NUCLEAR MEDICINE BOARD EXAM 2 LATEST VERSIONS AND STUDY GUIDE (VERSION A AND B) 2023-
2024 ACTUAL EXAM QUESTIONS AND CORRECT DETAILED ANSWERS
Radioactive isotope used for majority of cases - (answer) 99m Technetium
Why 99m Technetium - (answer) - 99m Tc gamma emitter
- scintillating crystal within gamma camera = detects gamma rays
Half life of 99m Technetium - (answer) 6 hours
99 Molybdenum - (answer) - 99m Technetium is there 'daughter'
- moly decays into 99m Tech
- half life = 3 days
- as moly decays = so does 99m tech = less radioactivity to work with
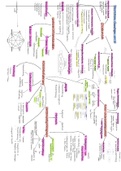
Generator - (answer) Generator is eluted (viles in the top, look at image) to supply the 99m Tc liquid
which is added to variety of pharmaceuticals (depending on type of scans)
How is Radiopharmaceutical liquid introduced to patient - (answer) - injected into pt vein
- inhaled
- ingested
Two types of kidney scans - (answer) - 99m Tc DMSA (scarring of kidney tissue following frequent UTIs)
- 99m TcMAG3 (kidney function, obstruction)
Why is an obstructed kidney brighter - (answer) Because it is obstructed so the radioactive isotope
can't leave the kidney
Thyroid scan - Marker where? - (answer) On sternal notch as thyroid gland shouldn't extend further
than the sternal notch
,NUCLEAR MEDICINE BOARD EXAM 2 LATEST VERSIONS AND STUDY GUIDE (VERSION A AND B) 2023-
2024 ACTUAL EXAM QUESTIONS AND CORRECT DETAILED ANSWERS
What happens with gastric emptying - (answer) - Eat scrambled eggs with 99m Technetium
- scan
- how much is left in stomach at 120minutes
- continue scanning until less than 10% is left (so we know how long it actually took to empty)
Heart scans - (answer) - MUGA (multigated acquisition, looks at efficiency of heart pumping)
- MPI (stress and rest, difference between permanent blood loss or temporary blood loss to L bottom
chamber)
PET Scan - (answer) Needs a pet camera, not a normal
Brown fat uptake - (answer) Happens when the patient gets cold
Muscle uptake - (answer) Happens when patient moves, uses muscles, etc
Basic Science
Isomers - (answer) Nuclides have same A, higher (less stable) energy state - denoted by letter m
example = technetium
Basic Science
Binding energy - (answer) - nearer nucleus = greater energy
- amount of energy needed to eject electron from shell
- K shell electrons = greater binding energy than M shell electrons
Basic Science
Ionisation - (answer) - orbital electron = given enough energy to be ejected from atom
- leaves vacancy = filled from next shell out
,NUCLEAR MEDICINE BOARD EXAM 2 LATEST VERSIONS AND STUDY GUIDE (VERSION A AND B) 2023-
2024 ACTUAL EXAM QUESTIONS AND CORRECT DETAILED ANSWERS
- = characteristic radiation
Basic Science
Excitation - (answer) - Orbital electron enough energy to be ejected from shell, but not enough to leave
atom
- Moves to outer orbit, then drops back
- gives extra energy = characteristic radiation (usually low energy
Basic Science
Nuclear Stability - (answer) - electrostatic repulsive force between protons in nucleus
- Weaker nuclear attractive force between all nucleons
- nucleus gets bigger = need more neutrons to stop nucleus from flying apart
Basic Science
Naturally occurring radionuclides - (answer) - heavy atoms with too many nucleons for stability
- decay by emitting particles and gamma rays until a stable protons:neutron ratio is reached
Basic Science
Artificially produced radionuclides - (answer) - stable nuclide and add protons or neutrons = upset
stable Z:N ratio
- unstable nucleus = emit particles and E.M radiation to reach stability
Basic Science
Someone with poor kidney function, will still decay at same rate? - (answer) No, it will just decay with
time as can't be excreted out
Basic Science
Nuclides with too few neutrons: can decay by... - (answer) - electron capture
, NUCLEAR MEDICINE BOARD EXAM 2 LATEST VERSIONS AND STUDY GUIDE (VERSION A AND B) 2023-
2024 ACTUAL EXAM QUESTIONS AND CORRECT DETAILED ANSWERS
- positron emission
Are produced using a cyclotron
Basic Science
Cyclotron - (answer) Using oscillating magnetic field to accelerate positively charged particles, which
are fired at target material
Basic Science
Positron emission - (answer) Basis for PET scanning
Basic Science
Xrays and gamma rays are both________.
