Human Endocrine System:
The environment in and around cells are continuously changing thus, human bodies
must adapt to these changes.
Homeostasis maintains a constant internal balance (equilibrium) despite changes in
the internal/external environments.
The nervous system and hormones respond to external changes and to control
conditions internally.
The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete organic compounds –
hormones (chemical messengers).
Thus, the endocrine system maintains homeostasis in the human body.
Endocrine glands - ductless glands that secrete hormones directly into the blood
stream and is transported to the targeted organ.
Exocrine glands – release their secretions via ducts to a body cavity or to the outside
(Salivary glands)
Hormones:
Organic chemical messengers.
Most hormones are proteins or steroids.
Secreted in small quantities directly into the bloodstream via endocrine glands.
Target organ - an organ effected by a hormone and has receptors for this hormone,
enabling it to respond.
A regulatory function that is stimulating or inhibiting.
Hormones are regulated by negative or positive feedback mechanisms, negative
feedback- any deviation from the normal levels (of substances or temp) elicits a
response that restores normal levels.
Glands and Their hormones:
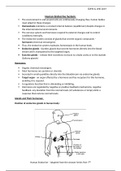
Position of endocrine glands in human body:
Human Endocrine – Adapted from the Answer Series Part I
, JFIN & LME 2019
Pituitary Gland:
Located at the base of the brain and attached to the hypothalamus (the link
between the nervous and endocrine systems)
Hypophysis (secretes hormones that affect most of the endocrine glands) consists of
two lobes:
1. Anterior lobe.
2. Posterior lobe.
Hormones of the Anterior Lobe:
TSH (thyroid stimulating gland):
Stimulates the thyroid to secrete the hormone thyroxin.
Growth hormone:
Promotes the growth of skeleton and muscles by stimulating proteins.
Growth disorders:
o Dwarfism, the hyposecretion (under secretion) of growth hormones.
o Gigantism, the hypersecretion (over secretion) of growth hormones.
Usually caused by a tumour in the hypophysis.
FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone):
Stimulates the development of primary follicles in the ovaries into mature
Graafian follicles.
In males it activates the germinal epithelium that produces sperm cells in the
testes.
LH (luteinising hormone):
Simulates ovulation in females and development of the corpus luteum in the
ovary.
In males it stimulates the cells of Leydig (in the testes) to produce
testosterone.
Prolactin:
Stimulates the mammary glands to produce milk after birth.
Hormones of the Posterior Lobe:
ADH (antidiuretic hormone):
Prevents dehydration.
Controls the reabsorption of water by the walls of the renal tubes and
collecting ducts more permeable to water. Thus, less water excreted through
urine.
Oxytocin:
Causes the contraction necessary for birth.
Contractions of the uterus stimulates the hypophysis to release more
oxytocin.
Examples of positive feedback mechanism (where increasing levels of one
hormone stimulates the release of more of the same hormones)
Human Endocrine – Adapted from the Answer Series Part I