Complete Answers
Oxidative Dominates low-powered activities, those that last in excess of several minutes.
Long >120 secs.
Aerobic
Low-intensity efforts (40%)
Aerobic.
Mitochondria of cells
Type I
Pyruvate (from glycolysis) or acetate (derived from fat or protein).
Pyruvate oxidized to produce 34 ATP (Fat, protein yield less).
Anything>120 seconds of sustained effort.
CrossFit's second fitness model The hopper
The hopper Fitness requires an ability to perform well at all tasks, even unfamiliar tasks,
tasks combined in infinitely varying combinations. In practice this encourages the athlete to
disinvest in any set notions of sets, rest periods, reps, exercises, order of exercises, routines,
periodization. Nature frequently provides large unforeseeable challenges; train for that by
striving to keep the training stimulus broad and constantly varied.
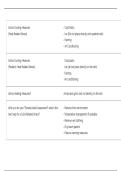
CrossFit's Third fitness model The metabolic pathways.
,The metabolic pathways contribution of total energy versus time Metabolic engines are
known as phosphagen pathway, glycolytic pathway, and the oxidative pathway. Fitness requires
competency and training in each of these pathways or engines. Balancing the effects of these
three pathways largely determines the how and why of the metabolic conditioning or cardio that
we do at CrossFit.
CrossFit's fourth fitness model Sickness-Wellness-Fitness Continuum.
Sickness-Wellness-Fitness Continuum Assumption is that if everything we can measure about
health will conform to a continuum then it seems that sickness, wellness, and fitness are different
measures of a single quality: health.
Based on measurements of: Blood pressure, body fat, bone density, triglycerides, HDL/LDL
cholesterol, glycated hemoglobin, muscle mass, etc.
Metabolic Conditioning (cardio) Biking, running, swimming, rowing, speed skating, and
cross-country skiing. Aerobic training benefits cardiovascular function and decreases body fat-
all good.
Allows us to engage in low-power extended efforts efficiently. Decreases in muscle mass,
strength, speed, and power. Aerobic activity may decrease anaerobic capacity.
Interval Training mixes bouts of work and rest in times intervals. Develops cardiovascular
system without an unacceptable loss of strength, speed, and power.
The bulk of metabolic training should be this type of training.
Tabata interval is an example of this.
, Increased maximal oxygen consumption.
Increased lactate threshold.
Increased efficiency.
Get all of the benefit of endurance work without the loss of strength, speed, and power.
Throwing Medicine ball work we favor provides both physical training and general
movement practice. Med ball drills add another potent stimulus for strength, power, speed,
coordination, agility, balance, and accuracy.
Nutrition proper diet can amplify or diminish the effect of your training efforts. Effective
means moderate in protein, carbs, and fat. Balanced macronutrient and healthy nutrition looks
like 40% carbs, 30% protein and 30% fat.
The Zone diet does an adequate job of jointly managing issues of blood glucose control,
proper macronutrient proportion, and caloric restriction whether your concern is athletic
performance, disease prevention and longevity, or body composition.
Sport Application of fitness in a fantastic atmosphere of competition and mastery. have less
predictable and more varied movements. Better at expression and testing of skills than it is at
developing these same skills. Mimics the demands of nature.
Theoretical Hierarchy of Development Pyramid from bottom to top:
Nutrition, Metabolic conditioning, gymnastics, weightlifting and throwing, sport.