Dr Dunja Aksentijevic
Control of Contraction of the Heart
Myogenic Hearts
• Vertebrates
• Able to generate spontaneous rhythmical depolarisation
o Rate varies
• Pace maker cells
o Determines contraction rate – fastest way of firing
o Fish use sinus venosus
o Other vertebrates = sinoatrial node
Pacemaker Cells
• Small, few myofibrils, mitochondria
• Don’t contract
• Unstable resting membrane potential
o Pacemaker potential
Hierarchy in Mammals
Fastest
Sinus node
Atrioventricular node
His bundle
Slowest
Purkinje fibres
• Conduction from SA to AV nodes via atrial muscle – slow
o Causes AV “pause”
▪ Allows ventricles to fill completely
▪ Prevents transmission of high rates from atria
• Through ventricles is fast transmission
o Allows apex to contract before base
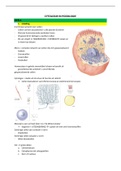
Cardiac Muscle
• Intercalated disks between cells formed by plasma membrane
o Have gap junctions for electrical conduction
o Desmosomes mechanically hold them together
• Syncytium needed for uninterrupted waves
• Sarcomere has the same bonding as skeletal (T tubules)
Pacemaker Action Potentials
1) “funny” channels open
2) Becomes more permeable to Na+
3) K+ efflux decreases
4) Membrane potential increases