, = THESPAIN
C ]
·
[electrical impulses] + glial cells
·
made up of neurons
-
·
PART ONE glial cells support neural cells
fiology of the mind ·
brain plasticity
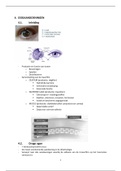
The Nervous System
a
·
starts
cell body ( the cells life
Support centers
·
neuroanatomy Axon (passes messages away from
cell body to other neurons)
heurotransmittermi he a
through synaptic gap Myelin Sheath /covers axon
of some neurons and helps speed
·
action potential :
a neural impulse Up neural impulses)
a brief electrical
Is charge that
travels down axon and is generated by Dendrites crecieve
·
·
,
messages
the movement of positively charged from other cells]
atoms in and out of channels in Neural Impulse
putenil
i
econ
the axons membrane
down the
·
action potential properties travelling
-
resting potential neurons start out in a
(depolarization
slightly negative charge Crepolarization L ))
=
=
())
-
Grefractory
period
e
-
threshold each neuron receives excititory and
inhibilitary signals from many transmitters when
transmitters reach dendrites. When
Es -
Is threshold =
neuron fires an action potential
all or none response a strong stimulus can trigger
-
+ 48 -
more neurons to fire and increase occurrence of them
↑
,
firing => doesn't effect action potential (CONSTANT)
-
synapse =
·
v
( unction between tip of axon and
·
is a
sending neuron + the denavite/cell body
of
Is the
the receiving neuron .
synaptic cleft
This
Selectric
tiny gar
r 55 - Threshold a
State
>
-
chemical >
-
electric)
hyperpolarization
S
nend
Smi 2
1 3 4
time (ms)
1. action potential stimulates vesicles in
axon terminal to release neurotransmitters
.
2 They cross synaptic gap and bind on to
receptor cites
synaptic
·
re up + ake
cleft
-
,
-
. the
3 neuron either fires or not
## =
⑤ 4
. neurotransmitters are reabsorbed
sites
- by
receptor sending neuron Sreuptake]
transmitter
.
on recieving neuron