Lecture 9: Gender dysphoria
Leerdoelen
To identify the characteristics of Gender Dysphoria (GD), including:
o The difference between GD in children vs adolescents and adults
o The diagnostic features and associated features
o Prevalence, development and course
o Risk and prognostic factors
o Culture-related diagnostics issues
o Diagnostic markers and functional consequences
o Differential diagnosis and comorbidity
To identify the various aspects to the etiology of GD
To identify the key components of the Dutch Approach to treating GD depending on age
To compare and distinguish prevalence rates of psychopathology between GD and normative samples at
various time points within treatment
To identify areas of well-being/psychopathology of concern for people with GD
To apply knowledge of GD and its characteristics to clinical examples
Concepts and terminology
Gender dysphoria: not being happy with your assigned birth gender which causes clinical distress. The main
treatment is physical instead of psychological as with other psychiatric disorders.
Outcomes: transition, distress which persists after transitioning, benefits and learning a lot about yourself
It’s about gender identity: who am I? It’s a very personal concept.
Gender role/expression: behavioral and emotional aspects of gender.
Sexual identity: how do you see yourself as a sexual romantic being?
Transgender/transsexual: identifying with another gender than the assigned birth gender. The term
transexual is not used a lot nowadays and indicates that their sexe has also changed by e.g. hormones.
Cisgender: cisgender en cisseksueel is iemand van wie de genderidentiteit overeenkomt met het
geboortegeslacht
Male-to-female (MtF) transwoman
Female-to-male (FtM) transman
Person (man/woman) with a trans history
Non-binary, gender queer, gender fluid, a-gender, etc.
Etiology
Etiology of gender dysphoria is still very unclear
Biological factors:
o Genes
o Brain anatomy
o Hormones & receptors (pre- & postnatal) e.g. high androgen exposure prenatally is potentially
involved
Psychological factors:
o Poor/absent parental relationships, childhood abuse, parental encouragement of gender variance
o Rejection, overprotection, lack of emotional warmth
Social factors: society learns us the difference between men and women
Manifestation
Children
o Early-onset (gender dysphoria starts in childhood and persists or re-ermeges after puberty) vs.
late-onset (gender dysphoria starts in early adulthood) timing
Review:
o Only 15.8% of all children with gender dysphoria persist
o Period between 10-13 year is crucial considering persisting of gender dysphoria:
Change in social environment
Anticipated & actual feminization/masculinization
Falling in love and sexual attractions
o Persisters are more often heterosexual (in their new gender)
, o Desisters are more often bisexual and gay (in their natal gender)
Nowadays the persistence rate of gender dysphoria is 20-40% according to research
Advice = watchful waiting
Different approaches considering gender dysphoria in children (topic which leads to discussion):
Case studies
The insecure anxious type
The overconfident inpatient type: they are convinced that the transition will resolve all problems
The rational open type: open to exploring their gender
Young versus older types: bodily changes are dependent on age
Transmen versus transwomen: transmen are often very rational and relaxed, transwomen can be a bit more
emotional and nagging. For females it is more accepted to behave ‘manly’ which makes it a bit more easier
to be transmen.
High psychiatric comorbidity: mainly depression and anxiety. About 50% percent has a psychiatric disorder.
But also high loneliness, unemployment rates, sexual problems, difficult social environment, discrimination,
suicide ideation (and attempts and death) en more often single. Transwomen often have more problems
than transmen.
Three factors are related to well-being:
o Social supports
o Internalized transphobia (reversed) that you have a faded attitude consisting your gender and
relates to self-
image
o Resilience/coping
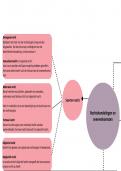
Gender minority stress
model:
Gender minority support model: