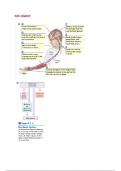
Problem 8 – Stress
Stress:
- long-term and chronic disturbance to physiological homeostasis
- stressors: stimuli that cause stress
- stress response: a physiological reaction caused by the perception of aversive or threatening
situations
- distress: stress that disrupts health or other aspects of functioning
- eustress: stress that improves health or other aspects of functioning
- sometimes people don’t have a coping strategy to deal with the stress
- a capacity for coping reduces the impact of potential stressors
- two important things about stress:
1. through the CNS psychological stressors exert wideranging effects on the physiology of the
body
2. some of these same effects on the body can be triggered by physiological stressors
ex. deviations from physiological homeostasis as in loss of blood
- is associated with an identifiable pattern of physiological changes
- Stress can be associated with
• active strategies and sympathetic domination
• passive strategies with a bias towards parasympathetic activity
- cytokine
• short-term cytokine induced inflammatory response help the body
• long term cytokine release is associated with a variety of adverse health consequences
- animals studies show that arousal in face of stressor leads to an emergency reaction
- sympathetic nervous system is excited:
→ adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) released into bloodstream in
increased amounts
→ hormones called corticosteroids secreted at high rate (mobilize metabolic resources in body)
Response to Stress:
Hans Selye’s Model
- General adaption syndrome (GAS): three predictable stages the body uses to respond to stressors
1. Alarm stage
• provides a burst of energy
• upon perceiving a stressor the body reacts with a “fight or flight” response
• the sympathetic nervous system is stimulated as the body’s resources are mobilized to meet
the threat or danger
2. Resistance stage
• the body’s attempts to resist or adapt to the stressor
• the body resists and compensates as the parasympathetic nervous system attempts to return
many physiological functions to normal levels
• body focuses resources against the stressor and remains on alert
3. Exhaustion stage
• energy is depleted
• if the stressors continue beyond the body’s capacity the resources become exhausted
→ the body is susceptible to disease and death
- criticism: overly simplistic → stress responses are complex and varied, with the exact response
depending on the stressor, its timing, the nature of the stressed person, and how the
stressed person reacts to the stressor
, Characterizing stress
Signs of Stress: arousal
- activation: confronted with stress and animal shows EEG arousal
→ there can not be stress without arousal
- in stress animals take both behavioral and physiological action
- emergency reaction: the set of reactions to stress
• the sympathetic nervous system is usually excited
→ thereby adrenalin (epinephrine) and noradrenalin (norepinephrine) are released into the
bloodstream in increased amounts
• the hormone corticosteroids are usually secreted at a high rate and they mobilize resources
in the body
→ long term excitation of these hormonal systems gives an indication of stress
Types of Stressors
External stimuli
- defined as stressors which trigger behavioral and physiological activation
- the stress-evoking capacity of external events can often be understood only by taking account of
their context and interpretation
- an animal for example is exposed to potential stressors
• confrontation with predators
• dealing with dominants of the group
• competing for food and rearing to rivals in overcrowded conditions
→ reaction is usually to make an appeasement posture or flee suppose the animal is healthy
- loud sounds, etc.
