a possible case
Analyse - Separate information into components Subject specific
and identify their characteristics
Annotate - Add notation or labelling to a graph, vocabulary
diagram or other drawing The following subject specific vocabulary provides
Apply - Put into effect in a recognised way definitions of key terms used in AQA’s AS and A-
Argue - Present a reasoned case level Science specifications.
Assess - Make an informed judgement
Comment - Present an informed opinion Accuracy - A measurement result is considered
Compare - Identify similarities and/ or differences accurate if it is judged to be close to the true
value. Calibration - Marking a scale on a
Consider - Review and respond to given
measuring instrument. This involves establishing
information
the relationship between indications of a
Contrast - Identify differences measuring instrument and standard or reference
Criticise - Access worth against explicit quantity values, which must be applied. For
expectations example, placing a thermometer in melting ice to
Debate - Present different perspectives on an see whether it reads 0 °C, in order to check if it
issue has been calibrated correctly.
Deduce - Draw conclusions from information Data - Information, either qualitative or
provided quantitative, that has been collected.
Describe - Give an account of Errors - See also uncertainties.
Design - Set out how something will be done Measurement error - The difference between a
Determine - Use given data or information to measured value and the true value.
obtain an answer Anomalies - These are values in a set of results
Develop - Take forward or build upon given which are judged not to be part of the variation
information caused by random uncertainty.
Discuss - Present key points Random error - These cause readings to be
Distinguish - List the differences between spread about the true value, due to results
different items varying in an unpredictable way from one
measurement to the next. Random errors are
Evaluate - Judge from available evidence
present when any measurement is made, and
Explain - Give reasons cannot be corrected. The effect of random errors
Explore - Investigate without preconceptions can be reduced by making more measurements
about the outcome and calculating a new mean.
Identify - Name or otherwise characterise Systematic error - These cause readings to differ
Justify - Support a case with evidence from the true value by a consistent amount each
time a measurement is made. Sources of
systematic error can include the environment,
Command words further elaboration
Name - Identify using a recognised technical term
Command words are the words and phrases used Outline - Set out main characteristics
in exams and other assessment tasks that tell Predict - Give a plausible outcome
students how they should answer the question. Relate - Give a technical term or its equivalent
The following command words are taken from Show - Provide structured evidence to reach a
Ofqual's official list of command words and their conclusion
meanings that are relevant to this subject. In
Sketch - Draw approximately
addition, where necessary, some of AQA’s own
State - Express in clear terms
command words and their meanings have also
been added to complement Ofqual's list. Suggest - Present a possible case
Analyse - Separate information into components Subject specific
and identify their characteristics
Annotate - Add notation or labelling to a graph, vocabulary
diagram or other drawing The following subject specific vocabulary provides
Apply - Put into effect in a recognised way definitions of key terms used in AQA’s AS and A-
Argue - Present a reasoned case level Science specifications.
Assess - Make an informed judgement
Comment - Present an informed opinion Accuracy - A measurement result is considered
Compare - Identify similarities and/ or differences accurate if it is judged to be close to the true
value. Calibration - Marking a scale on a
Consider - Review and respond to given
measuring instrument. This involves establishing
information
the relationship between indications of a
Contrast - Identify differences measuring instrument and standard or reference
Criticise - Access worth against explicit quantity values, which must be applied. For
expectations example, placing a thermometer in melting ice to
Debate - Present different perspectives on an see whether it reads 0 °C, in order to check if it
issue has been calibrated correctly.
Deduce - Draw conclusions from information Data - Information, either qualitative or
provided quantitative, that has been collected.
Describe - Give an account of Errors - See also uncertainties.
Design - Set out how something will be done Measurement error - The difference between a
Determine - Use given data or information to measured value and the true value.
obtain an answer Anomalies - These are values in a set of results
Develop - Take forward or build upon given which are judged not to be part of the variation
information caused by random uncertainty.
Discuss - Present key points Random error - These cause readings to be
Distinguish - List the differences between spread about the true value, due to results
different items varying in an unpredictable way from one
measurement to the next. Random errors are
Evaluate - Judge from available evidence
present when any measurement is made, and
Explain - Give reasons cannot be corrected. The effect of random errors
Explore - Investigate without preconceptions can be reduced by making more measurements
about the outcome and calculating a new mean.
Identify - Name or otherwise characterise Systematic error - These cause readings to differ
Justify - Support a case with evidence from the true value by a consistent amount each
time a measurement is made. Sources of
systematic error can include the environment,