Chapter 2
Nervous system: interconnected nerve fibers that functions to regulate response and
recovery from stress
Sympathetic nervous system: role in reactions to stress, prepares body to respond to
emergencies, to strong emotions (fear), to strenuous activity, mobilization and exertion of
energy (catabolic system)
Parasymaptheric nervous system: controls activities of organs under normal
circumstances, acts antagonistly agaisnt symapthetic nervous system, restores body to
normal state, digestion, relaxation or drowsiness after meal, conservation of bodily energy
(anabolic system)
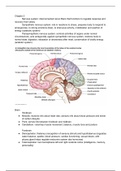
Brain
Hindbrain
● Medulla: recieves info about heart rate, sensory info about blood pressure and levels
of carbon dioxyde
● Pons: serves link between hindbrain and midbrain
● Cerebellum: voluntray muscle movement, balance, muscle tone and posture
Forebrain
● Diencephalon: thalamus (recognition of sensory stimuli) and hypothalamus (regulates
water balance, apetite, blood pressure, cardiac functioning, sexual desire, with
pituary gland helps regulate endocrine system aka hormones)
● Telencephalon: two hemispheres left and right cerebral cortex (intelligence, memory,
personality)
, Limbic system: border midline of the brain, stress and emotional responses: amygdala and
hippocampus are involved in detection of threat adn emotionally charged memories
(respectively)
Neurotransmitters: regulate nervous system functionning
Catecholamines: epinephrine and norepinephrine, sympathetic stimulation
Nervous system disorders
● Epilepsy: central nervous system, affects 130 000 Canadians, no specific cause
(idiopathic), severe injury to head, infectuous disease (meningitis or encephalitis) and
metabolic or nutritional disorders, may also be inherited
○ Marked by seizures, cannot be cured, but can often be successfully controlled
● Parkinson’s disease: progressive generation of basal ganglia which control smothe
motor coordination, tremors, slowness, rigidity
● Cerebral palsy: chronic, nonprogressive disorder marked by lack of muscle
control.stems from brain damage from lack of oxygen supply (childbirth), seizures,
spasms, mental handicap, problems w sight hearing and or speach
● Alzheimer’s: impariments in thinking and memory
● Multiple sclerosis: degenerative disease of brain tissue can cause paralysis,
blindness, deafness, mental deterioration, disinteration of myelin, autoimmune
disorder
● Huntington’s disease: hereditary disorder of the central nervous system, chronic
physical and mental deterioration, muscle spasms, loss of motor abilities, personality
changes
● Paraplegia (paralysis of lower extremities) quadreplegia (paralysis of all four
extremities)
Endocrine system
Pituary gland: locatd at the base of the brain, has two lobes
Anterior pituary lobe: hormones for growth, somatropic hormone, gonatropic
hormons, thyrotropic hormone, adrenocorticropic hormone
Posterior pituary lobe: produces oxytocin and vasopressin
Adrenal glands: two small glands located one on top of each of the kidneys, each consisting
of edrenal medulla and adrenal cortex
Endocrine system disorders
● Diabetes: body cannot use and manufacture insuline (Type1: autoimmune disorder,
partly genetic; Type 2: later on in life, disturbances in glucose metabolism),
thickening of arteries due to the buildup of wastes in blood
Cardiovascular system: composed of heart, blood vessels and blood, acts as transport
system of body
Disorders of cardiovascular system
Nervous system: interconnected nerve fibers that functions to regulate response and
recovery from stress
Sympathetic nervous system: role in reactions to stress, prepares body to respond to
emergencies, to strong emotions (fear), to strenuous activity, mobilization and exertion of
energy (catabolic system)
Parasymaptheric nervous system: controls activities of organs under normal
circumstances, acts antagonistly agaisnt symapthetic nervous system, restores body to
normal state, digestion, relaxation or drowsiness after meal, conservation of bodily energy
(anabolic system)
Brain
Hindbrain
● Medulla: recieves info about heart rate, sensory info about blood pressure and levels
of carbon dioxyde
● Pons: serves link between hindbrain and midbrain
● Cerebellum: voluntray muscle movement, balance, muscle tone and posture
Forebrain
● Diencephalon: thalamus (recognition of sensory stimuli) and hypothalamus (regulates
water balance, apetite, blood pressure, cardiac functioning, sexual desire, with
pituary gland helps regulate endocrine system aka hormones)
● Telencephalon: two hemispheres left and right cerebral cortex (intelligence, memory,
personality)
, Limbic system: border midline of the brain, stress and emotional responses: amygdala and
hippocampus are involved in detection of threat adn emotionally charged memories
(respectively)
Neurotransmitters: regulate nervous system functionning
Catecholamines: epinephrine and norepinephrine, sympathetic stimulation
Nervous system disorders
● Epilepsy: central nervous system, affects 130 000 Canadians, no specific cause
(idiopathic), severe injury to head, infectuous disease (meningitis or encephalitis) and
metabolic or nutritional disorders, may also be inherited
○ Marked by seizures, cannot be cured, but can often be successfully controlled
● Parkinson’s disease: progressive generation of basal ganglia which control smothe
motor coordination, tremors, slowness, rigidity
● Cerebral palsy: chronic, nonprogressive disorder marked by lack of muscle
control.stems from brain damage from lack of oxygen supply (childbirth), seizures,
spasms, mental handicap, problems w sight hearing and or speach
● Alzheimer’s: impariments in thinking and memory
● Multiple sclerosis: degenerative disease of brain tissue can cause paralysis,
blindness, deafness, mental deterioration, disinteration of myelin, autoimmune
disorder
● Huntington’s disease: hereditary disorder of the central nervous system, chronic
physical and mental deterioration, muscle spasms, loss of motor abilities, personality
changes
● Paraplegia (paralysis of lower extremities) quadreplegia (paralysis of all four
extremities)
Endocrine system
Pituary gland: locatd at the base of the brain, has two lobes
Anterior pituary lobe: hormones for growth, somatropic hormone, gonatropic
hormons, thyrotropic hormone, adrenocorticropic hormone
Posterior pituary lobe: produces oxytocin and vasopressin
Adrenal glands: two small glands located one on top of each of the kidneys, each consisting
of edrenal medulla and adrenal cortex
Endocrine system disorders
● Diabetes: body cannot use and manufacture insuline (Type1: autoimmune disorder,
partly genetic; Type 2: later on in life, disturbances in glucose metabolism),
thickening of arteries due to the buildup of wastes in blood
Cardiovascular system: composed of heart, blood vessels and blood, acts as transport
system of body
Disorders of cardiovascular system