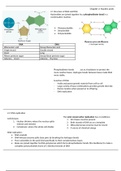
Chapter 2: Nucleic acids
2.1 Structure of RNA and DNA
Nucleotides are joined together by a phosphodiester bond in a
condensation reaction.
Mononucleotide
Dinucleotide
Polynucleotide
RNA DNA
Ribonucleic acid Deoxyribonucleic acid
Single strand Double strand
Short Long
Ribose pentose sugar Deoxyribose pentose sugar
Adenine – Uracil Adenine – Thymine
Phosphodiester bonds act as a backbone to protect the
more reactive bases. Hydrogen bonds between bases make DNA
more stable.
Function of DNA:
- Holds and passes genetic material from cell to cell
- Large variety of base combinations provides genetic diversity
- Rarely mutates when passed on to offspring
- DNA replication
2.2 DNA replication
The semi-conservative replication has 4 conditions:
Cell division: 1. All 4 bases must be present
1. Nuclear division: where the nucleus splits 2. Both strands of DNA act as a template
(mitosis and meiosis) 3. DNA polymerase enzyme must be resent
2. Cytokinesis: where the whole cell divides 4. A source of chemical energy
DNA replication:
DNA unwinds
DNA helicase enzyme splits base pairs by breaking the hydrogen bonds
Free nucleotides in the pool bind specifically to their complementary bases
Bases are joined together by DNA polymerase which forms phosphodiester bonds (the backbone) to make a
complete polynucleotide chains of 2 identical strands of DNA
2.1 Structure of RNA and DNA
Nucleotides are joined together by a phosphodiester bond in a
condensation reaction.
Mononucleotide
Dinucleotide
Polynucleotide
RNA DNA
Ribonucleic acid Deoxyribonucleic acid
Single strand Double strand
Short Long
Ribose pentose sugar Deoxyribose pentose sugar
Adenine – Uracil Adenine – Thymine
Phosphodiester bonds act as a backbone to protect the
more reactive bases. Hydrogen bonds between bases make DNA
more stable.
Function of DNA:
- Holds and passes genetic material from cell to cell
- Large variety of base combinations provides genetic diversity
- Rarely mutates when passed on to offspring
- DNA replication
2.2 DNA replication
The semi-conservative replication has 4 conditions:
Cell division: 1. All 4 bases must be present
1. Nuclear division: where the nucleus splits 2. Both strands of DNA act as a template
(mitosis and meiosis) 3. DNA polymerase enzyme must be resent
2. Cytokinesis: where the whole cell divides 4. A source of chemical energy
DNA replication:
DNA unwinds
DNA helicase enzyme splits base pairs by breaking the hydrogen bonds
Free nucleotides in the pool bind specifically to their complementary bases
Bases are joined together by DNA polymerase which forms phosphodiester bonds (the backbone) to make a
complete polynucleotide chains of 2 identical strands of DNA