with Complete Solutions
Nocturnal Dyspnea PND is a sign of congestive heart failure and often strikes one or two
hours after the person with heart failure has fallen asleep.
Specifically, dyspnea, "refers to the sensation of difficult or uncomfortable breathing,"according
to the National Center for Biotechnonoly Information. However, Dyspnea is not the same as
hyperventilation which consists of short, quick breaths and an inability to get one's breath.
Dyspnea can also be associated with exertion.
PND occurs by a fluid build up in the lungs entering the alveoli (air sacs) while a person sleeps.
The alveoli are responsible for oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange from the blood. During the
day, the fluid is retained in the legs. At night, while sleeping, the body resorbs this fluid resulting
in an increase in total blood volume and blood pressure leading to pulmonary hypertension or
edema. Many patients, without realizing the congestive heart failure nature of these symptoms
naturally counteract these symptoms by sleeping on several pillows or sleeping while sitting up.
One explanation for the onset of symptoms is that the left ventricle is starting to fail and is
unable to keep up with the performance of a perfectly healthy right ventricle. Other theories
according NCBI, include "decreased responsiveness of the respiratory center in the brain and
,decreased adrenergic (adrenalin-fueled) activity in the myocardium (heart muscles) during
sleep."
Common Causes of PND
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): a group of lung conditions including chronic
bronchitis and emphysema that affects the lungs' ability to function normally.
-Cor Pulmonale: "An acute strain or hypertrophy [abnormal enlargement] resulting from disease
of the lungs or of other blood vessels." (Dictionary.com)
- Heart failure
- Hypertensive heart disease
- Obesity (which aggravates
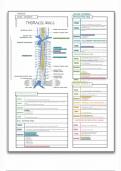
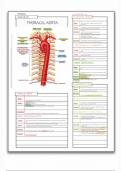
Upper Airway [6 components] All anatomic airway structures ABOVE vocal cords.
Includes nose, mouth, jaw, oral cavity, pharynx and larynx
,What are the 3 major functions of the upper airway? Warm, filter and humidify air as it
enters the body through the nose and mouth
Muscular tube that extends from the nose and mouth to the level of the esophagus and trachea?
Pharynx (throat). Composed of the naso, oro, and laryngopharynx. The laryngopharynx is
the lowest portion of the pharynx. Splits into two lumens at the base, larynx anteriorly and
esophagus posteriorly
Which of the following is the most commonly obstructed by foreign bodies? Pharynx
What is the name of the passageway shared by the digestive and respiratory systems for air and
food? Oropharynx
What leaf shaped structure closes during swallowing to prevent foods and foreign objects from
entering the trachea? Epiglottis
What part of the respiratory system contains the vocal chords? Larynx
, Where does the upper airway end and the lower airway begin? Larynx
Where is Sellick's maneuver applied? Cricoid Cartilage (SM)
The ring shaped structure that forms the lower portion of the larynx is called the Cricoid
Cartilage
Function of the lower airway exchange oxygen and CO2
All lung tissue is covered with a thin, slippery outer membrane called the Visceral Pleura
What lines the inside of the thoracic cavity Parietal Pleura
Bronchioles Thin, hollow tubes made of smooth muscle
Millions of thin-walled, balloon-like sacs tat serve as the functional site for O2 and CO2
exchange alveoli