Cognitive processes
- humans can stress themselves by cognitive triggers such as protracted and unsuccessful problem-
solving
- what evokes stress can be an event placed in the context of earlier experiences
- corticosteroid secretion is sensitive to situations placed in context
- ex. loss of control in a previous situation or frustration in general
- the comparison of expected and actual events lead to a triggering by the difference
- attempts to cope with cognitive challenges are associated with sympathetic activation
Physiological stimuli
- physiological disturbances trigger activation and corticosteroid release
- the mobilization of resources in this ‘general emergency reaction’ supports any specific action
also triggered
- ex. the physiological challenge such as loss of blood triggers specific behavioral homeostatic
actions such as seeking water and salt to correct the disturbance
Behavioral indices
- confronted with a stressor we might flee or fight, and activate the sympathetic system, and these
actions might or might not be successful
- another strategy is passivity with parasympathetic activation and inhibition of the sympathetic
system
- when an active strategy fails an animal switches to passive mode
→ a failure of strategy over long periods constitutes stress
Stress:
- long-term and chronic disturbance to physiological homeostasis
- stressors: stimuli that cause stress
- stress response: a physiological reaction caused by the perception of aversive or threatening
situations
- distress: stress that disrupts health or other aspects of functioning
- eustress: stress that improves health or other aspects of functioning
- sometimes people don’t have a coping strategy to deal with the stress
- a capacity for coping reduces the impact of potential stressors
- two important things about stress:
1. through the CNS psychological stressors exert wideranging effects on the physiology of the
body
2. some of these same effects on the body can be triggered by physiological stressors
ex. deviations from physiological homeostasis as in loss of blood
- is associated with an identifiable pattern of physiological changes
- Stress can be associated with
• active strategies and sympathetic domination
• passive strategies with a bias towards parasympathetic activity
- cytokine
• short-term cytokine induced inflammatory response help the body
• long term cytokine release is associated with a variety of adverse health consequences
- animals studies show that arousal in face of stressor leads to an emergency reaction
- sympathetic nervous system is excited:
→ adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) released into bloodstream in
increased amounts
→ hormones called corticosteroids secreted at high rate (mobilize metabolic resources in body)
Response to Stress:
Hans Selye’s Model
- General adaption syndrome (GAS): three predictable stages the body uses to respond to stressors
1. Alarm stage
• provides a burst of energy
• upon perceiving a stressor the body reacts with a “fight or flight” response
• the sympathetic nervous system is stimulated as the body’s resources are mobilized to meet
the threat or danger
2. Resistance stage
• the body’s attempts to resist or adapt to the stressor
• the body resists and compensates as the parasympathetic nervous system attempts to return
many physiological functions to normal levels
• body focuses resources against the stressor and remains on alert
3. Exhaustion stage
• energy is depleted
• if the stressors continue beyond the body’s capacity the resources become exhausted
→ the body is susceptible to disease and death
- criticism: overly simplistic → stress responses are complex and varied, with the exact response
depending on the stressor, its timing, the nature of the stressed person, and how the
stressed person reacts to the stressor
, Characterizing stress
Signs of Stress: arousal
- activation: confronted with stress and animal shows EEG arousal
→ there can not be stress without arousal
- in stress animals take both behavioral and physiological action
- emergency reaction: the set of reactions to stress
• the sympathetic nervous system is usually excited
→ thereby adrenalin (epinephrine) and noradrenalin (norepinephrine) are released into the
bloodstream in increased amounts
• the hormone corticosteroids are usually secreted at a high rate and they mobilize resources
in the body
→ long term excitation of these hormonal systems gives an indication of stress
Types of Stressors
External stimuli
- defined as stressors which trigger behavioral and physiological activation
- the stress-evoking capacity of external events can often be understood only by taking account of
their context and interpretation
- an animal for example is exposed to potential stressors
• confrontation with predators
• dealing with dominants of the group
• competing for food and rearing to rivals in overcrowded conditions
→ reaction is usually to make an appeasement posture or flee suppose the animal is healthy
- loud sounds, etc.
Cognitive processes
- humans can stress themselves by cognitive triggers such as protracted and unsuccessful problem-
solving
- what evokes stress can be an event placed in the context of earlier experiences
- corticosteroid secretion is sensitive to situations placed in context
- ex. loss of control in a previous situation or frustration in general
- the comparison of expected and actual events lead to a triggering by the difference
- attempts to cope with cognitive challenges are associated with sympathetic activation
Physiological stimuli
- physiological disturbances trigger activation and corticosteroid release
- the mobilization of resources in this ‘general emergency reaction’ supports any specific action
also triggered
- ex. the physiological challenge such as loss of blood triggers specific behavioral homeostatic
actions such as seeking water and salt to correct the disturbance
Behavioral indices
- confronted with a stressor we might flee or fight, and activate the sympathetic system, and these
actions might or might not be successful
- another strategy is passivity with parasympathetic activation and inhibition of the sympathetic
system
- when an active strategy fails an animal switches to passive mode
→ a failure of strategy over long periods constitutes stress