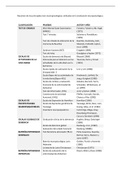
FINACC ONE PAGE SUMMARIES
, FINACC GENERAL THINGS
Depreciation: Production units Depreciation journals
CP x units produced and sold in year DR – Depreciation (P/L) xxx
total estimated production CR – Accumulated Depreciation (SFP) xxx
eg: DR – Deferred Tax (SFP) xxx
CP = 8 000. Estimated units to be produced and sold CR – Tax expense (P/L) xxx
over 5 years = 20 units. In 2021 produced and sold
3,5 units and in 2022 produced and sold 4,2
\ 2021: 8 000 x 3,5/20 = 1 400
\ 2022: 8 000 x 4,2/20 = 1 680
, IAS 1: PRESENTATION
GENERAL PRESENTATION NOTES inventory
IAS 1.61 requires that, if items include amounts which must be recovered in 12 months and after 12
A fair presentation in terms of IAS 1 Presentation of Financial months, the amounts must be disclosed separately
Statements is achieved if all appropriate IFRSs are complied with.
(IAS1.17) cash & cash equivalents
IAS 1.51 requires that the presentation currency is prominently In terms of IAS 1.66, if cash and cash equivalents is restricted from being used within 12 months after
shown. à The statements must prominently state that it is the reporting period end, it should be presented as a non-current asset.
Rand.
If an amount is material – IAS 1 should be considered in respect deferred tax asset
of disclosing this matter as a separate item IAS 1.56 prohibits the presentation of deferred tax liabilities/assets as current assets/liabilities.
Current liabilities (paragraph 69)
(a) it expects to settle the liability in its normal operating cycle (refer par.70 for normal operating cycle and paras. 76A&B for methods of settlement) (e.g. trade
liabilities);
(b) it holds the liability primarily for the purpose of trading (refer par.71 for examples) (e.g. FEC liability);
(c) the liability is due to be settled within twelve months after the reporting period (refer par.71 for examples, par 72 for refinancing and par 76A&B for methods of
settlement); or
Paragraph c): settled within 12 months = current
If a liability is current then it will stay current even if:
If breaches agreement with the effect that liability becomes payable on demand = current
• Original term was >12 months
Even if lender agrees AFTER reporting date but before authorization not to demand payment
• And agreement to refinance the liability / reschedule
= still current
payments on a long term basis is completed AFTER
If lender agrees BEFORE reporting date not to demand payment = non-current
reporting date before authorization.
Refinance: pay payment but immediately borrow again
Reschedule payments: agree to other payback items over a longer
period
**LINK TO IAS !0**
Therefore if refinance / reschedule payment for long term before
reporting date = non-current
(d) it does not have the right at the end of the reporting period to defer settlement of the liability for at least twelve months after the reporting period (refer par
72A&B).
Paragraph d) no right to defer settlement = current
If you have the right to defer and pay > 12 months after RD = non-current
BUT if linked to specific conditions that must be met in order to defer then those conditions must be
met AT reporting date (even if the lender only tested for compliance after reporting date)
If the conditions were NOT met at reporting date = will remain current (can’t defer)
If the conditions were met at reporting date = will change to non-current
None of the above? = NON-CURRENT
NB!!! HOW CAN SETTLEMENT TAKE PLACE
• Par. 76A: Settlement = transfer to counter party that results in extinguishment of the liability
• This can include cash or other economic resources (e.g. goods/services); or
• An entity’s own equity instruments (unless par. 76B applies)
• Par. 76B: If the counter party has the option to choose that the settlement of the liability will occur by the transfer of the entity’s own equity instruments and the
entity (in terms of IAS 32) classifies the option as an equity instrument, and recognises it separately from the liability as an equity component of a compound
financial instrument,
• then the settlement in an entity’s own equity instruments is not taken into account as a method of settlement (i.e. it does not influence the
assessment of current vs non-current).
• Note: See IAS 1.76 for disclosure if settlement takes place after reporting period end, but before AFS authorisation date.
Settlement
A B
Dt Inventory Counterparty has the option to chose equity of A as settlement
Cr Creditor
Creditor can be IAS 32 if equity or compound instrument (liability/equity)
, EXAMPLES:
On reporting date the loan was due within 12 months (as per par.
69(c). Also, no right to defer existed on reporting date. = non-
adjusting event.
Requires disclosure. See IAS 1.76 and IAS 10 Events after the
reporting period.
On reporting date the entity had right to defer settlement, BUT it
was subject to conditions that were NOT MET at reporting period
end.
◦ Specified conditions must be met at RD.
Therefore remains a current liability (conditions are only met after
reporting date)
◦ Instance a) On reporting date the loan was NOT due within 12
months
◦ Instance b) On reporting date the loan was due within 12
months and no right to defer existed on reporting date.
◦ Note: rectifying breach after reporting period end (but before
authorization date) -> disclosure (IAS 10)
◦ Note: Receiving grace period after reporting period end (but
before authorization date) -> disclosure (IAS 10)
On reporting date the entity had right to defer settlement beyond
12 months after reporting period end.
Right to defer à non-current
Possible disclosure i.t.o. par. 76.
Loan repaid in full = non-adjusting event.
