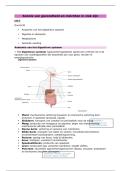
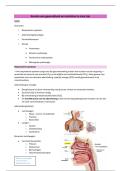
Intensive Care Exam New Version with All the 175
Questions from Actual Exam, Correct Answers and
Rationale
Section 1: General Assessment (Questions 1–35)
1. A 32-week preterm neonate has a heart rate of 160 bpm and irregular respirations. What
is the priority assessment?
A) Perform Apgar score.
B) Assess Ballard score.
C) Monitor oxygen saturation.
D) Check blood glucose.
Correct Answer: C) Monitor oxygen saturation.
Rationale: Irregular respirations in a preterm neonate suggest respiratory distress,
requiring immediate oxygen saturation monitoring. NCC Domain 1: Neonatal
assessment.
2. A 36-week neonate has a temperature of 36.2°C. What is the next step?
A) Place in radiant warmer.
B) Administer IV fluids.
C) Perform sepsis workup.
D) No action needed.
Correct Answer: A) Place in radiant warmer.
Rationale: Hypothermia in a neonate requires thermal support to prevent complications.
NCC Domain 1: Physical assessment.
3. A mother with gestational diabetes delivers a 39-week neonate. What is the priority
assessment?
A) Blood glucose screening.
B) Chest X-ray.
C) Hearing screen.
D) Bilirubin level.
Correct Answer: A) Blood glucose screening.
Rationale: Infants of diabetic mothers are at risk for hypoglycemia. NCC Domain 1:
Maternal-fetal assessment.
4. A neonate has a Ballard score indicating 34 weeks gestation. What finding supports this?
A) Creased soles and firm ear cartilage.
B) Minimal lanugo and some sole creases.
C) Thick lanugo and no sole creases.
D) Fully flexed posture and no lanugo.
Correct Answer: B) Minimal lanugo and some sole creases.
Rationale: 34-week gestation shows minimal lanugo and partial sole creases per Ballard
criteria. NCC Domain 1: Gestational age assessment.
5. A neonate’s respiratory rate is 70 breaths/min at rest. What is the next step?
A) Monitor for signs of respiratory distress.
B) Administer oxygen immediately.
, C) Obtain chest X-ray.
D) No action needed.
Correct Answer: A) Monitor for signs of respiratory distress.
Rationale: Tachypnea requires observation for grunting, flaring, or retractions. NCC
Domain 1: Neonatal assessment.
6. A 35-week neonate has a weak cry and poor suck. What assessment?
A) Neurological exam.
B) Blood glucose test.
C) Cardiac auscultation.
D) Abdominal palpation.
Correct Answer: A) Neurological exam.
Rationale: Weak cry and poor suck suggest neurological issues in preterm neonates. NCC
Domain 1: Physical assessment.
7. A neonate’s mother had chorioamnionitis. What assessment priority?
A) Sepsis screening.
B) Hearing test.
C) Glucose check.
D) Bilirubin level.
Correct Answer: A) Sepsis screening.
Rationale: Chorioamnionitis increases neonatal sepsis risk, requiring blood culture and
labs. NCC Domain 1: Maternal-fetal assessment.
8. A 38-week neonate has acrocyanosis. What is the next step?
A) No action needed.
B) Administer oxygen.
C) Obtain arterial blood gas.
D) Place in warmer.
Correct Answer: A) No action needed.
Rationale: Acrocyanosis is normal in newborns unless central cyanosis is present. NCC
Domain 1: Physical assessment.
9. A neonate has a heart murmur at 12 hours of life. What assessment?
A) Echocardiogram referral.
B) Immediate surgery.
C) Chest X-ray.
D) No action needed.
Correct Answer: A) Echocardiogram referral.
Rationale: Murmurs require evaluation for congenital heart defects. NCC Domain 1:
Physical assessment.
10. A 33-week neonate has poor tone. What assessment tool?
A) Ballard score.
B) Apgar score.
C) Brazelton assessment.
D) Dubowitz scale.
Correct Answer: A) Ballard score.
Rationale: Ballard score assesses gestational age and neuromuscular maturity. NCC
Domain 1: Gestational age assessment.