Only difference: - (answer) Both ionising electromagnetic radiation
Only difference:
- xray originate from electron shells of atom
- gamma rays originate from nucleus of atom
Basic Science
Exponential Decay - (answer) - Given large number of atoms the chance that one will decay in any time
period is governed by laws of probability
At = A0.e (- (upside down V)t)
A0 = Initial activity
At = activity after time t
2024 ACTUAL EXAM QUESTIONS AND CORRECT DETAILED ANSWERS
Radioactive isotope used for majority of cases - (answer) 99m Technetium
Why 99m Technetium - (answer) - 99m Tc gamma emitter
- scintillating crystal within gamma camera = detects gamma rays
Half life of 99m Technetium - (answer) 6 hours
99 Molybdenum - (answer) - 99m Technetium is there 'daughter'
- moly decays into 99m Tech
- half life = 3 days
- as moly decays = so does 99m tech = less radioactivity to work with
Generator - (answer) Generator is eluted (viles in the top, look at image) to supply the 99m Tc liquid
which is added to variety of pharmaceuticals (depending on type of scans)
How is Radiopharmaceutical liquid introduced to patient - (answer) - injected into pt vein
- inhaled
- ingested
Two types of kidney scans - (answer) - 99m Tc DMSA (scarring of kidney tissue following frequent UTIs)
- 99m TcMAG3 (kidney function, obstruction)
Why is an obstructed kidney brighter - (answer) Because it is obstructed so the radioactive isotope
can't leave the kidney
Thyroid scan - Marker where? - (answer) On sternal notch as thyroid gland shouldn't extend further
than the sternal notch
,NUCLEAR MEDICINE BOARD EXAM 2 LATEST VERSIONS AND STUDY GUIDE (VERSION A AND B) 2023-
2024 ACTUAL EXAM QUESTIONS AND CORRECT DETAILED ANSWERS
What happens with gastric emptying - (answer) - Eat scrambled eggs with 99m Technetium
- scan
- how much is left in stomach at 120minutes
- continue scanning until less than 10% is left (so we know how long it actually took to empty)
Heart scans - (answer) - MUGA (multigated acquisition, looks at efficiency of heart pumping)
- MPI (stress and rest, difference between permanent blood loss or temporary blood loss to L bottom
chamber)
PET Scan - (answer) Needs a pet camera, not a normal
Brown fat uptake - (answer) Happens when the patient gets cold
Muscle uptake - (answer) Happens when patient moves, uses muscles, etc
Basic Science
Isomers - (answer) Nuclides have same A, higher (less stable) energy state - denoted by letter m
example = technetium
Basic Science
Binding energy - (answer) - nearer nucleus = greater energy
- amount of energy needed to eject electron from shell
- K shell electrons = greater binding energy than M shell electrons
Basic Science
Ionisation - (answer) - orbital electron = given enough energy to be ejected from atom
- leaves vacancy = filled from next shell out
,NUCLEAR MEDICINE BOARD EXAM 2 LATEST VERSIONS AND STUDY GUIDE (VERSION A AND B) 2023-
2024 ACTUAL EXAM QUESTIONS AND CORRECT DETAILED ANSWERS
- = characteristic radiation
Basic Science
Excitation - (answer) - Orbital electron enough energy to be ejected from shell, but not enough to leave
atom
- Moves to outer orbit, then drops back
- gives extra energy = characteristic radiation (usually low energy
Basic Science
Nuclear Stability - (answer) - electrostatic repulsive force between protons in nucleus
- Weaker nuclear attractive force between all nucleons
- nucleus gets bigger = need more neutrons to stop nucleus from flying apart
Basic Science
Naturally occurring radionuclides - (answer) - heavy atoms with too many nucleons for stability
- decay by emitting particles and gamma rays until a stable protons:neutron ratio is reached
Basic Science
Artificially produced radionuclides - (answer) - stable nuclide and add protons or neutrons = upset
stable Z:N ratio
- unstable nucleus = emit particles and E.M radiation to reach stability
Basic Science
Someone with poor kidney function, will still decay at same rate? - (answer) No, it will just decay with
time as can't be excreted out
Basic Science
Nuclides with too few neutrons: can decay by... - (answer) - electron capture
, NUCLEAR MEDICINE BOARD EXAM 2 LATEST VERSIONS AND STUDY GUIDE (VERSION A AND B) 2023-
2024 ACTUAL EXAM QUESTIONS AND CORRECT DETAILED ANSWERS
- positron emission
Are produced using a cyclotron
Basic Science
Cyclotron - (answer) Using oscillating magnetic field to accelerate positively charged particles, which
are fired at target material
Basic Science
Positron emission - (answer) Basis for PET scanning
Basic Science
Xrays and gamma rays are both________.
Only difference: - (answer) Both ionising electromagnetic radiation
Only difference:
- xray originate from electron shells of atom
- gamma rays originate from nucleus of atom
Basic Science
Exponential Decay - (answer) - Given large number of atoms the chance that one will decay in any time
period is governed by laws of probability
At = A0.e (- (upside down V)t)
A0 = Initial activity
At = activity after time t