Complete Solutions
Heberden's nodes are seen with what connective tissue disease?
Bouchard's nodes?
both with OA
(Bouchard = closer to Body)
Patient receiving chemotherapy is experiencing anemia.
Management of anemia is based around _______.
How can this be accomplished? (3)
energy conservation! rest!
3 P's for energy conservation:
plan
prioritize
pace
,HIV is a ______ disease with _____ stages.
HIV is a continuous disease with 4 stages (stages 0-3) (vague
5th stage is "stage: unknown")
What are the stages of HIV?
stage 0: inferred from labs, early infection
stage 1, 2, 3: based on CD4+ T-lymphocyte count
What stage of HIV do we see HIV antibodies develop?
What is the typical CD4 count?
stage 1: antibodies develop
CD4: 500-1500
(normal CD4: 500-1600)
What are normal CD4 counts?
500-1600
What are the CD4 cell levels of the different HIV stages?
stage 1: 500-1500 (w/in normal limits)
stage 2: 200-499
stage 3: below 200, considered to have AIDS for surveillance
purposes
What CD4 count is considered AIDS?
below 200
stage 3 HIV
Can patient be reclassified to a lower HIV stage if CD4 counts
go up?
,no
ART usually raises CD4 counts but cannot regress staging
At any stage if client develops ________, they are classified as
_____.
at any stage if client develops opportunistic infection, they are
classified as having AIDS
(even if they have CD4 count >200 its considered AIDS)
What lab testing is done for HIV?
What order are the tests done?
EIA (enzyme immunoassay)(aka ELISA): done 1° to detect
antibodies
Western blot: to confirm diagnosis
What lab test confirms diagnosis of HIV?
western blot
(done after EIA/ELISA)
What HIV stage is considered the "symptomatic" stage?
stage 2
stage 1 is asymptomatic
You want _____ CD4 counts and ____ viral loads.
high CD4
low viral loads
Goals of antiretroviral therapy (ART) (4)
, reduce HIV morbidity
preserve immune system
suppress HIV load
prevent HIV transmission
What are the major side effects of ART? (6)
n/v/d
fatigue
weakness
rash
What is the most common HIV related malignancy?
Kaposi's sarcoma
Define candidiasis
fungal infection present in almost all HIV patients
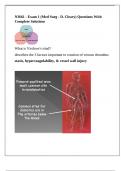
Kaposi's sarcoma
red-purple cutaneous lesions associated with HIV
What ART medication, when taken with high-fat, high-caloric
meals, increases peak plasma concentrations of capsules?
efavirenz (Sustiva)
_______ is a clinical syndrome that is characterized by a
progressive decline in cognitive, behavioral, and motor
functions as a direct result of HIV infection.
HIV encephalopathy
Define seroconversion