11. A neonate’s mother has hepatitis B. What assessment?
, A) Hepatitis B serology.
B) Blood glucose test.
C) Bilirubin level.
D) Hearing screen.
Correct Answer: A) Hepatitis B serology.
Rationale: Maternal hepatitis B requires neonatal screening and prophylaxis. NCC
Domain 1: Maternal-fetal assessment.
12. A 37-week neonate has jitteriness. What assessment?
A) Blood glucose test.
B) EEG monitoring.
C) Chest X-ray.
D) No action needed.
Correct Answer: A) Blood glucose test.
Rationale: Jitteriness may indicate hypoglycemia in term neonates. NCC Domain 1:
Physical assessment.
13. A neonate has asymmetric Moro reflex. What assessment?
A) Neurological exam.
B) Blood glucose test.
C) Cardiac auscultation.
D) Abdominal palpation.
Correct Answer: A) Neurological exam.
Rationale: Asymmetric Moro suggests neurological or musculoskeletal issues. NCC
Domain 1: Physical assessment.
14. A mother with preeclampsia delivers a 34-week neonate. What assessment?
A) Monitor for hypoglycemia.
B) Chest X-ray.
C) Hearing screen.
D) Bilirubin level.
Correct Answer: A) Monitor for hypoglycemia.
Rationale: Preeclampsia increases risk of neonatal hypoglycemia. NCC Domain 1:
Maternal-fetal assessment.
15. A 32-week neonate has nasal flaring. What assessment?
A) Oxygen saturation monitoring.
B) Blood glucose test.
C) Bilirubin level.
D) No action needed.
Correct Answer: A) Oxygen saturation monitoring.
Rationale: Nasal flaring indicates respiratory distress, requiring SpO2 monitoring. NCC
Domain 1: Neonatal assessment.
16. A neonate’s mother used cocaine during pregnancy. What assessment?
A) Neonatal abstinence scoring.
B) Blood glucose test.
C) Hearing screen.
D) Bilirubin level.
Correct Answer: A) Neonatal abstinence scoring.
Rationale: Cocaine exposure increases withdrawal risk, requiring Finnegan scoring. NCC
, Domain 1: Maternal-fetal assessment.
17. A 35-week neonate has a temperature of 35.8°C. What assessment?
A) Check environmental temperature.
B) Administer antibiotics.
C) Obtain blood culture.
D) No action needed.
Correct Answer: A) Check environmental temperature.
Rationale: Hypothermia may result from environmental factors in preterm neonates. NCC
Domain 1: Physical assessment.
18. A neonate has a head circumference of 38 cm (90th percentile). What assessment?
A) Head ultrasound.
B) Blood glucose test.
C) Chest X-ray.
D) No action needed.
Correct Answer: A) Head ultrasound.
Rationale: Macrocephaly requires evaluation for hydrocephalus or other issues. NCC
Domain 1: Physical assessment.
19. A 36-week neonate has poor feeding. What assessment?
A) Blood glucose and neurological exam.
B) Chest X-ray.
C) Hearing screen.
D) Bilirubin level.
Correct Answer: A) Blood glucose and neurological exam.
Rationale: Poor feeding may indicate hypoglycemia or neurological issues. NCC Domain
1: Physical assessment.
20. A neonate’s mother has HIV. What assessment?
A) HIV PCR testing.
B) Blood glucose test.
C) Bilirubin level.
D) Hearing screen.
Correct Answer: A) HIV PCR testing.
Rationale: Maternal HIV requires neonatal testing and prophylaxis. NCC Domain 1:
Maternal-fetal assessment.
21. A 34-week neonate has grunting respirations. What assessment?
A) Oxygen saturation and respiratory effort.
B) Blood glucose test.
C) Bilirubin level.
D) No action needed.
Correct Answer: A) Oxygen saturation and respiratory effort.
Rationale: Grunting indicates respiratory distress, requiring immediate assessment. NCC
Domain 1: Neonatal assessment.
22. A neonate has a Ballard score of 40 weeks but was born at 37 weeks. What assessment?
A) Evaluate for LGA status.
B) Blood glucose test only.
C) Chest X-ray.
D) No action needed.