Integumentary Questions
Chapters: 49, 50
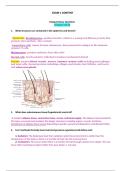
1. What structures are contained in the epidermis and dermis?
Epidermis: Keratinocytes- produce keratin, which is a waterproof fibrous protein that
protects skin and hair. Also contain:
Langerhans cells- ingest foreign substances, then present the antigen to the immune
system’s T cells
Melanocytes- produce melanin, hair/skin color
Merkel cells- touch-sensitive cells that transduce mechanical stimuli
Dermis: encases blood vessels, nerves, immune system cells including macrophages
and mast cells, dermal proteins including collagen and elastin, hair follicles, and sweat
and sebaceous glands
2. What does subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis) consist of?
It contains adipose tissue, connective tissue, nerves, and blood supply. The adipose tissue located in
this layer surrounds and insulates the deeper structures including organs, muscle, and bone.
Distribution of adipose tissue varies depending on gender, genetic predisposition, and lifestyle habits.
3. List 4 methods the body loses heat (temperature regulation) and define each:
1. Radiation: The body loses heat from radiation when the environment is colder than the
temperature of the body so there is a transfer of heat into the environment (
2. Conduction: This occurs when there is a transfer of heat through contact of an object. This can
occur when touching an object colder than your body i.e. Ice pack
, 3. Evaporation: If your skin or clothes are wet, the warm water will move to the surface of skin and
evaporate into the environment, especially in dry and windy conditions.
4. Convection: This is the transfer of heat from your body due to currents or winds, i.e. sitting in
front of a fan or cool breeze
4. Concave nails (spooning) are a sign of anemia.
A. True
B. False
Nails become concave in shape, which may indicate iron-deficiency anemia, sulfur protein deficiency,
hyperthyroidism, idiopathic or hereditary cause
5. Clubbing of the nails is indicative of a chronic cardiopulmonary disorder.
A. True
B. False
Clubbing (enlarged fingertip and expansion of soft tissue) of the nail is associated with chronic
cardiopulmonary conditions, liver disease, and GI tract disease.
6. What do thick nails indicate? What do thick, yellow nails indicate? (2 conditions):
1. Thick nails can be caused by Advanced age (nail growth rate goes down, causing nails to
thicken), Fungal infections (Onychomycosis: thick, yellow and brittle/crumbly), Poor circulation, and
Diabetes
2. Thick, yellow nails may indicate a fungal infection called Onychomycosis, lymphedema or a
chronic respiratory disease
7. List the types of primary skin lesions and briefly describe each, considering size, if applicable:
1. Macule: A flat, nonpalpable, discolored mark on the skin that is less than 1 cm in size
Ex- flat moles and freckles
-Patch: an irregularly shaped macule that is greater than 1 cm in diameter; ex- Vitiligo,
Mongolian spots
2. Papule: A solid, elevated bump that is palpable, firm, can be in the epidermis or dermis and is
less than 1 cm in diameter. Ex- Elevated moles, warts
3. Plaque: A solid, firm, and rough elevated lesion that is plateau-like and greater than 1 cm in size.
Ex- Psoriasis, eczema
4. Wheal: Elevated, irregular border, solid, pale red in color, size varies. Ex- Hives, insect bites
5. Nodule: A Firm or soft, elevated bump that can be in the epidermis or dermis and can extend up
to 1-2 cm into the skin. Ex- enlarged lymph nodes
6. Vesicle: A fluid-filled lesion that is elevated and round. Less than 1 cm in diameter. Ex- blister,
Chickenpox, Herpes simplex
7. Bulla: Same description as a vesicle, but greater than 1 cm in diameter
8. Cyst: Round, solid or fluid-filled below the skin (growth)