❖Anatomy and physiology
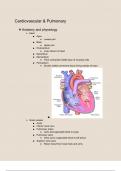
➢ Heart
■ Apex
● Lowest part
■ Base
● Upper part
■ Endocardium
● Lines interior of heart
■ Epicardium
■ Myocardium
● Thick contractile middle layer of muscles cells
■ Pericardium
● Double walled connective tissue lining outside of heart
◆
➢ Great vessels
■ Aorta
■ Inferior vena cava
■ Pulmonary artery
● Carry deoxygenated blood to lungs
■ Pulmonary veins
● Veins carry oxygenated blood to left atrium
■ Superior vena cava
● Return blood from head neck and arms
,➢ Heart chambers and valves
➢ Cardiac conduction system
■ SA node
● Normal pacemaker of the heart
■ AV node
■ Common AV bundle
■ R and L bundle branches
■ Purkinje fibers
■
➢ Innervation of the heart
■ Intrinsic to SA node
■ HR, rhythm and contractility are influenced by autonomic nervous system
■ Vagus and sympathetic
● Symp
◆ Epinephrine and norepinephrine
◆ Stimulate to beat faster (chronotropic effect)
◆ Contraction
● Parasympathetic
◆ Acetylcholine
◆ VAGUS nerve
◆ Slows HR
➢ Neural reflexes and circulatory
■ Baroreceptors
● Mechanoreceptors
● Detect change in pressure
● Carotid artery
● sympathetic nervous
◆ Increased CO
◆ Contractility
◆ Vaso constriction
◆ Increased BP
● Parasympathetic
◆ Decrease HR
◆ Decrease in contract
◆ Decrease BP
■ Chemoreceptor
● Chemosensitive cells
● Carotid bodies
● Respond to change in blood oxygen
● Decreased O2
◆ They increase depth and rate of breathing
◆ Parasympathetic reduces HR and contract
● If hypoxemia persists
◆ CNS will be stimulated by increase in sympathetic
, ■ Valsalva maneuver
● Forced expiration against a closed glottis increases intrathoracic
pressure
● Increased central venous pressure
● Decreased venous return
● The decrease in BP and CO are sensed by baroreceptors which
increase HR and contractility
● The increase in BP is sensed by baro and then reflexively
decrease HR through parasympathetic
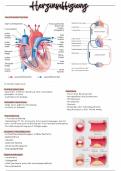
➢ Cardiac cycle
➢ Hypovolemia
■ Decreased blood volume
■ OH, tachyvardia, elevated body temp
■ Causes
● Sodium retention
● Excess intake of fluids
■ Sx
● Swelling in legs
● Ascites
● Fluid in lungs
➢ Plasma
■ Liquid component of blood
➢ RBC
■ Hemoglobin
➢ Blood platelets
■ Assist in blood clotting by clumping together at a bleeding site and forms
a plug
➢ WBC
■ Neutrophils
● Help protect against infections by injecting bacteria
■ Lymphocytes
● T and natural killer cells
● Protect against viral infections and destroy some cancer cells
● B cells → develop into cell that produce antibodies
■ Monocytes
● Ingest dead or damaged cells
■ Eosinophils
● Kill parasites, destroy cancer cells
● Allergic response
■ Basophils
● Allergic response
, ❖
➢ Anatomic dead space
■ Volume of air that occupies non respiratory conducting airways
➢ Expiratory reserve volume
■ Max volume of air that can be exhaled after a normal expiration
● 15%
➢ Forced expiratory volume
■ Maximal volume air exhaled in a specified period of time
➢ Forced vital capacity
❖ Cardiomyopathy
➢ Group of conditions that affect myocardium
■ Dilated
■ Hypertrophic
■ Restrictive
➢ Etiology
■ Valvular heart disease
■ CAD
➢ s/s
■ Breathlessness
■ Swelling of legs
■ Ankles and feet
■ Bloating in abdomen
■ Fatigue
■ Irregular heartbeat
■ Dizziness
➢ Tx
■ Dilated
● ACE inhibitors
● BB
● Digoxin
● Diuretics
■ Hypertrophic
● Medications to slow HR
● Lopressor and calcium channel blockers
■ Restrictive