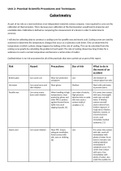
Chromatography is analytical technique that can be used as a process of
separating mixtures of compounds. This process exists of two distinct phases
before it gets completed; these phases are the stationary phase and the
mobile phase. The stationary phase acts as a solid. Compounds in the mixtures
when the paper absorbs the pigment, and the mobile phase is when the
solvent is used in the process moves through the paper. The moving solvent
spots the amount of the different component of the mixture dissolved.
The process is used to identify whether a substance is pure or not. The
technique has two major ways used to identify the component within its
mixture. These are stationary or paper and thin layer chromatography.
Factors that affect chromatography,
Temperature / volatility– if the room temperature is high, the solvent be
quicker in moving the pigment upwards in the chromatography paper. if the
room temp. is below average it may cause the practical may take up more time
than normal.
Concentration of pigment used – if the pigment or mysterious substance used
for the chromatography is not dense enough it may cause the reading of the
experiment not accurate enough for us to take measurements and thus
resulting in not finding out the published Rf value to name the pigments we
got.
Affinity – this means how pure the molecule is. This is based on the substance
absorption for example, in the experiment of amino acids we used 3 amino
acids in their own way of affinity and solubility.
Polarity – as the polarity moves through the paper, it is affected by the
molecules.
Size of the molecule – molecules with smaller size moves faster than the
molecules with larger size.
After doing each practical, we find the retention factor (Rf value) which is a
distance moved by the solute divided by the distance moved by the solvent on
a chromatography paper or plate.
, Rf value = distance moved by the solute / distance moved the solvent
HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography)
This type of chromatography has the elevated level of accuracy and precision
across each run. In this like other the liquids are used as mobile phase, and it is
the more identified way to get accurate results.
Gas chromatography
This type of chromatography includes the sample which is vaporised into the
gas carrier through a chromatography. As the solvent travel through each
column, it reacts with different components to varying degrees. This causes
them to separate many separate times.
Chromatography Paper of extracted plant pigments
The paper technique chromatography is a useful way of identifying the
different plant pigments. It has two separate phases such as stationary phase
and mobile phase. The mobile phase is the solvent that moves up the paper
and as it does, it dissolves the substances or components and carries them up.
This allows them to separate and become visible. And the stationary phase
remains on the chromatography paper and does not move up the paper.
Factors
Equipment. Using right equipment helps to get right spots, which ends up
getting more accurate results.
Temperature. Includes room temperature. For example, if the room
temperature is hot, it will help the compounds to get separated faster.
In this experiment the equipment’s that I used,
Boiling tube
Bung
Rack
Chromatography paper
Spinach leaf