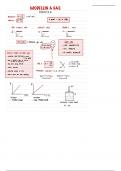
Microscopes can be used to analyse cell components and observe organelles.
Magnification tells you how many times bigger the image produced by the microscope is
than the real-life object
Resolution is the clarity of an image.
- The ability to distinguish between objects that are close together (lower nm means
higher resolution as this distance is needed to see those two objects clearly and
distinctly)
- The minimum distance between two objects in which they can still be viewed as
separate
Total Magnification = Magnifying power of objective lens X magnifying power of the eyepiece lens
TYPES OF MICROSCOPES:
Optical (light) microscopes:
Use light to form an image (visible light with a wavelength from 400 to 700nm)
This limits the resolution of optical microscopes (maximum resolution of 200nm)
o Using light it is impossible to distinguish between two objects that are closer than half the
wavelength of light (wavelength of visible light is between 500-650nm)
Maximum resolution of around 200nm (0.2micrometres)
Allow magnification of up to x1500
ADVANTAGES:
o Cheap and easy to use
o Portable (able to be used in the field as well as in the laboratories)
o Can study whole living organisms
DISADVANTAGES:
, o Poor resolution (200nm) so cannot see smaller organelles (ribosomes, lysosomes,
endoplasmic reticulum)
ELECTRON MICROSCOPES:
Electron microscopes use electrons to form an image
This greatly increases the resolution of electron microscopes compared to optical microscopes,
giving a more detailed image
- A beam of electrons has a much smaller wavelength than light, so an electron microscope
can resolve (distinguish between) two objects that are extremely close together
Electron microscopes have a maximum resolution of around 0.2nm (around 1000 times greater than
that of optical microscopes) so can see smaller organelles (such as ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum
or lysosomes)
The maximum useful magnification of electron microscopes is about x1,500,000
The image seen using an electron microscope is called an electron micrograph
Transmission electron microscope:
TEMs use electromagnets to focus a beam of electrons
This beam of electrons is transmitted through the specimen
Denser parts of the specimen absorb more electrons
- This makes these denser parts appear darker on the final image produced
ADVANTAGES:
o High magnification (x2million) and high resolution (0.1-2nm)
o This allows the internal structures within cells or even organelles to be seen
DISADVANTAGES:
o Large and expensive
o Significant skill needed to use
o Sample must be dehydrated/chemically fixed (viewed in a vacuum so NOT ALIVE)
o 2D, black and white image produced
, o Can only be used with very thin specimens
o The lengthy treatment required to prepare specimens means that artefacts can be
introduced (artefacts look like real structures but are actually the results of preserving and
staining – i.e., not part of the specimen)
Scanning electron microscope:
SEMs scan a beam of electrons across the specimen
Electrons bounce off the surface of the specimen and the electrons are detected, forming an image
ADVANTAGES:
• 3D image produced so external 3D structure of specimens is observed
• Can be used on thick specimens
• High magnification up to X200,000 (x15-200,000)
DISADVANTAGES:
• Large and expensive
• Significant skill needed to use
• Sample must be dead – viewed in a vacuum
• Lower resolution than TEMs (0.5-4nm)
• Black and white image
Laser scanning confocal microscope:
A thick section of tissue or small living organisms are scanned with a laser beam
- The laser beam is reflected by the fluorescent dyes
Multiple depths of the tissue section/organisms are scanned to produce an image
o The laser beam is building up the image layer by layer.
o Assemble the pixel information into one image (displayed on computer screen)
The cells being viewed must be stained with fluorescent dyes
ADVANTAGES:
• LSCM generates high resolution images (10nm). Magnification is (x10,000)
• Have depth sensitivity (can focus on structures at different depths within a sample)
• Can view whole, living specimens
• Can be used on thick specimens
• 3D