The Eye & Ear: Special Sense Organs
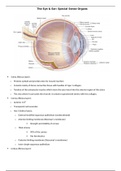
Sclera (fibrous layer):
o Protects eyeball and provides sites for muscle insertion
o Consists mainly of dense connective tissue with bundles of type 1 collagen.
o Tendons of the extraocular muscles which move the eyes insert into the anterior region of the sclera
o The area where it surrounds the choroid, it contains suprachoroid lamina with less collagen.
Cornea (fibrous layer):
o Anterior 1/6th
o Transparent and avascular
o Has 5 distinct layers:
o External stratified squamous epithelium (nonkeratinized)
o Anterior limiting membrane (Bowman’s membrane)
Strength and stability of cornea
o Thick stroma
90% of the cornea
Has keratocytes
o Posterior limiting membrane (Descemet’s membrane)
o Inner simple squamous epithelium
Limbus (fibrous layer):
, o Encircles the cornea
o This is where cornea merges with sclera
o The bowman’s membrane here becomes more stratified as the conjunctiva that covers the anterior part of the
sclera.
o Has progenitor cells that move to the corneal epithelium
o Fluid (aqueous humor) moves through channels of trabecular meshwork into the canal of Schlemm (scleral
venous sinus) which encircles the eye. From there it drains into small blood vessels of sclera.
Choroid (vascular layer):
o Consists of loose well-vascularized connective tissue
o Has many melanocytes which prevent light from entering the eye except through the pupil
o Has 2 layers:
o Inner choroido-capillary lamina:
Rich microvasculature important for nutrition of outer retinal layers
o Bruch’s membrane:
Composed of collagen and elastic fibers surrounding the retina’s pigmented layer
Ciliary body (vascular layer)
o Encircles the lens, posterior to the limbus
o Rests on the sclera
o Important structures:
o Ciliary muscle:
Most of the ciliary body’s stroma
Has 3 groups of smooth muscles
Their contraction change the shape of the lens for visual accommodation
o Ciliary processes:
Have Na+/K+ - ATPase activity and secrete aqueous humor
o This fluid is secreted into the posterior chamber (between lens and iris) and moves through
the pupil into the anterior chamber (between iris and cornea) and then drains at the angle
formed by the angle formed by the cornea and the iris into the canal of Schlemm.
o Ciliary zonule:
Composed of fibrillin 1 and 2
Hold the lens in place
Iris (vascular layer):
o Has a central pupil
o Its posterior surface is filled with melanin which blocks all light entering the eye except passing through the pupil.
Sclera (fibrous layer):
o Protects eyeball and provides sites for muscle insertion
o Consists mainly of dense connective tissue with bundles of type 1 collagen.
o Tendons of the extraocular muscles which move the eyes insert into the anterior region of the sclera
o The area where it surrounds the choroid, it contains suprachoroid lamina with less collagen.
Cornea (fibrous layer):
o Anterior 1/6th
o Transparent and avascular
o Has 5 distinct layers:
o External stratified squamous epithelium (nonkeratinized)
o Anterior limiting membrane (Bowman’s membrane)
Strength and stability of cornea
o Thick stroma
90% of the cornea
Has keratocytes
o Posterior limiting membrane (Descemet’s membrane)
o Inner simple squamous epithelium
Limbus (fibrous layer):
, o Encircles the cornea
o This is where cornea merges with sclera
o The bowman’s membrane here becomes more stratified as the conjunctiva that covers the anterior part of the
sclera.
o Has progenitor cells that move to the corneal epithelium
o Fluid (aqueous humor) moves through channels of trabecular meshwork into the canal of Schlemm (scleral
venous sinus) which encircles the eye. From there it drains into small blood vessels of sclera.
Choroid (vascular layer):
o Consists of loose well-vascularized connective tissue
o Has many melanocytes which prevent light from entering the eye except through the pupil
o Has 2 layers:
o Inner choroido-capillary lamina:
Rich microvasculature important for nutrition of outer retinal layers
o Bruch’s membrane:
Composed of collagen and elastic fibers surrounding the retina’s pigmented layer
Ciliary body (vascular layer)
o Encircles the lens, posterior to the limbus
o Rests on the sclera
o Important structures:
o Ciliary muscle:
Most of the ciliary body’s stroma
Has 3 groups of smooth muscles
Their contraction change the shape of the lens for visual accommodation
o Ciliary processes:
Have Na+/K+ - ATPase activity and secrete aqueous humor
o This fluid is secreted into the posterior chamber (between lens and iris) and moves through
the pupil into the anterior chamber (between iris and cornea) and then drains at the angle
formed by the angle formed by the cornea and the iris into the canal of Schlemm.
o Ciliary zonule:
Composed of fibrillin 1 and 2
Hold the lens in place
Iris (vascular layer):
o Has a central pupil
o Its posterior surface is filled with melanin which blocks all light entering the eye except passing through the pupil.