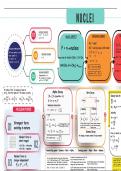
, Module 4:
- CURRENT = rate of flow of charge : I = Q/t
Current = I - measured in amps A
Charge = Q - measured in coulombs C
Elementary unit charge = 1.6 *10^-19
Atoms = 0 charge
Kirchoffs first law = sum of current entering a junction. Sum of the currents leaving the junction
E.g- of circuit where the law is shown
DRIFT VELOCITY = average velocity that charged particles attains due to an applied electric field
Current from drift velocity : I = nAev
CONDUCTOR:= a material with a very high free electron density ( metals have 10^29 electrons per
m^3)
SEMI-CONDUCTOR = a material with an intermediate free electron density but the electron density
will change when conditions change e.g- temperature
INSULATOR = a material with very low free electron density
POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE. = work done by a component on each charge to decrease their energy
measured in volts
EMF = work done by power source on each charge to incraese their energy measured in volts
VOLTAGE= used interchangeably with emf and pd
EMF sources increase the energy of the charges, P.Ds decreaes the energy of each charge
Work done by a component in a circuit = W(emf) = Q * emf
W(resistor) = Q * V
Velocity of electrons in accelerated by an ekec tric field in a vacuum:
- W= Q * emf
- conservation of energy : W = KE + GPE + EPE
- CURRENT = rate of flow of charge : I = Q/t
Current = I - measured in amps A
Charge = Q - measured in coulombs C
Elementary unit charge = 1.6 *10^-19
Atoms = 0 charge
Kirchoffs first law = sum of current entering a junction. Sum of the currents leaving the junction
E.g- of circuit where the law is shown
DRIFT VELOCITY = average velocity that charged particles attains due to an applied electric field
Current from drift velocity : I = nAev
CONDUCTOR:= a material with a very high free electron density ( metals have 10^29 electrons per
m^3)
SEMI-CONDUCTOR = a material with an intermediate free electron density but the electron density
will change when conditions change e.g- temperature
INSULATOR = a material with very low free electron density
POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE. = work done by a component on each charge to decrease their energy
measured in volts
EMF = work done by power source on each charge to incraese their energy measured in volts
VOLTAGE= used interchangeably with emf and pd
EMF sources increase the energy of the charges, P.Ds decreaes the energy of each charge
Work done by a component in a circuit = W(emf) = Q * emf
W(resistor) = Q * V
Velocity of electrons in accelerated by an ekec tric field in a vacuum:
- W= Q * emf
- conservation of energy : W = KE + GPE + EPE