Amounts included in current assets/liabilities, but realisation/payment after 12 months?
= should be disclosed
, FINACC GENERAL THINGS
Depreciation: Production units Depreciation journals
CP x units produced and sold in year DR – Depreciation (P/L) xxx
total estimated production CR – Accumulated Depreciation (SFP) xxx
eg: DR – Deferred Tax (SFP) xxx
CP = 8 000. Estimated units to be produced and sold CR – Tax expense (P/L) xxx
over 5 years = 20 units. In 2021 produced and sold
3,5 units and in 2022 produced and sold 4,2
\ 2021: 8 000 x 3,5/20 = 1 400
\ 2022: 8 000 x 4,2/20 = 1 680
, IAS 1: PRESENTATION
GENERAL PRESENTATION NOTES inventory
IAS 1.61 requires that, if items include amounts which must be recovered in 12 months and after 12
A fair presentation in terms of IAS 1 Presentation of Financial months, the amounts must be disclosed separately
Statements is achieved if all appropriate IFRSs are complied with.
(IAS1.17) cash & cash equivalents
IAS 1.51 requires that the presentation currency is prominently In terms of IAS 1.66, if cash and cash equivalents is restricted from being used within 12 months after
shown. à The statements must prominently state that it is the reporting period end, it should be presented as a non-current asset.
Rand.
If an amount is material – IAS 1 should be considered in respect deferred tax asset
of disclosing this matter as a separate item IAS 1.56 prohibits the presentation of deferred tax liabilities/assets as current assets/liabilities.
Current liabilities (paragraph 69)
(a) it expects to settle the liability in its normal operating cycle (refer par.70 for normal operating cycle and paras. 76A&B for methods of settlement) (e.g. trade
liabilities);
(b) it holds the liability primarily for the purpose of trading (refer par.71 for examples) (e.g. FEC liability);
(c) the liability is due to be settled within twelve months after the reporting period (refer par.71 for examples, par 72 for refinancing and par 76A&B for methods of
settlement); or
Paragraph c): settled within 12 months = current
If a liability is current then it will stay current even if:
If breaches agreement with the effect that liability becomes payable on demand = current
• Original term was >12 months
Even if lender agrees AFTER reporting date but before authorization not to demand payment
• And agreement to refinance the liability / reschedule
= still current
payments on a long term basis is completed AFTER
If lender agrees BEFORE reporting date not to demand payment = non-current
reporting date before authorization.
Refinance: pay payment but immediately borrow again
Reschedule payments: agree to other payback items over a longer
period
**LINK TO IAS !0**
Therefore if refinance / reschedule payment for long term before
reporting date = non-current
(d) it does not have the right at the end of the reporting period to defer settlement of the liability for at least twelve months after the reporting period (refer par
72A&B).
Paragraph d) no right to defer settlement = current
If you have the right to defer and pay > 12 months after RD = non-current
BUT if linked to specific conditions that must be met in order to defer then those conditions must be
met AT reporting date (even if the lender only tested for compliance after reporting date)
If the conditions were NOT met at reporting date = will remain current (can’t defer)
If the conditions were met at reporting date = will change to non-current
None of the above? = NON-CURRENT
NB!!! HOW CAN SETTLEMENT TAKE PLACE
• Par. 76A: Settlement = transfer to counter party that results in extinguishment of the liability
• This can include cash or other economic resources (e.g. goods/services); or
• An entity’s own equity instruments (unless par. 76B applies)
• Par. 76B: If the counter party has the option to choose that the settlement of the liability will occur by the transfer of the entity’s own equity instruments and the
entity (in terms of IAS 32) classifies the option as an equity instrument, and recognises it separately from the liability as an equity component of a compound
financial instrument,
• then the settlement in an entity’s own equity instruments is not taken into account as a method of settlement (i.e. it does not influence the
assessment of current vs non-current).
• Note: See IAS 1.76 for disclosure if settlement takes place after reporting period end, but before AFS authorisation date.
Settlement
A B
Dt Inventory Counterparty has the option to chose equity of A as settlement
Cr Creditor
Creditor can be IAS 32 if equity or compound instrument (liability/equity)
, EXAMPLES:
On reporting date the loan was due within 12 months (as per par.
69(c). Also, no right to defer existed on reporting date. = non-
adjusting event.
Requires disclosure. See IAS 1.76 and IAS 10 Events after the
reporting period.
On reporting date the entity had right to defer settlement, BUT it
was subject to conditions that were NOT MET at reporting period
end.
◦ Specified conditions must be met at RD.
Therefore remains a current liability (conditions are only met after
reporting date)
◦ Instance a) On reporting date the loan was NOT due within 12
months
◦ Instance b) On reporting date the loan was due within 12
months and no right to defer existed on reporting date.
◦ Note: rectifying breach after reporting period end (but before
authorization date) -> disclosure (IAS 10)
◦ Note: Receiving grace period after reporting period end (but
before authorization date) -> disclosure (IAS 10)
On reporting date the entity had right to defer settlement beyond
12 months after reporting period end.
Right to defer à non-current
Possible disclosure i.t.o. par. 76.
Loan repaid in full = non-adjusting event.
Amounts included in current assets/liabilities, but realisation/payment after 12 months?
= should be disclosed