3
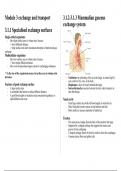
exchange system
3.1.1 Specialised exchange surfaces
Single-celled organisms
- H
ave high surface area to volume ratio, because
-> short diffusion distance
-> large surface area allow maximum absorption of nutrient and gas
exchange
Multicellular organisms
- H ave low surface area to volume ratio, because
-> have longer diffusion distance
- Have evolved specialised organ system for exchanging substances
* *As the size of the organism increases, its surface area to volume ratio
increases. - V entilation:the refreshing of the air in the lungs,to ensure high O2
conc. and low CO2 conc. in the body
Features of good exchange surface - Diaphragm:a layer of muscle beneath the lungs
- A large surface area - Intercostal muscles:muscles between the ribs, whichcontracts to
- A permeable thin barrier to reduce diffusion distance raise the ribcage
- A good blood supply to maintain steep concentration gradient, so
rapid diffusion can occur Nasal cavity
- I t has large surface area with rich blood supply to warm the air
- Hairy lining that secretes mucus to trap bacteria and dust
- Moist surface to increase humidity of inhaled air
Trachea
- T he main airway leading from the back of the mouth to the lungs
- Supported by c-shaped cartilage that supports the trachea and
prevent it from collapsing
- C-shaped cartilage allows the food to swallow down the oesophagus
- Contains elastic fibres and goblet cells
, Goblet cells
- It secretes mucus into the trachea lining to trap dust and bacteria
Bronchus
- I t is the extension of the trachea that splits into the left and right
lung, which then divide to form bronchioles
- Contains cartilage, elastic fibres and goblet cells
Bronchioles
- I t is surrounded by smooth muscle and elastic fibres but no cartilage,
which can contract, making the airway constrict
- Lined with a layer of epithelium for gas exchange, does not contain
goblet cells
Alveoli
- I t is the air sac where gas exchange occurs
- It is made of a thin layer of epithelial cell, collagen and elastic fibres,
does not have goblet cells
- The layer of elastic fibres recoils, so that air can move out of the
alveoli
- A watery fluid lines the alveoli
-> to allow gas to dissolve in the watery fluid for more efficient gas
exchange
-> decreases the surface tension at the air-liquid interface which Inhalation
prevents the collapse of alveoli - iaphragm:contract to move down and become flatter
D
- External intercostal muscle:move up and out
Why lungs have a good gas exchange surface? - Thoracic volume:increase
- A lthough individual alveoli is small, there are a large amount of - Thoracic pressure:decrease
alveoli, which provides a large total surface area for gas exchange - Air flows into the lungs
- It has short diffusion distance between the alveoli and capillary wall
- It has rich blood supply to maintain steep concentration gradient Exhalation
- iaphragm:relaxes and move up
D
- External intercostal muscle:move down and in
- Thoracic volume:decrease
- Thoracic pressure:increase
- Air flows out of the lungs