Why does culture matter?
It shapes how we think and how we react
Global exchanges and communication are reshaping cultures.
Studying culture allows us to understand globalization, nationalism, political
frictions, customs and rituals of people’s communities and groups
What is culture?-> a contested concept
‘It’s one of the most complicated words in the English language’
Noun: everything that does not grow alone -> expanded: cultivating
Culture as a lived experience one cited to a specific group
Cultural studies approach: culture is not out there
Two possible ways to define it:
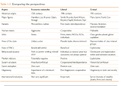
High culture: the best of what society produces -> lit, fine arts, ballet, classical
music
It’s a form of human, civilisation that counters ‘anarchy of the raw and
cultivated’
Ordinary culture: culture is society’s way of life -> it’s ordinary, it belongs to
a group of pp, it’s about the creation of everyday meanings -> values, norms,
material goods
The democratic hedge: humanities traditionally studied ‘high’ culture, paying little
attention to ordinary culture.
Raymond williams (1921-1958): cultural materialism
Culture has 2 aspects : the known meanings and directions.
Culture is both traditional and creative. We use the word culture in these 2 sense: a
way of life; and the arts+ learning.
Culture as part of the social fabric-> defining it as the study of rltshps
3 types of cultures:
Lived culture of a particular place and time
Recorded cultures, from art to most everyday facts
Culture of the selective tradition -> connecting lived culture+ recorded culture.
Cultural materialism : HOW & WHY?
You cannot isolate culture from material condit°, econ possibilities, social posit°
of the creator
It involves the exploration of significat° in the context of the means of condit°
and production
Culture components
Institutions: involved in creating culture (gov, schools, companies)
Formations: (cultural icons studied at school)
, Modes of production: material conditions (infrastructure, money..)
Identification: how people identity (style, aesthetic)
Reproduction: how is culture reproduced, remembered, archived?
Organisation: how is that archive and remembrance organised
CS, its Marxist heritage, and it’s critique of Marx
CS responds to : ideology, historical materialism ( the material conditions of life ate
historically shaped), hegemony
WHAT IS MARXISM?:
main idea: historical materialism-> theory that relates the production and reproduction of the
culture to the org of the material conditions of life.
Marxist def of culture: Culture is a corporeal force into the socially organised production on of
material conditions of existence (not everyone has the same conditions).
Relations of production?
- The economic structure of society: real foundation, legal and polit structures aride on
and define forms of counciousness
For Marxism culture is political: its
expressive of social relations of class -
> ruling ideas : dominant intellectual
force
As a result:
Naturalises social order as an
invetable fact
Obscures the underlying
CS criticism, against Marxist economic determinism: culture is a site of tension ands conflict
it is too simple to argue that its relies by the dominant class alone
Revisions of Marxism: Althusser
Ideology constitutes the subject, as a lived experience, as misrecognition of
existence, involved in the reproduction of social fabric.
Stuart hall
What is social formation?:
A complex structure of different instances
It’s not the result of single, base-superstructure
Society is not a closed system. Elements in a social formation are distinct but CONNECTED.
The concept of ARTICULATION; you need to do 2 things.
You need to form distinct sounds
See the interaction between different sounds
Antonio Gramsci
Culture is imbedded in power relations
Why proletariat vote fascist?: due to social authority +
ruling class cannot just work for force.
It shapes how we think and how we react
Global exchanges and communication are reshaping cultures.
Studying culture allows us to understand globalization, nationalism, political
frictions, customs and rituals of people’s communities and groups
What is culture?-> a contested concept
‘It’s one of the most complicated words in the English language’
Noun: everything that does not grow alone -> expanded: cultivating
Culture as a lived experience one cited to a specific group
Cultural studies approach: culture is not out there
Two possible ways to define it:
High culture: the best of what society produces -> lit, fine arts, ballet, classical
music
It’s a form of human, civilisation that counters ‘anarchy of the raw and
cultivated’
Ordinary culture: culture is society’s way of life -> it’s ordinary, it belongs to
a group of pp, it’s about the creation of everyday meanings -> values, norms,
material goods
The democratic hedge: humanities traditionally studied ‘high’ culture, paying little
attention to ordinary culture.
Raymond williams (1921-1958): cultural materialism
Culture has 2 aspects : the known meanings and directions.
Culture is both traditional and creative. We use the word culture in these 2 sense: a
way of life; and the arts+ learning.
Culture as part of the social fabric-> defining it as the study of rltshps
3 types of cultures:
Lived culture of a particular place and time
Recorded cultures, from art to most everyday facts
Culture of the selective tradition -> connecting lived culture+ recorded culture.
Cultural materialism : HOW & WHY?
You cannot isolate culture from material condit°, econ possibilities, social posit°
of the creator
It involves the exploration of significat° in the context of the means of condit°
and production
Culture components
Institutions: involved in creating culture (gov, schools, companies)
Formations: (cultural icons studied at school)
, Modes of production: material conditions (infrastructure, money..)
Identification: how people identity (style, aesthetic)
Reproduction: how is culture reproduced, remembered, archived?
Organisation: how is that archive and remembrance organised
CS, its Marxist heritage, and it’s critique of Marx
CS responds to : ideology, historical materialism ( the material conditions of life ate
historically shaped), hegemony
WHAT IS MARXISM?:
main idea: historical materialism-> theory that relates the production and reproduction of the
culture to the org of the material conditions of life.
Marxist def of culture: Culture is a corporeal force into the socially organised production on of
material conditions of existence (not everyone has the same conditions).
Relations of production?
- The economic structure of society: real foundation, legal and polit structures aride on
and define forms of counciousness
For Marxism culture is political: its
expressive of social relations of class -
> ruling ideas : dominant intellectual
force
As a result:
Naturalises social order as an
invetable fact
Obscures the underlying
CS criticism, against Marxist economic determinism: culture is a site of tension ands conflict
it is too simple to argue that its relies by the dominant class alone
Revisions of Marxism: Althusser
Ideology constitutes the subject, as a lived experience, as misrecognition of
existence, involved in the reproduction of social fabric.
Stuart hall
What is social formation?:
A complex structure of different instances
It’s not the result of single, base-superstructure
Society is not a closed system. Elements in a social formation are distinct but CONNECTED.
The concept of ARTICULATION; you need to do 2 things.
You need to form distinct sounds
See the interaction between different sounds
Antonio Gramsci
Culture is imbedded in power relations
Why proletariat vote fascist?: due to social authority +
ruling class cannot just work for force.