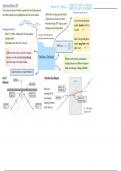
Glossary
Term Definition
Aquatic Live in water.
Terrestrial Live on land.
Rotted Degraded organic matter.
Hypothesis An idea that can be tested through study or investigation.
Habitat The place where an organism lives.
What is the biosphere?
• This is the part of the earth where life is possible.
• Includes the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere.
• Contains all living things and dead organic matter.
Who lives in the biosphere?
• Plants, animals, microorganisms, aquatic and terrestrial organisms.
• Dead organic matter is broken down by bacteria.
Dependence in the biosphere
• Plants provide food and shelter to animals.
• Animals help plants reproduce by dispersing seeds and pollen.
Seven life processes of organisms
1. Nutrition
o Plants are makers; animals are consumers.
2. Grow
o Organisms evolve from one cell to many cells.
3. Reproduction
o Produce offspring to ensure survival.
4. Respiration (breathing)
o Energy is released from food in cells (mitochondria).
5. Excretion
o Waste products are removed.
6. Sensitivity
o Reaction to the environment (light, heat, etc.).
7. Movement
o Animals move to avoid danger.
Copyright © The Teacher's Pet Natural Sciences Grade 7 (Via Afrika) Page 2 of 29
, Requirements for life
Water
• Plants: from soil.
• Animals: drink or via food.
Temperature
• Difference between shaded and open areas.
• Measured with a thermometer.
Soil
• Determine which plants can grow.
• Types: sandy, clayey, loamy.
Gases
• CO₂: needed for photosynthesis.
• O₂: for breathing.
• N: for proteins and chlorophyll.
Energy of the sun
• Essential for photosynthesis.
• Sunlight drives the energy cycle.
Adaptation to habitat
• Cactus: stores water.
• View: win and push.
• Birds: feathers for flying.
Copyright © The Teacher's Pet Natural Sciences Grade 7 (Via Afrika) Page 3 of 29